|
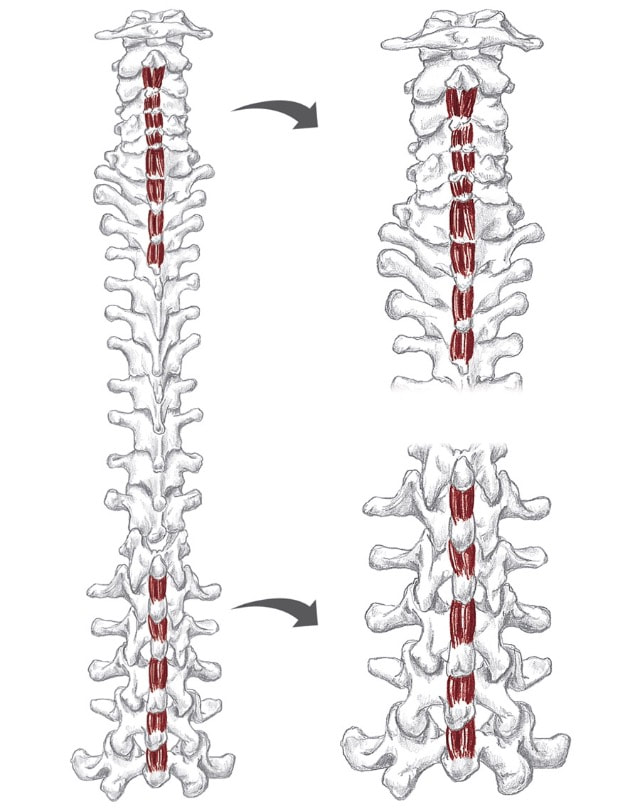
mul-tif-i-di Action Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
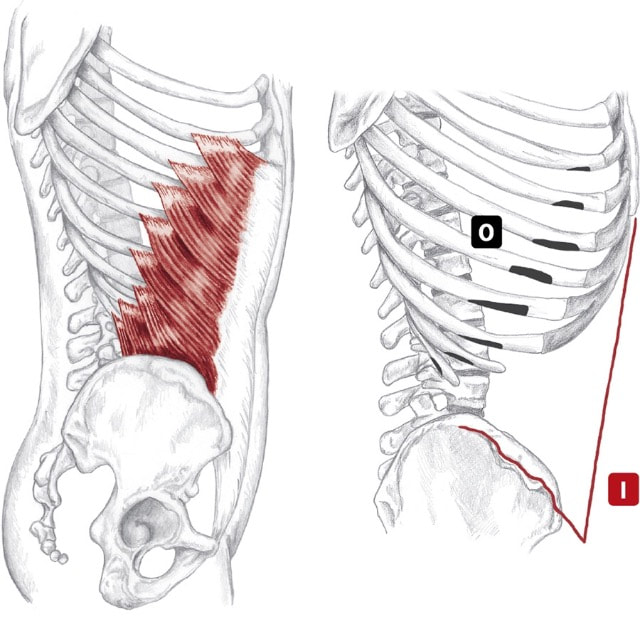
Location: Deep to erectors, lateral to spine BLMs: Spinous and transverse processes Action: "Extend and/or rotate your spine"
0 Comments
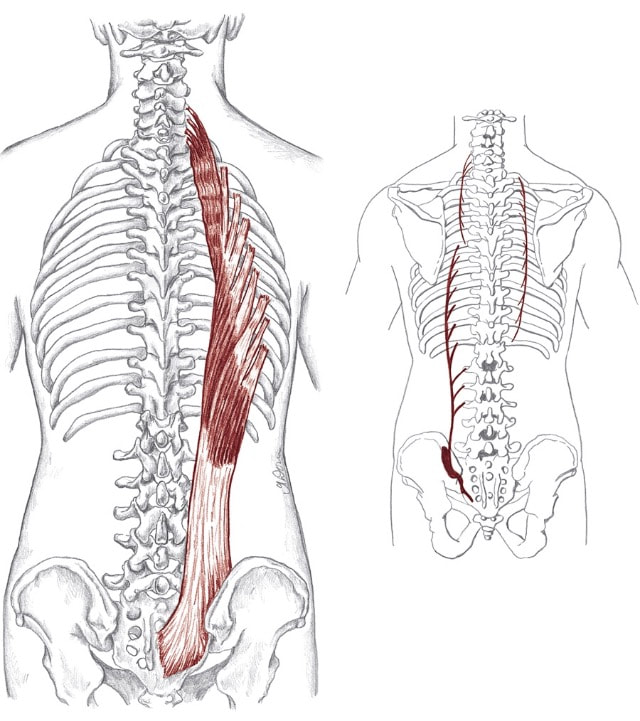
lon-jis-i-mus Action Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
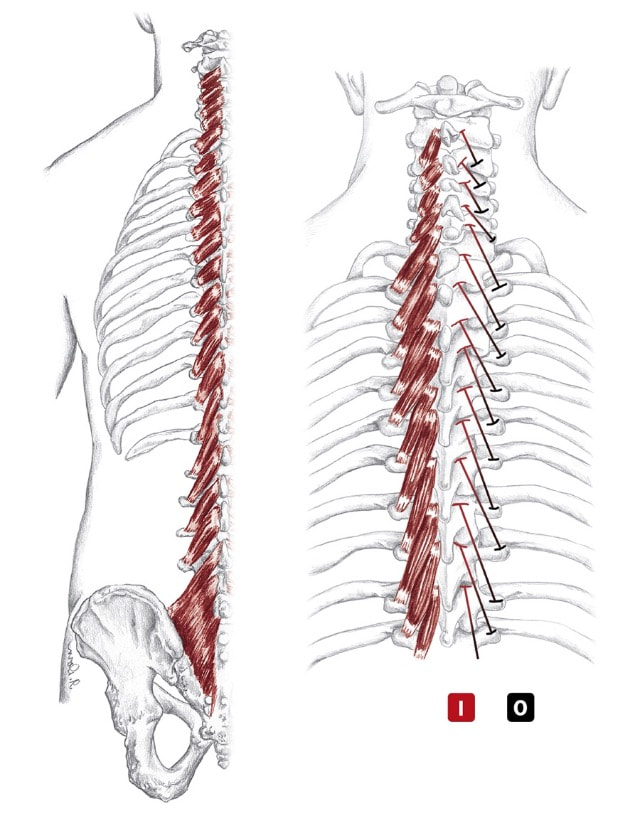
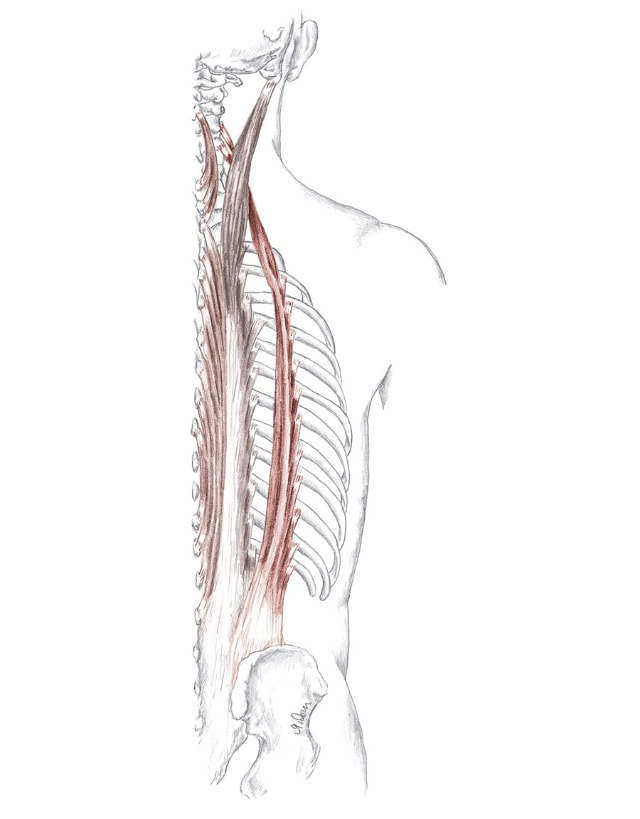
Location: Lateral to spinalis fibers BLMs: Spinous processes of all vertebrae Action: "Extend your spine" Developed by world-renowned musculoskeletal expert Dr. Andreo Spina, Functional Range Conditioning (FRC) is a comprehensive joint training system based in scientific principals and research.
There are 3 main goals when training using FRC system and all are closely interrelated, and acquired simultaneously:
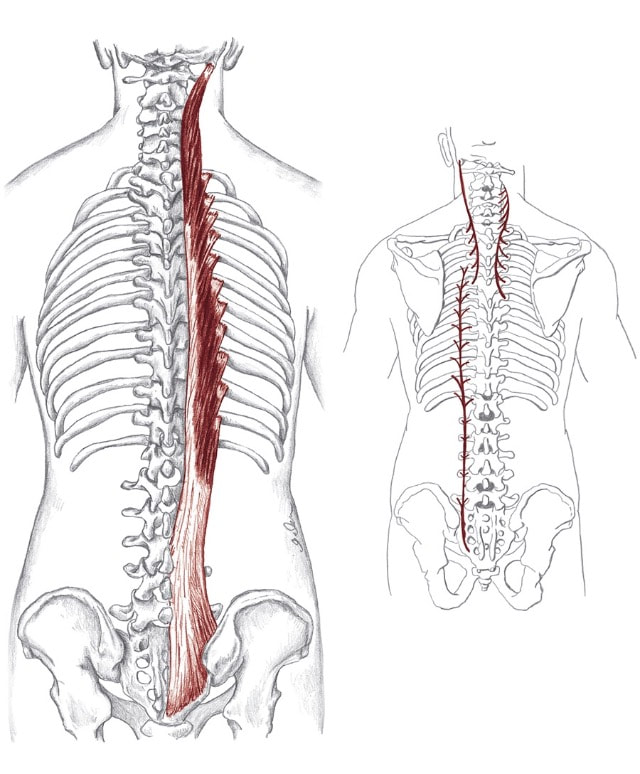
in-ter-trans-verse-er-i Action
Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin Cervical:
Lumbar:
Insertion Cervical:
Lumbar:
Nerve
in-ter-spi-na-lis Action
Origin Cervical:
Lumbar:
Insertion Cervical:
Lumbar:
Nerve
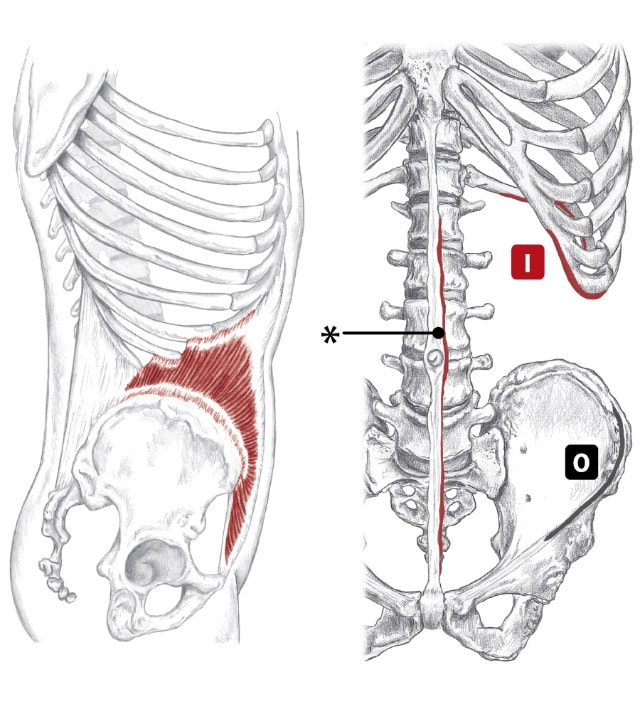
o-bleek Action
Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
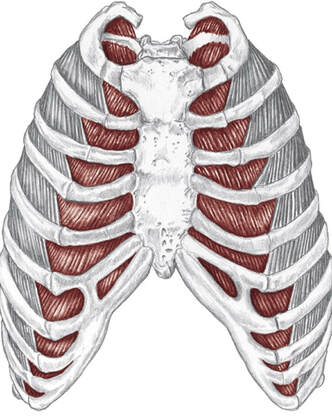
kos-tal Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
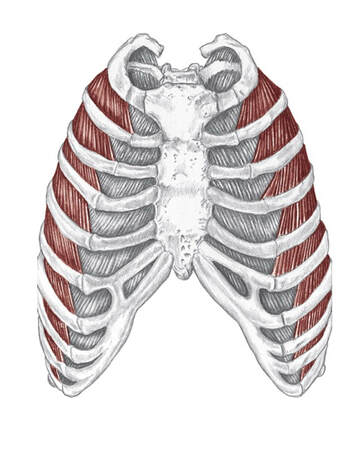
Location: Spaces between the ribs BLMs: Body of the ribs Action: "Exhale" il-ee-o-kos-ta-lis Action Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Location: Lateral to longissimus fibers BLMs: Spinous processes of all vertebrae Action: "Extend your spine" or "raise your feet slightly" o-bleek Action Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Location: Lateral surface of abdomen BLMs: Iliac crest, bottom edge of ribs Action: "Rotate your trunk to the opposite side" kos-tal Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Location: Spaces between the ribs BLMs: Body of the ribs Action: "Inhale" (Spinalis, Longissimus, Iliocostalis) Action Unilaterally:
Bilaterally:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
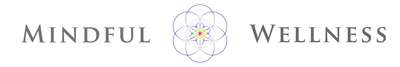
Location: Alongside the spine BLMs: Spinous processes of all vertebrae Action: "Extend your spine" or "raise your feet slightly" kwod-rait-us fe-mo-ris Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
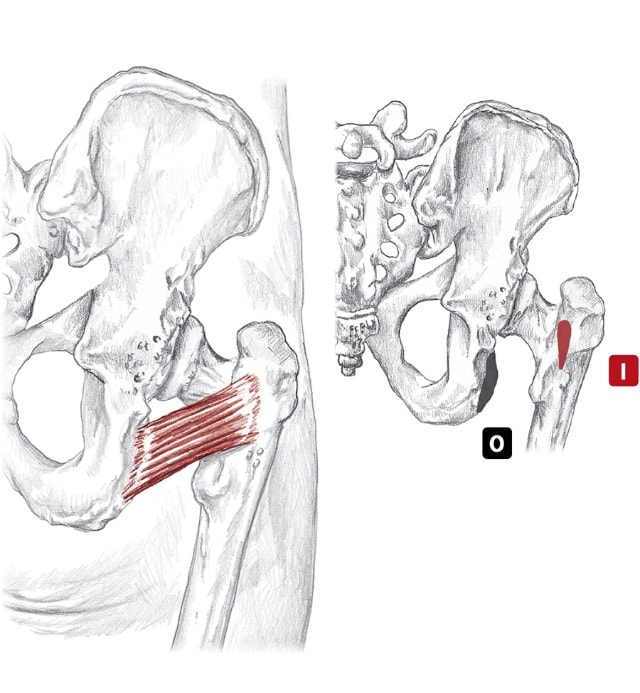
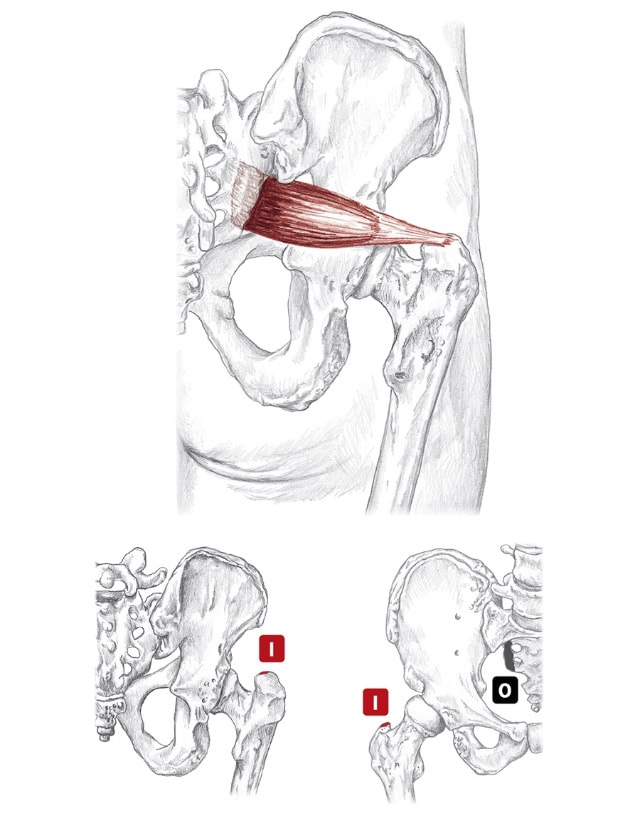
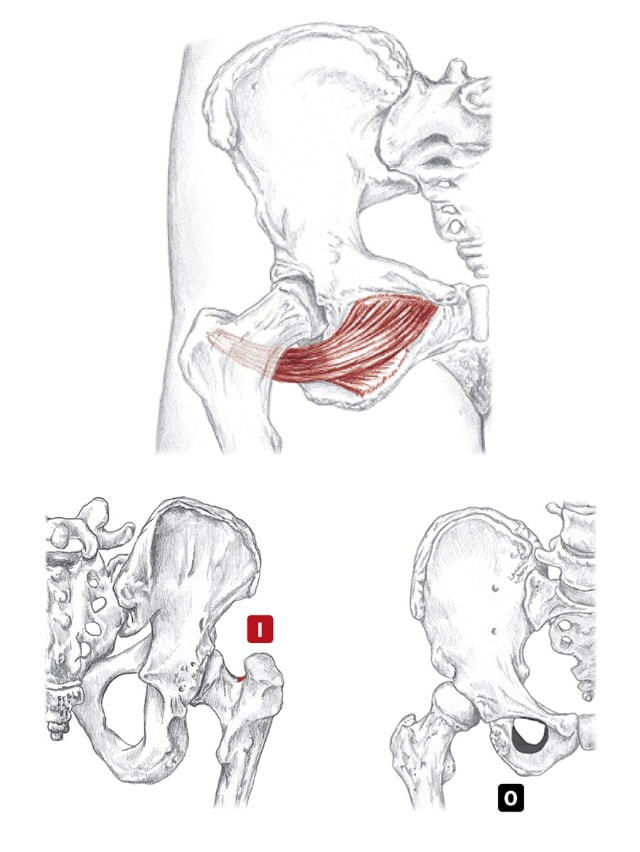
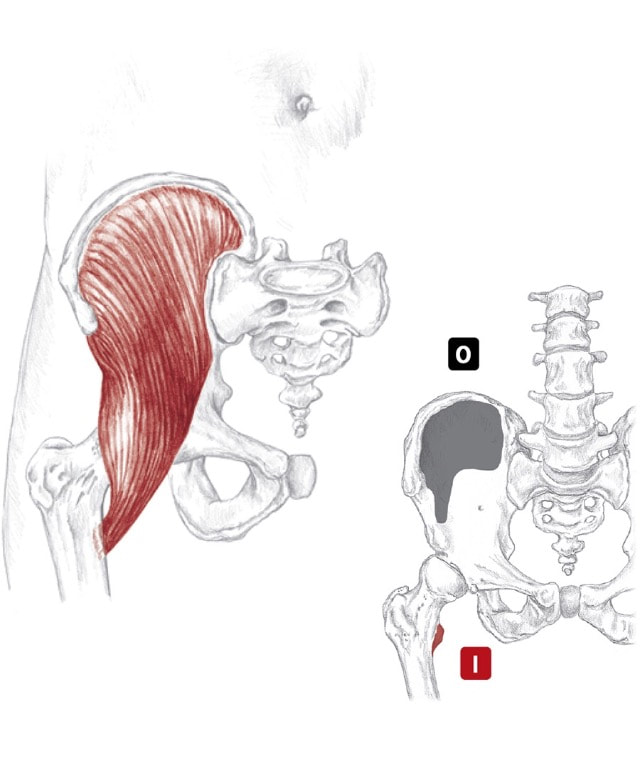
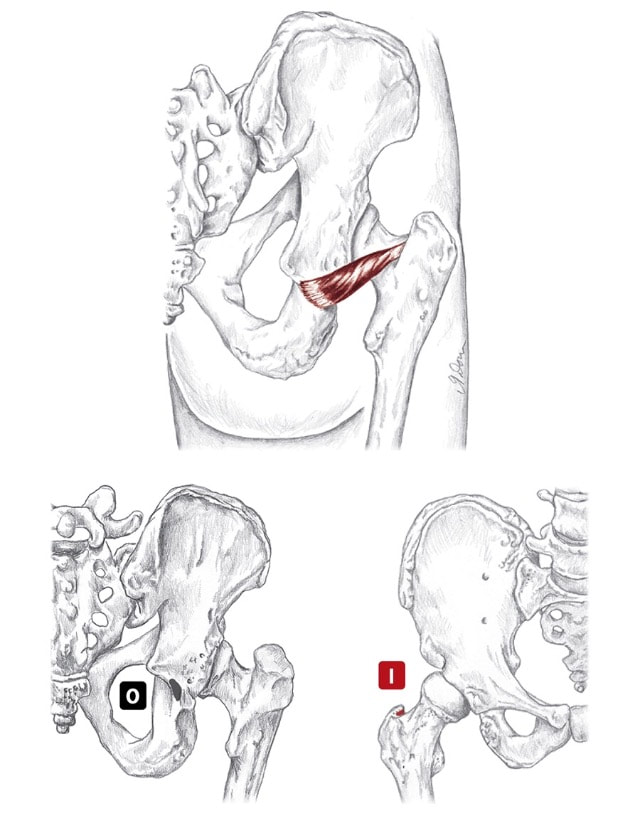
Location: Deep to gluteus maximus BLMs: Greater trochanter, ischial tuberosity Action: "Laterally rotate your hip" pir-i-form-is Action
Origin
Insertion
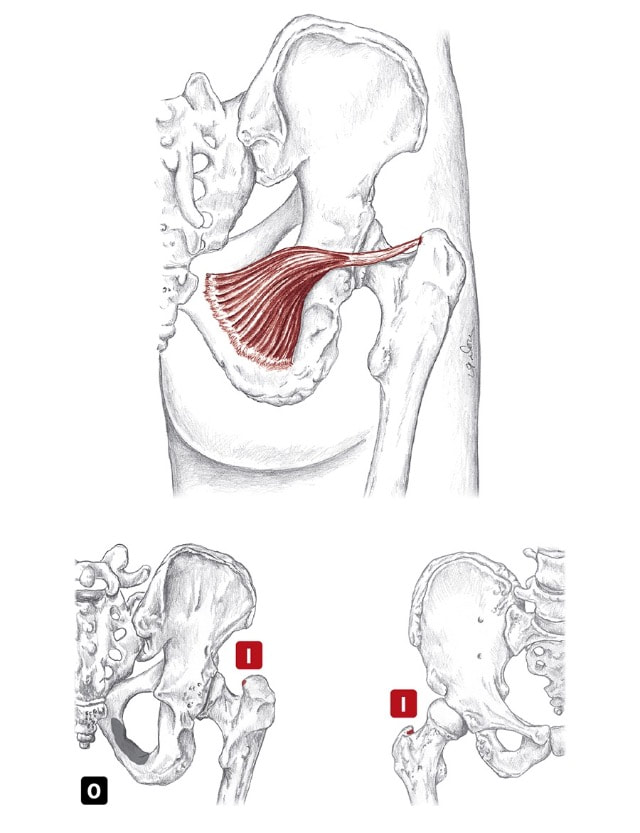
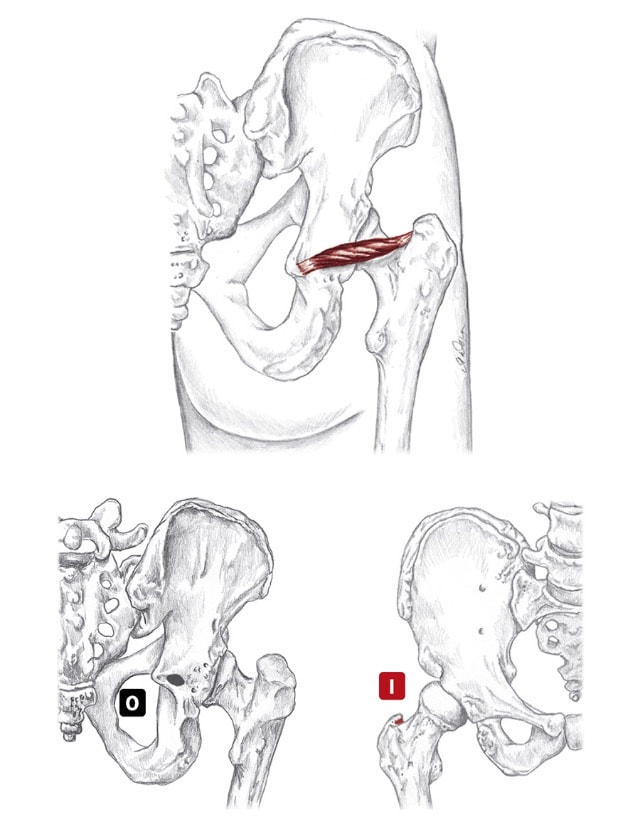
Nerve
Location: Deep in gluteus maximus BLMs: Sacrum, greater trochanter Action: "Laterally rotate your hip" pek-tin-e-us Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
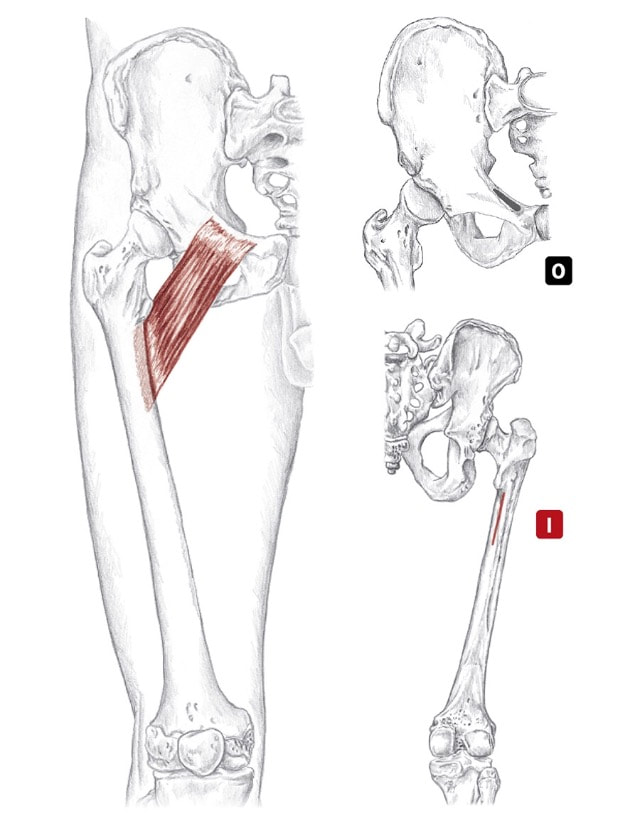
Adductor group Location: Superficial and deep, medial thigh BLMs: Pubic tubercle, rami and ischial tuberosity Action: "Squeeze your thighs together" ob-tu-ra-tor in-tur-nus Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
ob-tu-ra-tor ex-tur-nus Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
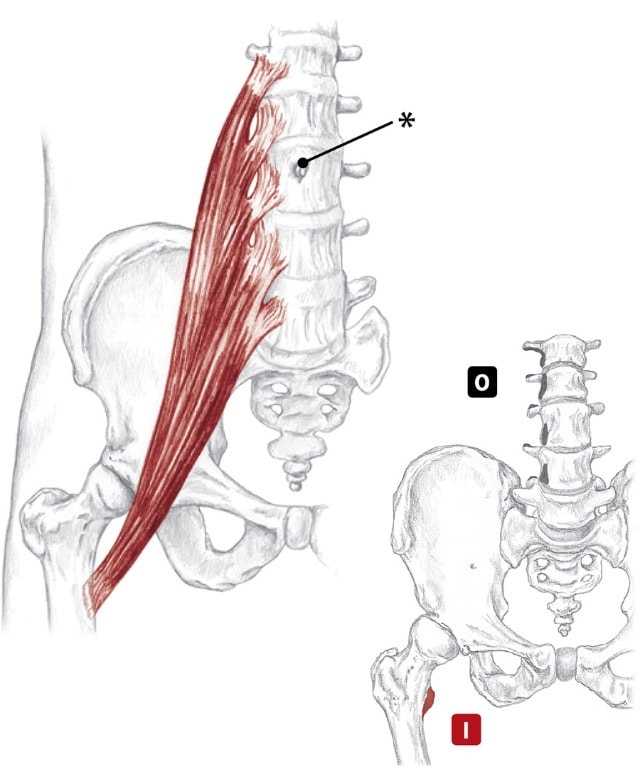
i-lee-a-cus Action With the origin fixed:
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Location: Deep in abdomen BLMs: Iliac fossa and crest Action: "Bring your knee toward your chest" or "flex your hip" gra-cil-is Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Adductor group Location: Superficial and deep, medial thigh BLMs: Pubic tubercle, rami and ischial tuberosity Action: "Squeeze your thighs together" sar-tor-ee-us Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
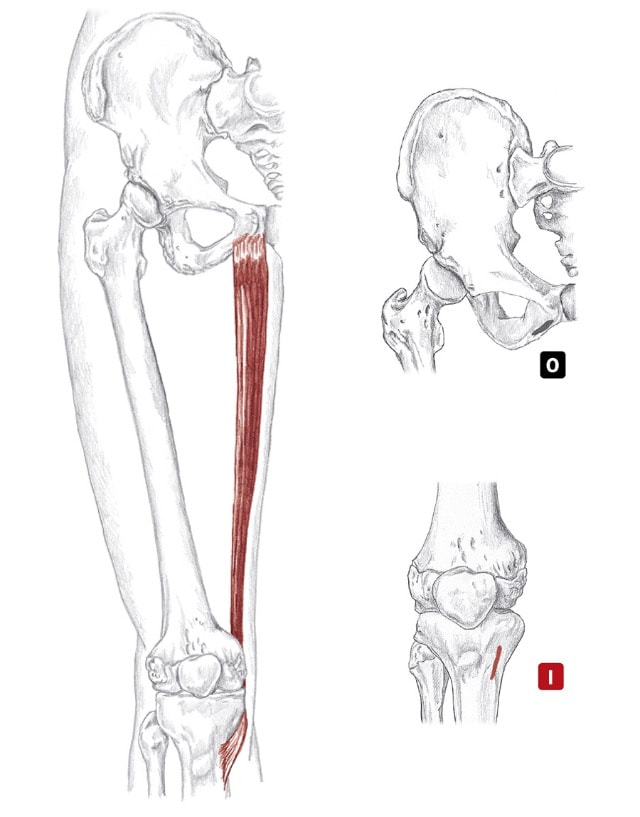
Location: Superficial, slender BLMs: ASIS, pes anserinus region Action: "Bring your knee toward the ceiling" or "flex your hip" jem-el-us Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
jem-el-us Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
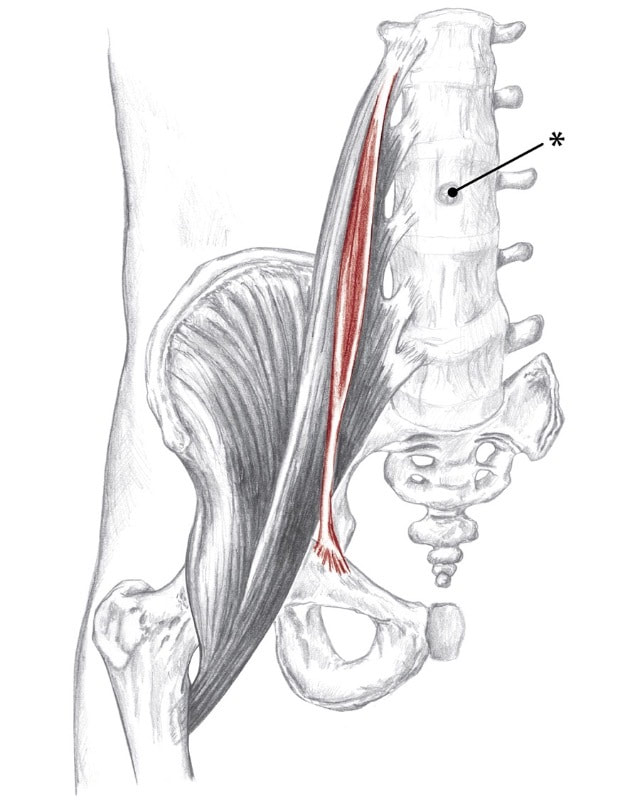
so-as Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
so-as Action With the origin fixed:
Insertion
Nerve
Location: Deep in abdomen, lateral to navel BLMs: Bodies of lumbar vertebrae Action: "Bring your knee toward your chest" or "flex your hip" bi-seps fe-mor-is Action
Origin Long head:
Insertion
Nerve Long head:
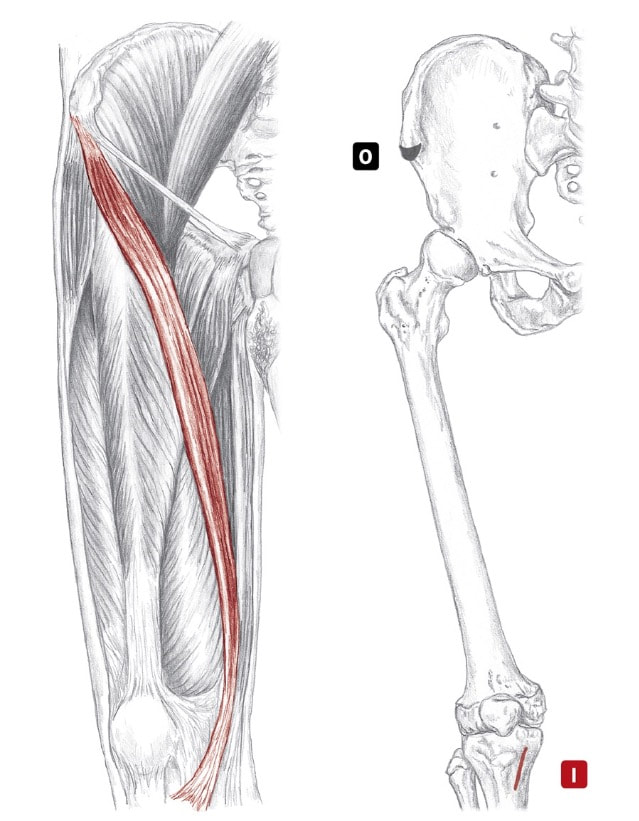
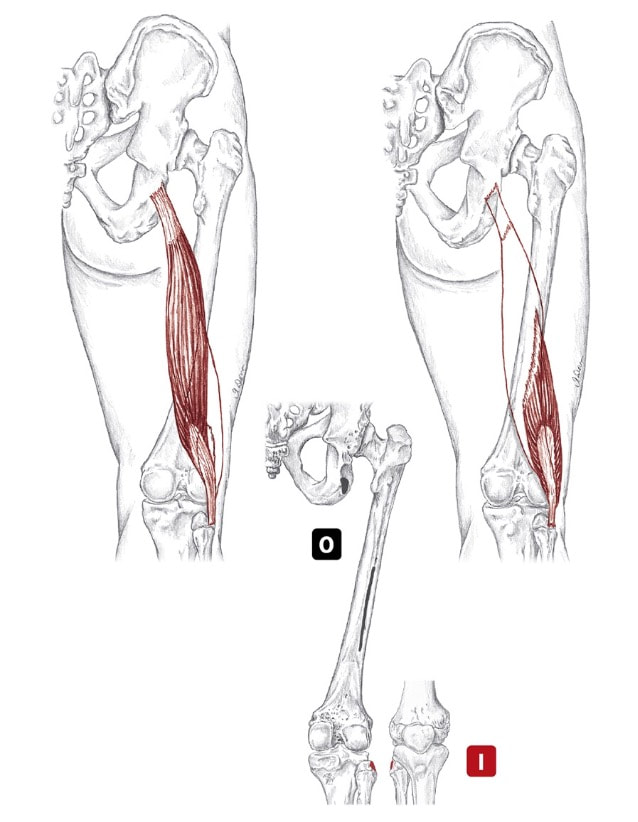
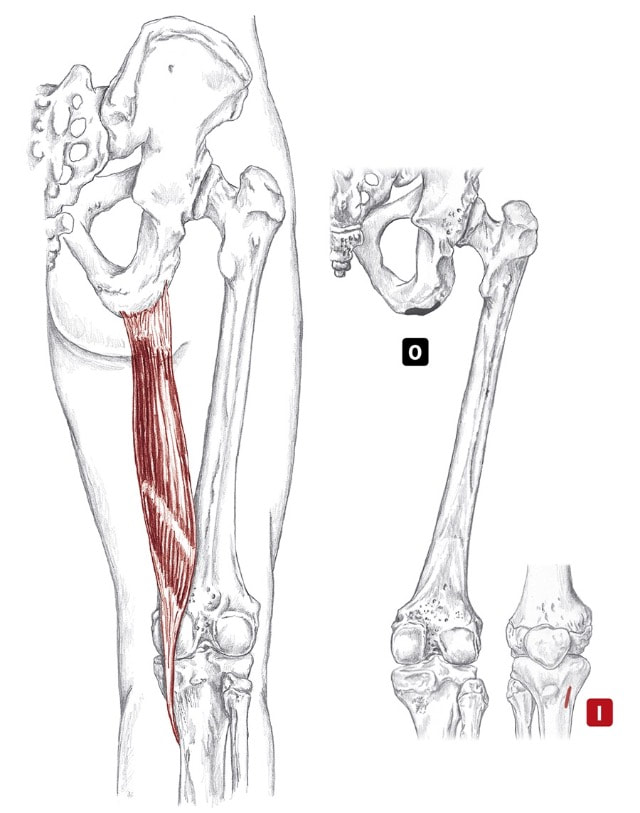
Hamstrings as a group Location: Superficial, posterior thigh BLMs: Ischial tuberosity, tendons of posterior knee Action: "Bend your knee" or "extend your hip" sem-eye-ten-di-no-sus Action
Origin
Insertion
Nerve
Hamstrings as a group Location: Superficial, posterior thigh BLMs: Ischial tuberosity, tendons of posterior knee Action: "Bend your knee" or "extend your hip" |
The Awareness domain contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of self in an effort to intellectualize health concepts.
The Lifestyle domain builds off intellectual concepts and offers practical applications.
Taking care of yourself is at the core of the other domains because the others depend on your health and wellness.
Archives
May 2024
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

