|
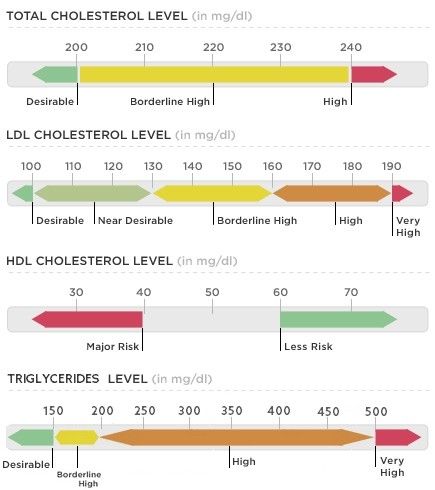
It's that time: time to test your blood. Most blood tests include a fasting lipid panel to assess one's risk of cardiovascular disease. A lipid panel is a test that measures fats and fatty substances used as a source of energy in the body. Lipids include cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). What Are Triglycerides?
Triglycerides are a powerful cardiovascular risk marker. Elevated triglyceride levels are a hallmark of too many carbohydrates in the diet. 60 percent of fructose is shunted toward the liver, where it is converted to triglycerides (which causes heart disease) (Gundry, 2017). In fact, fructose, which is the sugar found in most processed foods (often in the form of high-fructose corn syrup) can only be metabolized by your liver. If you eat a typical Western-style diet, you consume high amounts of it. The overload of fructose ends up damaging your liver in the same way alcohol and other toxins do (Mercola, 2017). What about Cholesterol? Our culture is obsessed with cholesterol levels, to the point that one in four adults in the U.S. take a statin drug to lower cholesterol levels. Nevertheless, elevated cholesterol levels are rarely a risk factor for heart disease, although elevated triglycerides clearly are. Fortunately, elevated triglycerides can easily be corrected and lowered to an ideal level of below 75 with the proper lifestyle interventions. The following tests can give you a far better assessment of your heart disease risk than your total cholesterol alone:
Influence of Triglycerides on Leptin High triglyceride levels (over 100 mg/dL) is known to cause leptin resistance. Leptin is a hormone located in fat cells, and like most hormones, it's function is complex. Leptin is tied to the coordination of our metabolic, hormonal, and behavioral response to starvation. Leptin essentially controls mammalian metabolism. Leptin decides whether to make us hungry and store more fat or burn fat. In other words, when your stomach is full, fat cells release leptin to tell your brain to stop eating. This is why people with low levels of leptin are prone to overeating. One study observed participants with a 20 percent drop in leptin experienced a 24 percent increase in hunger and appetite, influencing their cravings for calorie-dense, high-carbohydrate foods, especially sweets, salty snacks, and starchy foods. The researchers discovered the drop in leptin was caused by sleep deprivation. Leptin is also a pro-inflammatory molecule - it controls the creation of other inflammatory moleciles in your fat tissue throughout your body. This explains why overweight individuals are susceptible to inflammatory problems. Leptin is ranked highly on the body's chain of command, so imbalances tend to spiral downward and wreak havoc on virtually every system of the body beyond those directly controlled by leptin. Leptin, like insulin, is negatively influenced by carbohydrates. The more refined and processed the carbohydrate, the more imbalanced leptin levels become. When the body is overloaded and overwhelmed by substances that cause continuous surges in leptin, leptin receptors begin to turn off and you become leptin resistant. So even though leptin is now elevated, it doesn't work - it won't signal to your brain that you're full so you can stop eating. Not a single drug or supplement can balance leptin levels. But better sleep, as well as better dietary choices will (Perlmutter, 2013). Causes of High Triglycerides
The main culprit Preventing cardiovascular disease involves reducing chronic inflammation in your body, and a proper diet is an absolute cornerstone. Although saturated fat has taken the blame for causing heart disease for the last several decades, the primary culprit in heart disease is sugar consumption. A 2015 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association concluded that there is " a significant relationship between added sugar consumption and increased risk for cardiovascular mortality." the 15-year study, which included data for 31,000 Americans, found that those who consumed 25 percent or more of their daily calories as added sugars were more than twice as likely to die form heart disease as those who got less than 10 percent of their calories from sugar. On the whole, the odds of dying from heart disease rose in tandem with the percentage of added sugar in the diet regardless of the age, sex, physical activity level, and body mass index (Dhurandhar & Thomas, 2014). A 2014 study came to very similar conclusions. Here, those who consumed the most sugar - about 25 percent of their daily calories - were twice as likely to die form heart disease as those who limited their sugar intake to 7 percent of their total calories (Yang et al., 2013). A 2013 study, published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, looked at the differing effects of high-fat diets versus low-fat diets on blood lipid levels. The study included 32 studies and found that high-fat diets resulted in significantly greater improvements in reductions of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides and benificial increases in HDL cholesterol (Schwingshackl et al., 2013). How to Lower Triglycerides
Consider a Detox
The Dangers of StatinsSo, why are we all obsessed with total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol when we know they aren’t the primary culprits for heart attacks? Because a multi-billion dollar drug industry exists behind the number-one best-selling class of drugs on the market: Statins. Of course, the choice to take medications, if referred by your physician is, and should, always be your choice. However, you have the right to be fully informed of the side effects of consuming anything. With this in mind, it is important to be aware of the unintended side effects of taking statins. A study published in Clinical Cardiology concluded that "Statin therapy is associated with decreased myocardial [heart muscle] function," which often leads to heart failure. The study did not address causes, but it's widely known that statins lower your CoQ10 levels by blocking the pathway involved in cholesterol production -- the same pathway by which Q10 is produced. Statins also reduce the blood cholesterol that transports CoQ10 and other fat-soluble antioxidants. The loss of CoQ10 leads to loss of cell energy and increased free radicals which, in turn, can further damage your mitochondrial DNA, effectively setting into motion an evil circle of increasing free radicals and mitochondrial damage (Mercola, 2011). Moreover, for those at risk of heart disease taking statins who are unwilling or unable to bring down their cholesterol and/or triglyceride levels naturally with dietary changes, the potential for liver or muscle damage should be acknowledged. In addition, the potential for brain-related side effects, such as memory loss and confusion, as well as Parkinson’s-like symptoms is of concern. Statin drugs also appeared to increase the risk of stroke and developing diabetes. In 2013, a study of several thousand breast cancer patients reported that long-term use of statins may as much as double a woman's risk of invasive breast cancer. There are 71 diseases that may be associated with these drugs, and this is only the tip of the iceberg. There are actually over 900 studies showing the risks of statin drugs, which include:
Plant-based diets have been shown to lower cholesterol just as effectively as first-line statin drugs, but without the risks. In fact, the "side effects" of healthy eating tend to be good - less cancer and diabetes risks and protection of the liver and brain (Gregor, 2015). What Should you Eat? ReferencesBaker, A. (2012). What's the real driver of elevated cholesterol? hint: it's not saturated fat! - Nourish Holistic Nutrition. [online] Nourish Holistic Nutrition. Available at: nourishholisticnutrition.com/whats-the-real-driver-of-elevated-cholesterol/ [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019].
Dhurandhar, N. and Thomas, D. (2015). The Link Between Dietary Sugar Intake and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. JAMA, 313(9), p.959. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.18267 [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Gregor, M. (2015) How Not to Die. London: Pan Books Gundry, S. (2017). The Plant Paradox. New York, NY: Harper Wave Hyman, M. (2016). 7 Ways to Optimize Cholesterol. [online] Dr. Mark Hyman. Available at: https://drhyman.com/blog/2016/01/14/7-ways-to-optimize-cholesterol/ [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Mercola, J. (2017). Fat for Fuel. Carlsbad, CA: Hayhouse Inc. Mercola, J. (2011). New Study Shows Using Statins Actually Harms Heart Function. [online] Mercola.com. Available at: https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2011/06/22/new-study-show-using-statins-actually-worsens-your-heart-function.aspx [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Mercola, J. (2015). Conventional Heart Disease Advice May Make Matters Worse. [online] Mercola.com. Available at: https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2015/08/02/heart-disease-risk-factors.aspx [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Perlmutter, D (2013). Grain Brain. New York, NY: Little Brown Ray, K. et al. (2010). Statins and All-Cause Mortality in High-Risk Primary Prevention. Archives of Internal Medicine, 170(12), p.1024. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2010.182 [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Rubinstein, J., Aloka, F. and Abela, G. (2009). Statin Therapy Decreases Myocardial Function as Evaluated Via Strain Imaging. Clinical Cardiology, 32(12), pp.684-689. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.20644 [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Schwingshackl, S., et al. (2013). Comparison of Effects of Long-Term Low-Fat vs High-Fat Diets on Blood Lipid Levels in Overweight and Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 113(12), pp. 1640-61. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2013.07.010 [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Wallerwellness.com. (2019). Understanding Triglycerides. [online] Available at: https://www.wallerwellness.com/health-and-aging/understanding-triglycerides [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Williams, J. (2017). How To Lower Dangerously High Triglyceride Levels. [online] Renegade Health. Available at: http://renegadehealth.com/blog/2017/03/31/how-to-lower-dangerously-high-triglycerides-levels [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019]. Yang, Q., et al. (2014). Added Sugar Intake and Cardiovascular Diseases Mortality Among US Adults. JAMA Internal Medicine, 174(4), pp.516-24. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13563 [Accessed 8 Feb. 2019].
1 Comment
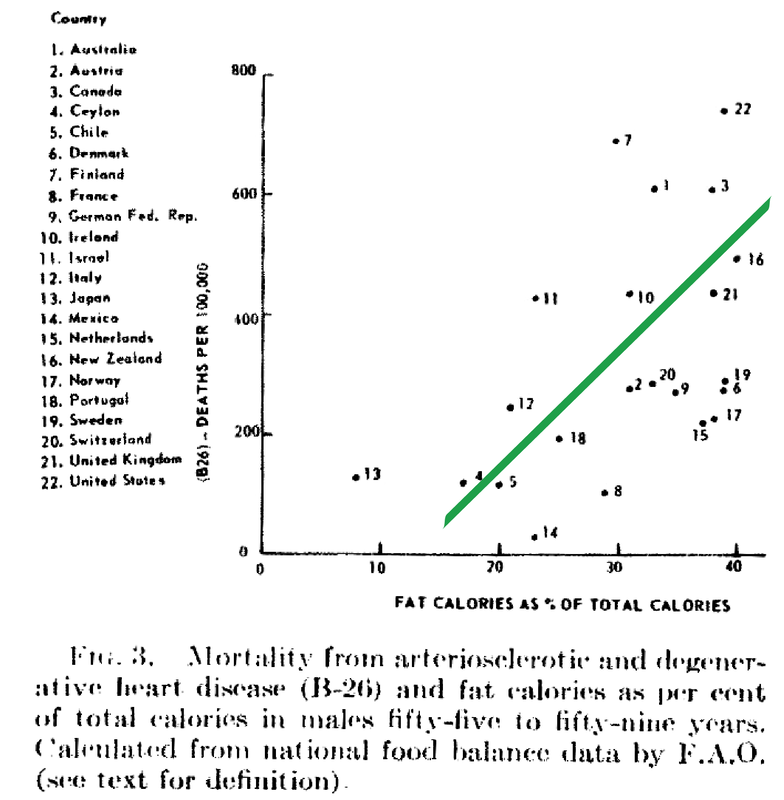
Despite food manufacturers claiming that refined vegetable oils were healthy, Americans experienced an up-rise in heart disease during the early 20th century. Like many new inventions, few questions were initially posited. Unfortunately, an alternate nutrient took the blame due to the research of a single scientist. In 1951, American physiologist and professor Ancel Keys went to Europe in search of the cause of cardiovascular disease. In his quest, he went to observe the eating habits of individuals living Naples, Italy due to reports of a low prevalence of heart disease. During this time, post-war conditions resulted in finite and unusual circumstances in regards to agriculture and infrastructure. Therefore what Keys perceived as a cultural tradition was dubbed the "Mediterranean diet". Keys observed the residents in Naples consumed primarily pasta and plain pizza, with vegetables, olive oil, cheese, fruit for dessert, a moderate amount of wine, and very little meat (except among individuals belonging to a higher socioeconomic status). Through an informal study measuring cholesterol serum levels among Rotary club members (those who could not afford meat, but could afford cheese) conducted by Keys's wife, whom at the time was a medical technologist, Keys deduced that avoiding meat resulted in a lower incidence of heart attacks. Ancel Keys continued on his biased search for proof that a diet high in saturated fat is correlated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. He eventually compiled data from six more countries with high rates of heart disease and diets typically high in saturated fat. At first glance, Keys's research seemed logical and compelling. The evidence was based on the premise that individuals in America, who consumed high amounts of saturated fat, died from heart disease at a higher rate than individuals in Japan, who consumed low amounts of saturated fat.
Unfortunately, Keys had gained the interest of people in positions of power. Upon President Eisenhower's heart attack in 1955, Keys proposed his theory to the president's primary care physician, Paul Dudley White. Days following, White began to advise to the public to reduce the consumption of saturated fat and cholesterol in an effort to prevent cardiovascular disease. Through his connections and influence, Keys soon joined the nutrition committee of the American Heart Association (AHA) which, based on Keys's research, released a report in 1961 that advised patients with a high risk of cardiovascular disease to reduce their consumption of saturated fat. (Interestingly enough, the AHA began its rise to prominence in 1948, the same year Proctor & Gamble donated over $1.7 million to the organization - resulting in the AHA indebted to Crisco.) In 1961, Time magazine placed Ancel Keys on the front cover touting him as "the twenthiest century's most influential nutrition expert." By 1970, Keys published the Seven Countries Study, which detailed his original research - this study has now been cited in over a million other scientific publications. While Keys associative observations between saturated fat and cardiovascular disease never proved causation, he had won the battle of public opinion. With the help of Ancel Keys, the American medical community and mainstream media has advised consumers to stop eating the animal products that have been consumed for centuries, replacing them with bread, pasta, margarine, low-fat dairy, and vegetable oil. This was the dietary shift that was codified by the United States government in the late 1970s. References Central Committee for Medical And Community Program of the American Heart Association. (1961). Dietary Fat and Its Relation to Heart Attacks and Strokes. Circulation [online] 23, pp.133-36. Available at: https://circ.ahajournals.org/content/circulationaha/23/1/133.full.pdf [Accessed 26 Jan. 2019]
Keys, A. (1953). Atherosclerosis: A Problem in Newer Public Health. Journal of Mt. Sinai Hospital, [online] 20(2), pp.118-39. Keys, A. (1970). Coronary Heart Disease in Seven Countries. Circulation. 41 (1), pp.1186-95. Keys, A. (1995). Mediterranean Diet and Public Health: Personal Reflections. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, [online] 61 (6), pp.1321S-1323S. Available at: https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/61.6.1321s [Accessed 26 Jan. 2019] Marvin, H. (1964). The 40 Year War on Heart Disease. New York: American Heart Association. Mercola, J. (2017). Fat For Fuel. Carlsbad, California: Hay House. Teichholz, N. (2014). The Big Fat Surprise. New York: Simon & Schuster, pp.32-33. A leading cardiovascular research scientist upends the low-salt myth, proving that salt may be one solution to—rather than a cause of—our nation’s chronic disease crises.
Sure to change the national conversation about this historically treasured substance, The Salt Fix elegantly and accessibly weaves the research into a fascinating new understanding of salt’s essential role in your health and what happens when you aren’t getting enough—with far-reaching, even heart-stopping, implications. We’ve all heard the recommendation: eat no more than a teaspoon of salt a day for a healthy heart. But there’s one big problem with this: the vast majority of us don’t need to eat low-salt diets. In fact, for most of us, more salt would be better for our health, rather than less. (Not to mention, much tastier.) Scientific research suggests that the optimal range for sodium intake is 3 to 6 grams per day (about 1 ⅓ - 2 ⅔ teaspoons of salt) for healthy adults. Now, Dr. James DiNicolantonio reveals the incredible, often baffling story of how salt became unfairly demonized—a never-before-told, century-spanning drama of competing egos and interests. Not only have we gotten it wrong, we’ve gotten it exactly backwards: eating more salt can help protect you from a host of ailments, including internal starvation, insulin resistance, diabetes, and even heart disease. (The real culprit? Another white crystal—sugar.) Dr. DiNicolantonio in The Salt Fix shows how eating the right amount of this essential mineral will help you beat sugar cravings, achieve weight loss, improve athletic performance, increase fertility, and thrive with a healthy heart. James J. DiNicolantonio, Pharm. D., is a respected cardiovascular research scientist, doctor of pharmacy at Saint Luke's Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Missouri, and the associate editor of British Medical Journal's (BMJ) Open Heart. He is the author or coauthor of approximately 200 publications in medical literature. His research has been featured in The New York Times, ABC’s Good Morning America, TIME, Fox News, U.S. News and World Report, Yahoo! Health, BBC News, Daily Mail, Forbes, National Public Radio, and Men’s Health, among others.
Physiologically, fasting:
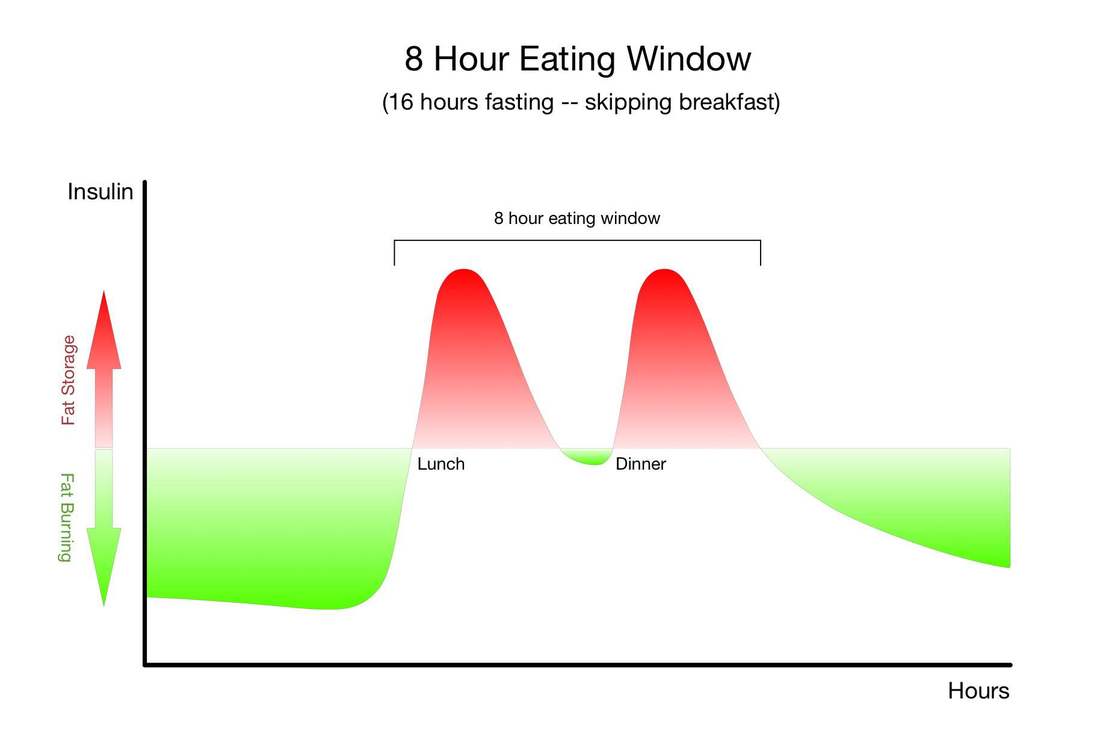
The only other strategy that has so many research-baked benefits for longevity is long-term calorie restriction, which requires a significant long-term reduction in the amount of food you eat so that you are essentially living on the brink of starvation. Compliance with calorie-restricted diets is abysmal. Fortunately, there are many ways to fast, and there is likely a form of fasting out there that you will be able to tolerate and incorporate into your life. It's important for you to remember that fasting can provide nearly identical benefits without the pain, suffering, and compliance challenges of calorie restriction. Instead of regulating how much food you eat, as with long-term calorie restriction, you only need to modify when you eat - and of course wisely choose the foods you do eat.Simply cycling between periods of eating and fasting on a daily, weekly, or monthly schedule has been shown to provide many of the same benefits as long-term calorie restriction. Choosing when to eat and when to fast in this way is known as "intermittent fasting." "Don't eat less - eat less often." |
The Awareness domain contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of self in an effort to intellectualize health concepts.
The Lifestyle domain builds off intellectual concepts and offers practical applications.
Taking care of yourself is at the core of the other domains because the others depend on your health and wellness.
Archives
May 2024
Categories
All
|




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

