Magnesium deficiency is often misdiagnosed because it does not show up in blood tests - only 1% of the body's magnesium is stored in the blood99% of magnesium is stored inside of cells, of that, 95% is stored in mitochondria. So if your blood magnesium levels are low, your incredibly deficient in magnesium.
Consider Dr. Norman Shealy's statements, "Every known illness is associated with a magnesium deficiency" and that, "magnesium is the most critical mineral required for electrical stability of every cell in the body. A magnesium deficiency may be responsible for more diseases than any other nutrient." The truth he states exposes a gapping hole in modern medicine that explains a good deal about iatrogenic death (death caused by "medicine") and disease. Because magnesium deficiency is largely overlooked, millions of Americans suffer needlessly or are having their symptoms treated with expensive drugs when they could be cured with magnesium supplementation. One has to recognize the signs of magnesium thirst or hunger on their own since allopathic medicine is lost in this regard. It is really something much more subtle then hunger or thirst but it is comparable. In a world though where doctors and patients alike do not even pay attention to thirst and important issues of hydration, it is not hopeful that we will find many recognizing and paying attention to magnesium thirst and hunger, which is a dramatic way of expressing the concept of magnesium deficiency. Few people are aware of the enormous role magnesium plays in our bodies. Magnesium is by far the most important mineral in the body. After oxygen, water, and basic food, magnesium may be the most important element needed by our bodies; vitally important, yet hardly known. It is more important than calcium, potassium or sodium and regulates all three of them. Millions suffer daily from magnesium deficiency without even knowing it. In fact, there happens to be a relationship between what we perceive as thirst and deficiencies in electrolytes. I remember a person asking, "Why am I dehydrated and thirsty when I drink so much water?" Thirst can mean not only lack of water but it can also mean that one is not getting enough nutrients and electrolytes. Magnesium, Potassium, Bicarbonate, Chloride and Sodium are some principle examples and that is one of the reasons magnesium chloride is so useful. You know all those years, when doctors used to tell their patients 'its all in your heads,' were years the medical profession was showing its ignorance. It is a torment to be magnesium deficient on one level or another. Even if it's for the enthusiastic sport person whose athletic performance is down, magnesium deficiency will disturb sleep and background stress levels and a host of other things that reflect on the quality of life. Doctors have not been using the appropriate test for magnesium - their serum blood tests just distort their perceptions. Magnesium has been off their radar screens through the decades that magnesium deficiencies have snowballed. Symptoms of Magnesium DeficiencyThe first symptoms of deficiency can be subtle - as most magnesium is stored in the tissues, leg cramps, foot pain, or muscle 'twitches' can be the first sign. Other early signs of deficiency include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness. As magnesium deficiency worsens, numbness, tingling, seizures, personality changes, abnormal heart rhythms, and coronary spasms can occur. A full outline of magnesium deficiency was beautifully presented in a recent article by Dr. Sidney Baker. "Magnesium deficiency can affect virtually every organ system of the body. With regard to skeletal muscle, one may experience twitches, cramps, muscle tension, muscle soreness, including back aches, neck pain, tension headaches and jaw joint (or TMJ) dysfunction. Also, one may experience chest tightness or a peculiar sensation that he can't take a deep breath. Sometimes a person may sigh a lot." "Symptoms involving impaired contraction of smooth muscles include constipation; urinary spasms; menstrual cramps; difficulty swallowing or a lump in the throat-especially provoked by eating sugar; photophobia, especially difficulty adjusting to oncoming bright headlights in the absence of eye disease; and loud noise sensitivity from stapedius muscle tension in the ear." "Other symptoms and signs of magnesium deficiency and discuss laboratory testing for this common condition. Continuing with the symptoms of magnesium deficiency, the central nervous system is markedly affected. Symptoms include insomnia, anxiety, hyperactivity and restlessness with constant movement, panic attacks, agoraphobia, and premenstrual irritability. Magnesium deficiency symptoms involving the peripheral nervous system include numbness, tingling, and other abnormal sensations, such as zips, zaps and vibratory sensations." "Symptoms or signs of the cardiovascular system include palpitations, heart arrhythmias, and angina due to spasms of the coronary arteries, high blood pressure and mitral valve prolapse. Be aware that not all of the symptoms need to be present to presume magnesium deficiency; but, many of them often occur together. For example, people with mitral valve prolapse frequently have palpitations, anxiety, panic attacks and premenstrual symptoms. People with magnesium deficiency often seem to be "uptight." Other general symptoms include a salt craving, both carbohydrate craving and carbohydrate intolerance, especially of chocolate, and breast tenderness." Magnesium is needed by every cell in the body including those of the brain. It is one of the most important minerals when considering supplementation because of its vital role in hundreds of enzyme systems and functions related to reactions in cell metabolism, as well as being essential for the synthesis of proteins, for the utilization of fats and carbohydrates. Magnesium is needed not only for the production of specific detoxification enzymes but is also important for energy production related to cell detoxification. A magnesium deficiency can affect virtually every system of the body. One of the principle reason doctors write millions of prescriptions for tranquilizers each year is the nervousness, irritability, and jitters largely brought on by inadequate diets lacking magnesium. Persons only slightly deficient in magnesium become irritable, highly-strung, and sensitive to noise, hyper-excitable, apprehensive and belligerent. If the deficiency is more severe or prolonged, they may develop twitching, tremors, irregular pulse, insomnia, muscle weakness, jerkiness and leg and foot cramps. If magnesium is severely deficient, the brain is particularly affected. Clouded thinking, confusion, disorientation, marked depression and even the terrifying hallucinations of delirium tremens are largely brought on by a lack of this nutrient and remedied when magnesium is given. Because large amounts of calcium are lost in the urine when magnesium is under supplied, the lack of this nutrient indirectly becomes responsible for much rampant tooth decay, poor bone development, osteoporosis and slow healing of broken bones and fractures. With vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), magnesium helps to reduce and dissolve calcium phosphate kidney stones. Magnesium deficiency may be a common factor associated with insulin resistance. Symptoms of MS that are also symptoms of magnesium deficiency include muscle spasms, weakness, twitching, muscle atrophy, an inability to control the bladder, nystagmus (rapid eye movements), hearing loss, and osteoporosis. People with MS have higher rates of epilepsy than controls. Epilepsy has also been linked to magnesium deficiencies.[1] Gastrointestinal UPSET with MagnesiumSome individuals report gastrointestinal upset with magnesium, likely due to the citrate (helpful for endothelial and metabolic function), which typically has a high bioavailability. The nature of magnesium salts is the resulting osmotic effect - the potential laxative effect is due to magnesium (salts) remaining in the intestines causing water to be drawn toward the salts for equilibrium, leading to gastrointestinal distress. While it is often recommended to take magnesium with food, some potential methods to offset the laxative effect would be to consume it fasted, augmenting absorption, and/or improve hydration by consuming more water, ideally prepared by reverse osmosis. Another way you can avoid that laxative effect is stop the consumption of magnesium citrate and taking molecular hydrogen, which contains pure ionic metallic magnesium. early warning symptoms suggestive of magnesium insufficiency
Possible manifestations of magnesium deficiency includeSevere magnesium deficiency can result in low levels of calcium in the blood (hypocalcemia). Magnesium deficiency is also associated with low levels of potassium in the blood (hypokalemia). Magnesium levels drop at night, leading to poor REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep cycles and unrefreshed sleep. Headaches, blurred vision, mouth ulcers, fatigue and anxiety are also early signs of depletion. We hear all the time about how heart disease is the number one health crisis in the country, about how high blood pressure is the "silent killer", and about how ever increasing numbers of our citizens are having their lives and the lives of their families destroyed by diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, and a host of other chronic diseases. Signs of severe magnesium deficiency include
Magnesium deficiency is synonymous with diabetes and is at the root of many if not all cardiovascular problems. Magnesium deficiency is a predictor of diabetes and heart disease both; diabetics both need more magnesium and lose more magnesium than most people. In two new studies, in both men and women, those who consumed the most magnesium in their diet were least likely to develop type 2 diabetes, according to a report in the January 2006 issue of the journal Diabetes Care. Until now, very few large studies have directly examined the long-term effects of dietary magnesium on diabetes. Dr. Simin Liu of the Harvard Medical School and School of Public Health in Boston says, "Our studies provided some direct evidence that greater intake of dietary magnesium may have a long-term protective effect on lowering risk," said Liu, who was involved in both studies. The thirst of diabetes is part of the body's response to excessive urination. The excessive urination is the body's attempt to get rid of the extra glucose in the blood. This excessive urination causes the increased thirst. But we have to look at what is causing this level of disharmony. We have to probe deeper into layers of cause. The body needs to dump glucose because of increasing insulin resistance and that resistance is being fueled directly by magnesium deficiency, which makes toxic insults more damaging to the tissues at the same time. When diabetics get too high blood sugars, the body creates "ketones" as a by-product of breaking down fats. These ketones cause blood acidity which causes "acidosis" of the blood, leading to Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), This is a very dangerous condition that can lead to coma and death. It is also called "diabetic acidosis", "ketosis", "ketoacidosis" or "diabetic coma". DKA is a common way for new Type 1 diabetics to be diagnosed. If they fail to seek medical advice on symptoms like urination, which is driving thirst they can die of DKA. Oral magnesium supplements reduce erythrocyte[2] dehydration.[3] In general, optimal balances of electrolytes are necessary to maintain the best possible hydration. Diabetic thirst is initiated specifically by magnesium deficiency with relative calcium excess in the cells. Even water, our most basic nutrient starts having a hard time getting into the cells with more going out through the kidneys. If your magnesium supplementation is not working as desired, it may be due to a lack of available ATP. It would be advised to take a bioavailable form of niacinamide to facilitate NAD+ production, approximately 30 minutes before taking the magnesium supplement. A great bioavailable source of B-vitamins, including niacinamide, is local bee pollen. Autism and Magnesium DeficiencyWhen dealing with ASD and other neurological disorders in children it is important to know the signs of low magnesium: restless, can't keep still, body rocking, grinding teeth, hiccups, noise sensitive, poor attention span, poor concentration, irritable, aggressive, ready to explode, easily stressed. When it comes to children today we need to assume a large magnesium deficiency for several reasons. 1) The foods they are eating are stripped of magnesium because foods in general, as we shall see below are declining in mineral content in an alarming way. 2) The foods many children eat are highly processed junk foods that do not provide real nutrition to the body. 3) Because most children on the spectrum are not absorbing the minerals they need even when present in the gut. Magnesium absorption is dependent on intestinal health, which is compromised totally in leaky gut syndromes and other intestinal problems that the majority of autism syndrome disorders. 4) Because the oral supplements doctors rely on are not easily absorbed, because they are not in the right form and because magnesium in general is not administered easily orally. Modern medicine is supposed to help people not hurt them, but with their almost total ignorance of magnesium doctors end up hurting more than they help for many of the medical interventions drive down magnesium levels when they should be driving them up. Many if not most pharmaceutical drugs drive magnesium levels into very dangerous zones and surgery done without increasing magnesium levels is much more dangerous then surgery done with. The foundation of medical arrogance is actually medical ignorance and the only reason ignorance and arrogance rule the playing field of medicine is a greed lust for power and money. Human nature seems to be at its worst in modern medicine when it should be at its best. It is sad that people have to suffer needlessly and extraordinarily tragic that allopathic medicine has turned its back on the Hippocratic Oath and all that it means. Resources[1] https://www.nhfw.info/magnesium.html
[2] Red blood cells are also known as RBCs, red blood corpuscles (an archaic term), haematids or erythrocytes (from Greek erythros for "red" and kytos for "hollow", with cyte translated as "cell" in modern usage). The capitalized term Red Blood Cells is the proper name in the US for erythrocytes in storage solution used in transfusion medicine. [3] J. Clin. Invest. 100(7): 1847-1852 (1997). doi:10.1172/JCI119713. The American Society for Clinical Investigation
1 Comment
How would you like to build new neural connections so that you can align your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors with what you ultimately want to achieve? You're in luck. You are innately endowed with the ability to train your brain to become an elite performer (if that's what you desire to do). Your Mental World For a moment, imagine your brain as if it is it's own planet. Your "neural planet" has a population of some 85 billion neurons. Just as people in close proximity interact with one another, neurons communicate to each other via synapses and neurotransmitters. A synapse is an electrochemical junction between two nerve cells, in which impulses pass by diffusion of chemicals, also referred to as neurotransmitters. If you took a consensus of your mental world, neurons of different sizes would be visible all over. Neurons that fire together look somewhat like a social gathering occurring. From a bird's-eye view, you would be able to see "remote villages" variably exchanging conversation, "towns" making more connections, and "large metropolitan areas" continuously in contact. Synapses vary in size because the frequency of neural communication dictates the size and efficiency of their pathway. Infrequently used trails can become freeways and vice versa. This connection between neurons, and clusters of neurons, is the essential function of the brain. Every time you think, feel, act, emotionalize, or remember, you reinforce existing brain neural connections or create new ones. There are neural patterns for everything, from standing to reading this page. The innumerable patterns in which your brain cells connect and share information reflects your brain's capacity to perform. Neuroplasticity: The Brain's Ability to Change ItselfThe old scientific paradigm held that you can't teach an old dog new tricks. Fortunately, the old paradigm has evolved and incorporated the science of neuroplasticity, which suggests the brain can change and it can happen at any time. Like plastic, neurons can mold into new forms, creating new connections. Any time you learn a new skill, the brain is changing by making new neural connections. Whether it is learning to play an instrument, speaking a new language, discovering a new route home, eating whole foods, and so much more, your brain begins to change itself. Learning is forging new connections. Remembering is maintaining and sustaining those connections. And just like a relationship, the more communication that occurs, the more bondage that takes place. Neurons are the same way. What is really fascinating, is that you can change your brain, not only by doing, but also by thinking. Researchers have demonstrated that the act of focusing and being present through meditation changes the brain in many ways. Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to change itself, and it's the innate ability that you can harness to help you attain your goals. Continental Shift: Three Ways Neuroplasticity WorksYou are able to reshape your brain using the same principles that your brain was built - neurons firing and wiring, syncing and linking together. There are three ways that neuroplasticity can change your mind:
More neurons, more connections, and more efficient connections. These are the three ways to exponentially transform your life. But, there is a caveat. As an adult, some of your neuroplasticity is turned off. But once again, you're in luck, you can turn it back on. Teaching Old Dogs New TRicks: Turning On NeuroplasticityAs an infant, the brain is a sponge, absorbing what it can in an effort increase the chances of survival. As you age, your neuroplasticity slows down as new memories and skills are created; habitual patterns begin to direct most of your daily activities, and novel ideas get pushed to the back burner. As an adult, learning processes, beliefs, and behaviors become, more or less "fixed" within the neural pathways of the brain. This means the plasticity switch is predominately in the "off" position, to varying degrees in each individual. One person may be so set in their ways that to try to get them to see things from a new perspective is like talking to a brick wall. Whereas another person may be more flexible and is able to take all sides into consideration. In either case, neuroplasticity can work at any age, so in the case of that brick wall, the only thing holding them back is themselves. They're not old dogs who can't learn new tricks, they're just uninformed, or perhaps unwilling. Here are six time-tested principles to turn on neuroplasticity:
Here are some more ways to activity neuroplasticity:
Clearly more is better. Neuroplasticity is a ongoing process, and if you are committed to being the best version of yourself, then it is a lifelong process. References Assaraf, J. (2018). Innercise. Cardiff, CA: Waterside Press.
Dr. Joe Dispenza is teaching the world how to empower and heal our mind through meditation and mindfulness. His studies have proven that when well practiced these tools can put us on the path to understanding and breaking deep-rooted bad habits and even heal illnesses. The author of Becoming Supernatural explains how to stop your mind from controlling you on this episode of Impact Theory with Tom Bilyeu.
Transcript: It's a scientific fact that the hormones of stress downregulate genes and create disease. Long-term effects. Human beings because of the size of the neocortex, we can turn on the stress response just by thought alone. As I think about our problems and turn on those chemicals. That means then our thoughts could make us sick. So if it's possible, that our thoughts could make us sick then it is possible then our thoughts could make us well? The answer is absolutely yes. Everybody welcome to Impact Theory. Our goal with this show and company is to introduce you to the people and ideas that will help you actually execute on your dreams. Alright today's guest is a New York Times bestselling author and one of the most sought-after speakers in the world. He's lectured and given advanced workshops in more than 30 countries across five continents all with the aim of helping people better understand and unlock the power of their mind. His expertise is the intersection of the fields of neuroscience, epigenetics and quantum physics and he's partnered with other scientists across multiple disciplines to perform extensive research on the effects of meditation using advanced technologies such as epigenetic testing brain mapping with EEG s and gas-discharge visualization technology. Through his work he is endeavouring to help advance both the scientific community and the public at large as understanding of mind derived health optimization, a topic he covered extensively in his groundbreaking book, You Are The Placebo. His teaching has had such a profound impact on the way that people perceive a wide range of brain related topics around mindfulness and well-being. [that] He's a faculty member at the quantum University in Hawaii the Omega Institute for holistic studies in New York and the Kerr Paulo Centre for yoga and health in Stockbridge, Massachusetts. He's also an invited chair of the research committee at life University in Atlanta, as well as a corporate consultant where he delivers his lectures and workshops for businesses. So, please help me in welcoming the man who has appeared in such films as Heal, People Versus the State of Illusion and Unleashing Creativity, the author of the recent book Becoming Supernatural, Dr. Joe Dispenza. Thanks for being here. So, diving into your world and how you perceive the sense of self and the way that you marry science to - the way that we form memories the way that we live in a perpetual state of reliving our past and things like that. It's really, really incredible and I want to dive into the whole notion of you sort of being a habitual construct like what? What is that? What is the habit of you? Well a habit is a redundant set of automatic unconscious thoughts, behaviors and emotions that's acquired through repetition. The habit is when you've done done something so many times that your body now knows how to do it better than your mind. So if you think about it, people wake up in the morning, they begin to think about their problems. Those problems are circuits, memories in the brain, each one of those memories are connected to people and things at certain times and places. And, if the brain is a record of the past, the moment they start their day, they're already thinking in the past. Each one of those memories has an emotion. Emotions are the end product of past experiences. So the moment they recall those memories of their problems, they all of a sudden feel unhappy, they feel sad, they feel pain. Now how you think and how you feel creates your state of being. So the person's entire state of being when they start their day is in the past. So what does that mean? The familiar past will sooner or later be predictable future. So, if you believe that your thoughts have something to do with your destiny and you can't think greater than how you feel, or feelings have become the means of thinking, by very definition of emotions you're thinking in the past. And for the most part you're going to keep creating the same life. So then people grab their cell phone they check their WhatsApp. They check their texts. They check their emails. They check Facebook. They take a picture of their feet. They post it on Facebook. They tweet something, they do Instagram. They check the news and now they feel really connected to everything that's known in their life. And then they go through a series of routine behaviors. They get out of bed on the same side. They go to the toilet. They get a cup of coffee. They take a shower, they get dressed, they drive to work the same way. They do the same things. They see the same people, that pushed the same emotional buttons, and that becomes the routine and it becomes like a program. So now they've lost their free will to a program, and there's no unseen hand doing it to them. So when it comes time to change the redundancy of that cycle becomes a subconscious program. So now 95% of who we are by the time we're 35 years old is a memorized set of behaviors, emotional reactions, unconscious habits, hardwired attitudes, beliefs and perceptions that function like a computer program. So then person can say with their five percent of their conscious mind. I want to be healthy. I want to be happy. I want to be free, but the body's on a whole different program. So then how do you begin to make those changes? Well, you have to get beyond the analytical mind because what separates the conscious mind from the subconscious mind is the analytical mind and that's where meditation comes in, because you can teach people through practice how to change their brainwaves, slow them down. And, when they do that properly they do enter the operating system where they can begin to make some really important changes. So most people then wait for crisis or trauma or disease or diagnosis, you know, they wait for loss some tragedy to make up their mind to change and my message is, "Why wait?" You can learn and change in a state of pain and suffering or you can learn and change in a state of joy and inspiration. I think right now the cool thing is that people are waking up. That's really interesting. And where I found the the deepest hooks into how powerful this can be for somebody is when you talk about trauma and you've talked about how people experience a traumatic event, but they then basically rehearse it and how that then has this knock-on effect. So, what is that? Why do people find it so hard to get past trauma? Well, the stronger the emotional reaction you have to some experience in your life, the higher the emotional quotient, the more you pay attention to the cause, and the moment the brain puts all of its attention on the cause, it takes a snapshot and that's called a memory. So long-term memories are created from very highly emotional experiences. So what happens then is that people think neurologically within the circuitry of that experience and they feel chemically within the boundaries of those emotions. And so when you have an emotional reaction to someone or something most people think that they can't control their emotional reaction. Well, it turns out if you allow that emotional reaction, it's called a refractory period to last for hours or days, that's called the mood. I say to someone, "Hey, what's up think?" "I'm in a mood," "Well, why are you in a mood?" "Well I had this thing happen to me five days ago and I'm having one long emotional reaction." If you keep that same emotional reaction going on for weeks or months that's called temperament. Why is he so bitter? I don't know. Let's ask him. Why is he so bitter? "Why are you bitter?" "Well, I had this thing happened to me nine months ago." And if you keep that same emotional reaction going on for years on end that's called a personality trait. And so learning how to shorten your refractory period of emotional reactions is really where that work starts. So then people when they have an event what they do is they keep recalling the event because the emotions of stress hormones the survival emotions are saying pay attention to what happened, because you want to be prepared if it happens again. Turns out most people spend 70% of their life living in survival and living in stress. So they're they're always anticipating the worst-case scenario based on a past experience and they're literally, out of the infinite potentials in the quantum field, they're selecting the worst possible outcome and they're beginning to emotionally embrace it with fear and their conditioning their body into a state of fear. Do that enough times, the body has a panic attack without you. You can't even predict it because it's programmed subconsciously. So then you say to the person, "Why are you this way?" And they'll say, "I am this way because of this event that happened to me 15 or 20 years ago," and what that means from biological standpoint is that they haven't been able to change since that event. So then the emotions from the experience tend to give the body and the brain a rush of energy. So people become addicted to the rush of those emotions and they use the problems and conditions in their life to reaffirm their limitation, so at least they can feel something. So now when it comes time to change you say the person, "Why are you this way?" Well, every time they recall the event they're producing the same chemistry in their brain and body as if the event is occurring, firing and wiring the same circuits and sending the same emotional signature to the body. Well, what's the revelant behind that? Well, your body is the unconscious mind. It doesn't know the difference between the experience that's creating the emotion and the emotion that you're creating by thought alone. So the body's believing it's living in the same past experience 24 hours a day, seven days a week, 365 days a year. And so then when those emotions influence certain thoughts, and they do, and then those thoughts create the same emotions, and those same emotions influence the same thoughts, now the entire person's state of being is in the past. So then the hardest part about change is not making the same choice as you did the day before a period. And the moment you decide to make a different choice get ready because it's going to feel uncomfortable, it's going to feel unfamiliar. So why does it feel so uncomfortable? Is it because of the neurons that fire together wire together? So there's like an easiness to that loop. (Just because, literally, and you've talked very eloquently about this the way that the neurons connect in the brain how rapidly. I've seen you show footage of how rapidly those connections happen, which is pretty incredible." Is that what makes it so discomforting for people? I think that the bigger thing is that as we keep firing and wiring those circuits, they become more hardwired. So there you have a thought and then the program runs but it's the emotion that follows the thought. If you have a fearful thought you're gonna feel anxiety, the moment you feel anxiety your brains checking in with your body and saying, " Yeah, you're pretty anxious." So then you start thinking more corresponding thoughts equaled how you feel. Well, the redundancy of that cycle conditions the body to become the mind. So now when it comes time to change, a person steps into that river of change and they make a different choice in all of a sudden they don't they don't feel the same way. So the body says, "Well, you've been doing this for 35 years." Well, you're gonna just stop feel suffering and stop feeling guilty and stop feeling shameful and you're not gonna complain, or blame, or make excuses, or feel sorry for yourself. The body's in the unknown. So the body says I want to return back to familiar territory. So the body starts influencing the mind then it says, "Start tomorrow, you're too much like your mother. You'll never change. This isn't gonna work for you. This doesn't feel right." And so if you respond to that thought as if it's true, that same thought will lead to the same choice, which will lead to the same behavior, which will create the same experience, which produce the same emotion. I want to talk about that notion. Give me a little more detail. We mean by the body becomes the mind or the unconscious mind. What do you mean by that exactly? Well, those are two different things. Your body is your unconscious mind. In a sense, if you're sitting down and you start thinking about some future worst-case scenario that you're conjuring up in your mind and you begin to feel the emotion of that event, your body doesn't know the difference between the event that's taking place in your world, outer world, and what you're creating by emotion or thought alone. So most people then, they're constantly reaffirming their emotional states. So when it comes time to give up that emotion they can say, "I really want to do it," but really the body is stronger than the mind because it's been conditioned that way. So, the servant now has become the master and the person all of a sudden once they step into that unknown, they'd rather feel guilt and suffering because at least they can predict it. Being in the unknown is a scary place for most people because the unknown is uncertain. People say to me, "Well, I can't predict my future. I'm in the unknown." And I always say, "The best way to predict your future is to create it. Not from the known but from the unknown. What thoughts do you want to fire and wire in your brain? What behaviors do you want to demonstrate in one day? The act of rehearsing mentally, closing your eyes and rehearsing the action. The rehearsing the reaction of what you want. The action of what you want by closing your eyes and mentally rehearsing some action. If you're truly present, the brain does not know the difference between what you're imaging and what you're experiencing in 3D world. So then you begin to install the neurological hardware in your brain to look like the event has already occurred. Now your brain is no longer a record of the past. Now, it's a map to the future. And if you keep doing it, priming it that way, the hardware becomes a software program and who knows you just may start acting like a happy person. And then I think the hardest part is to teach our body emotionally what the future will feel like ahead of the actual experience. So, what does that mean? You can't wait for your success to feel empowered. You can't wait for your wealth to feel abundant. You can't wait for your your new relationship to feel love, or your healing to feel whole. I mean that's the old model of reality of cause and effect, you know waiting for something outside of us to change how we feel inside of us and when we feel better inside of us. We pay attention to whatever caused it. But what that means then is that from the Newtonian world that most people spend their whole life living in lack, waiting for something to change out there. What do you mean the Newtonian world? Newtonian world is all about the predictable. It's all about predicting the future. But the quantum model of reality isn't is about causing an effect. The moment you start feeling abundant and worthy you are generating wealth. The moment you're empowered and feel it, you're beginning to step towards your success the moment. You start feeling whole, your healing begins. And when you love yourself and you love all of life, you'll create an equal. And now you're causing and effect and I think that's that the difference between living as a victim - In your world saying "I am this way because of this person or that thing or this experience. They made me think and feel this way." When you switch that around you become a creator of your world and you start saying, "My thinking and my feeling is changing an outcome in my life." And now that's a whole different game and we start believing more that were creators of reality. So, how do we go from, "Okay, I have this negative emotion. It's controlling my life. It's got me in this cycle of I think about this emotion, which triggers a chemical reaction, which trains my body to feel that way, which makes it easier more likely I will do it again, and so now I'm in this vicious cycle." And it's unconscious right. You said, "Does your thinking create your environment, or does your environment create your thinking," which I thought was really, really interesting. So, how do we then go from that, like mechanistically, to begin this visualization process of something that's empowering, its me in a different state, it's my future self. Is it meditation? What does that look like? If you're not being defined by a vision of the future, then you're left with the old memories of the past and you will be predictable in your life. And, if you wake up in the morning and you're not being defined by a vision in the future as you see the same people and you go to the same places and you do the exact same thing at the exact same time, it's no longer that your personality is creating your personal reality. Now your personal reality is affecting or creating your personality. Your environment is really controlling how you think and feel unconsciously, because every person every thing every place every experience has a neurological network in your brain. Every experience that you have with every person produces an emotion. So some people will use their boss to reaffirm their addiction to judgment. They'll use their enemy to reaffirm their addiction to hatred. They'll use their friends to reaffirm their addiction to suffering. So now they need the outer world to feel something. So, to change them is to be greater than your environment, to be greater than the conditions in your world and the environment is that seductive. So then why is meditation the tool? Well, let's sit down. Let's close our eyes. Let's disconnect from your outer environment. So if you're seeing less things is less stimulation going to your brain if you're playing soft music or you have earplugs in, less sensory information coming to your brain. So you're disconnecting from environment if you can sit your body down and tell it to stay like an animal stay right here. I'm gonna feed you when we're done. You can get up and check your emails. You can do all your texts, but right now you're gonna sit there and obey me. So then, when you do that properly and the you're not eating anything or smelling anything or tasting anything, you're not up experiencing and feeling anything, you would have to agree with me that you're being defined by a thought, right? So when the body wants to go back to its emotional past, and you become aware that your attention is on that emotion, and where you place your attention is where you place your energy, you're siphoning your energy out of the present moment into the past and you become aware of that. And, you settle your body back down in the present moment because it's saying "Well, it's eight o'clock. You normally get upset because you're in traffic around this time and here you are sitting and we're used to feeling anger and you're off schedule. Oh, it's 11 o'clock and usually check your emails and judge everybody." Well, the body is looking for that that predictable chemical state every time you become aware that you're doing that and your body is craving those emotions and you settle it back down into the present moment, you're telling the body it's no longer the mind, that you're the mind. And now your will is getting greater than the program. And if you keep doing this over and over again, over and over again, over and over again, just like training a stallion or a dog, it's just gonna say, "I'm gonna sit." And the moment that happens, when the body's no longer the mind, when it finally surrenders, there's a liberation of energy. We go from particle to wave, from matter to energy, and we free ourselves from the chains of those emotions that keep us in the in the familiar past and we've seen this thousands of times. In fact, we can actually predict it now on a brain scan. That's so interesting. Let's go a little bit harder on metacognition, the notion that you don't have to believe everything you think. I love the way that you talk about that. Hmm. Yeah, and we have a huge frontal lobe. It's 40% of our entire brain, and most people when they have a thought they just think that that's the truth. And, I think one of my greatest realizations in my own journey was just because you have a thought, it doesn't necessarily mean it's true. So if you think 60 to 70 thousand thoughts in one day, and we do, and 90% of those thoughts are the same thoughts as the day before and you believe that your thoughts have something to do with your destiny, your life's not gonna change very much. Because the same thought leads to the same choice, the same choice leads to the same behavior, the same behavior creates the same experience, and the same experience produces the same emotion. And so then, the act of becoming conscious of this process, to begin to become more aware of how you think, how you act, and how you feel, it's called metacognition. And so then, why is that important? Because the more conscious you become of those unconscious states of mind and body, the less likely you're gonna go unconscious during the day. And that thought is not gonna slip by your awareness unchecked. It means to know thyself. And the word meditation means to become familiar with. So as you become familiar with the thoughts the behaviors and the emotions of the old self, you're retiring that old self as you fire and wire new thoughts and condition the body into a new emotional state. If you do that enough times, it'll begin to become familiar to you. So it's so important. Just like a garden, if you're planting a garden, you've got to get rid of the weeds. You got to take the plants from the past year and you got to pull them out. The rocks that sift to the top that are like our emotional blocks, they have to be removed that soil has to be tenderized and broken down. We have to we have to make room to plant the new garden. So primarily, we learn the most about ourselves and others when we're uncomfortable, because the moment you move into that uncomfortable state, normally a program jumps in. When that program jumps in, it's because the person doesn't want to be in the present moment and engage it consciously. So when you teach people how to do that with a meditative process, turns out that when they're in their life, they're less likely to emotionally react. They're less likely to be so rigid and believe the thoughts they were thinking. They're more aware of when they go unconscious back into a habit, and that is what starts the process of change. And, so we have to unlearn before we relearn. We have to break the habit of the old self before we reinvent a new self. We have to pre-synaptic connections and sprout new connections. We have to unfire and unwire and refire and rewire. We have to unmemorize emotions that are stored and then recondition the body that to a new mind into a new emotion. Like the deprogram and reprogram, that's the act, and it's a two-step process. Yeah, I like the way that you call that out as an action. There was another thing that you said that I thought was really powerful, about how insights themselves are essentially inert, they don't do anything. What what then do we do with an insight? How do we take a breakthrough moment and make sure that it's not just a breakthrough moment? Like I guarantee people watching right now are having like a hundred aha moments. For sure, that was definitely the case for me as I was researching you and when you said that I was like and that's the danger that you have the aha and then nothing. Yeah, and it is a danger, because then people will will shrink back into mediocracy and they'll use the insight to excuse them from taking a leap. They'll say, "Yeah, you know, I have a chemical imbalance in my brain. Yeah, my father was really overbearing, he was a perfectionist. That's why I am the way I am." You know people, they come up with stuff to excuse themselves. The insight is actually giving them permission to stay limited. And it's an amazing idea because they'll say to you that they really want to get over their anxiety. But let's ok. Let's take your ex-husband. Let's put him in a straitjacket. Let's duct tape them and shoot them to the moon know what I mean. What are you gonna do now? You still have to make those changes. And so then the person's enemy dies or they're something shifts in their life and that person's gone, they'll find another person to hate. This is just how we function as human beings. We just slide another reason to feel those emotions. So I think I think when people start to understand this, you know, I think knowledge is power. But knowledge about yourself is self empowerment. So how much of this is really learning to just bifurcate the world into (there's) negative emotions that have negative neurochemistry - associated with, and you said that in those states if you're living in a perpetual state of stress hormones and things like that illness is like a step away and then just the other side of that is understanding - (but there's) [and] this whole other side of positive energy, which happiness, joy, empowerment - whatever that you know neurochemical cocktail is, but that when you're on that side your immune system is more likely to function well. Is that just sort of bringing it down to like a really base level. Yeah, that's sort of one of the biggies. Well, let's talk about it in terms of survival or creation As I said 70% of the time people live in stress and living in stress is living in survival. Now, all organisms in nature can tolerate short-term stress, you know a deer gets chased by a pack of coyotes, when it out runs the Coyotes it goes back to grazing and the event is over. And the definition of stress is when your brain and body are knocked out of balance, out of homeostasis. The stress response is what the body innately does to return itself back to order. So you're driving down the road, someone cuts you off, you jam on the brakes, you may give them the finger and then you settle back down and the event is over and boom now everything's back back to normal. But what if it's not a predator that's waiting for you outside the cave, but what if it's your coworker sitting right next to you and all day long you're turning on those chemicals because they're pushing all your emotional buttons. When you turn on the stress response, and you can't turn it off, now you're headed for a disease because no organism in nature can live an emergency mode for that extended period of time. It's a scientific fact that the hormones of stress down regulate genes and create disease, long term effects. Human beings, because of the size of the neocortex, we can turn on the stress response just by thought alone, I can think about our problems and turn on those chemicals. That means then our thoughts could make us sick. So if it's possible that our thoughts could make us sick, is it possible that our thoughts could make us well? The answer is absolutely, yes. So then what are the emotions that are connected to survival? Let's name them, anger, aggression, hostility, hatred, competition, fear, anxiety, worry, pain, suffering, guilt, shame, unworthiness, envy jealousy. Those are all created by the hormones of stress. And psychology calls them normal human states of consciousness, I call those altered states of consciousness. So then we tend to remember those traumatic events more because in survival, you better be ready if it happens again. And in one's survival gene is switched on you could have ten really great things that happen to you in your day and you just have one bad thing that happens and you cannot take your attention off that unhappy thing because the survival gene is switched on. It's really interesting. How does epigenetics come into play in all this. What's actually happening? You've talked pretty profoundly about proteins and like really at a deep level how we're signalling to our genetics to create these kinds of changes. What does that actually look like? Well, epigenetics. Epi means above the gene. And many years ago after the DNA helix was discovered by Watson and Crick, they said the blueprints of life, you know, all diseases are created from genes. It turns out less than 5%, more like 1%. of people on the planet are born with a genetic condition like type 1 diabetes or Tay-sachs disease or sickle cell anemia. The other 95 to 99 percent are created by lifestyle and by choices. You can take to identical twins with the exact same genome, one dies at 51, the other one dies at 85, same gene different environment. So, all of a sudden they said, "We lied. That was wrong. It's not genes that create disease. It's the environment that signals the gene that creates disease." Well, ok, but that's not the whole truth too because you could have two people working side by side in the same factory, one gets cancer after being exposed to a carcinogenic for 25 years, both working for 25 years, he other one has no cancer at all. So there must be some internal order that would cause one person to not get it while another one does. So is it possible then, if the environment signals the gene, and it does, and the end product of an experience in the environment is called an emotion, can you signal the gene ahead of the environment by embracing an elevated emotion? We've done the research on this where we measured 7,500 different gene expressions in a group of people. It came to an advanced event for four days. And we had them doing a seated meditation, a walking meditation, a laying down meditation, a standing meditation. And at the end of four days, just four days, the common eight genes that were upregulated, two genes to suppress cancer cells and tumor growth; two genes for neurogenesis the growth of new neurons in response to novel experiences; and learning the gene that signals stem cells to go to damaged areas and repair them; the gene for oxidative stress was upregulated. We started seeing all these genes that are very, very healthy to cause the body to flourish. Imagine if people were doing that for three months. We also measured telomeres - the little shoestrings on the end of DNA that tell us our biological age. We asked people to do the work meditation five out of seven days for 60 days. Measure their telomeres that determine their biological age. sixty days later, seventy four percent of the people lengthen their telomeres, 40 percent significant change, twenty percent a very remarkable change. That means that they got a little bit of their life back if it lengthened by ten percent. They got 10% of their life back. That's incredible. Before I ask my last question tell these guys where they can find you online. Sure. My website is just https://drjoedispenza.com. You can follow us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, we're all over. And then my final question. What's the impact that you want to have on the world? I think that the end game for me is to empower people to such a degree that they realize that they need less things outside of them to make them happy, less things outside of them to regulate their moods and their behaviors, and that they begin to use the kind of the power that we all have access to, and into really, and to change the world, to make a difference so that there's more peace, here's more wholeness, there's more connection. That we support and love each other, and we serve better. And I think that we have to start for the most part if everybody's working on themselves. And trying doing their best to present the greatest ideal of themselves to the world, I think the world would be a better place. And so, that's my passion and I'm witnessing it happening now the more than I ever thought I would. That was incredible Joe. Thank you so much for being here and amazing having you. Transcript:
Remember that time Ron believed that Harry gave him Liquid Luck? Felix Felicis, known in the wizarding world as Liquid Luck, is a magical potion that gives it’s drinker good fortune. For a period of time, everything the drinker attempts will be successful. So in the following scene we see Ron dominate the quidditch match, and become Gryffindor’s latest hero. But of course there’s a catch, Harry didn’t actually put the potion in Ron’s drink at all. This is a prime example of the placebo effect. A placebo is a treatment with no active therapeutic properties. And it’s often used as the control in clinical trials to test the effectiveness of new pharmaceutical drugs. But the effect refers to the physiological phenomenon that usually happens to the control group who was given the placebo treatment. Their condition improves in a way that is often comparable and sometimes even better than the control group, even though they weren’t given any drugs at all. In cases where the placebo outperforms the drug, researchers come to the conclusion that the pharmaceutical should be deemed ineffective. But why aren’t they more interested in the fact that these people are getting better with no medicine at all? It’s no secret that the healthcare industry needs sick people in order to turn over a profit. In a 2018 report, the investment banking company Goldman Sachs looked into the investment potential of biotech research companies who are attempting to create “one shot cures.” Their conclusion? Cures could be bad for business. They stated “While this proposition carries tremendous value for patients and society, it could represent a challenge for genome medicine developers looking for sustained cash flow.” So should we really be surprised that nobody’s putting money behind self-healing research? You can’t exactly put “belief” in tablet form and sell it to patients. But that’s sort of what placebos are. The examples of miraculous placebo effect results are pretty much endless, so we’ll just look at a few. In 2001, Irving Kirsch from Harvard Medical School used the Freedom of Information Act to obtain data of clinical trials of top antidepressants. He found that in over half of these trials, the drugs didn’t outperform the placebos, and concluded that 80% of the success in those trials was due to the placebo effect. Several studies have shown that the placebo effect can also affect physical performance. In one of these studies, a group of weight lifters were told that they were being given a legal anabolic steroid. Each of those athletes set all-time personal records in every exercise tested after being administered the fake steroid. So we have the ability to improve mental conditions and physical performance with our mind, but can the placebo effect go as far as surgery? According to this study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, yes. A group of 180 patients with osteoarthritis of the knee were split into three groups. One group underwent an operation that shaves down the damaged cartilage, one group received a flushing of the knee joint, and one group received a faux surgery. Complete with pre-op, post-op, small incisions on the knee to produce scars, and audio cues that an operation was taking place. And the results were startling, the patients were followed up with at various times throughout recovery with the last check-in being 24 months after surgery. The data showed that “At no point did either of the intervention groups report less pain or better function than the placebo group.” And they concluded, “Finally, health care researchers should not underestimate the placebo effect, regardless of its mechanism.” Some have argued that the placebo effect boils down to good old fashioned bedside manner. In fact, the Senior Medical Fellow at the American Council on Science and health has claimed that it really just goes back to the soul of medicine — ritual, symbolism, trust, hope, and compassion. And it’s true that the doctor-patient relationship plays a large role in the effectiveness of treatment. Patients with optimistic and compassionate doctors tend to fare better than those who receive treatment from unenthusiastic ones. But it’s doubtful that this can explain the magic of the placebo effect entirely. After all, there’s something going on physiologically. And to get a better understanding of just what that is, we’re going to have to dive a little deeper. Bruce Lipton is a cellular biologist who’s research gives us some insight into the mechanism that allows us to heal ourselves. Once upon a time, the planet was populated with single-celled organisms. They did alright for themselves, the protein building blocks of the cells acted as receptors and effectors that took in environmental information and responded accordingly. But after some time these cells started to join together, forming communities that acted as units. As a means of survival, special cells were tasked with acting as a centralized info processing system or what we would call a brain. In this way, highly evolved animals were able to take in even more information from the environment and relay it to all of the cells throughout the body. This was great for organizing the flow of signal molecules that regulate the cells’ behaviors.But it also meant that individual cells had to relinquish control to the brain. And as proud owners of these brains, we can all attest that sometimes our mind generates emotions that are unrelated to our environment and definitely not necessary or conducive to our survival. And these emotion are so strong that they have the ability to override the system. So that’s great news, right? We can just think happy, healthy, positive thoughts to override the system and cure ourselves of any disease. Well, not exactly. There’s an important distinction to be made about the instructions that our mind is sending to the rest of our body. Some are coming from our conscious mind, but most are coming from our subconscious mind. And unfortunately, the one that we have control over is only driving the bus about 5% of the time. Our conscious mind is where we generate thoughts, but our subconscious mind is actually where most of our instructions are coming from whether we realize it or not. Our subconscious mind acts out of habits and experiences that are formed over a lifetime, but most of which are programmed before we even reach adolescence. It’s where we store all of our fears and past traumas, so it’s no surprise that it might be operating under disempowering programs which conflict with the best intentions of our conscious mind. But it isn’t all doom and gloom. Dr. Lipton believes that these programs can be easily overwritten through things like meditation, hypnotherapy, and various other forms of energy psychologies. But how could these woo woo sounding modalities possibly work better than the chemicals that directly alter the functions and behaviors of particular cells? It turns out that cells respond much better to energy signals than they do to chemical signals. When a chemical bond is made, most of the cell’s energy is wasted through chemical coupling. So very little energy is left to take in information and respond to the signal. On the other hand, energy signals link with a cell’s available energy to relay environmental information which according to Oxford biologist C.W.F. McLare makes them 100% more efficient at receiving and responding to signals. So now the placebo effect results aren’t such a mystery. We see why simply thinking our health will improve can be just as, if not more powerful than a chemical telling our cells to do something different. After all, thoughts are just energetic vibrations. Now all of this isn’t to say that pharmaceuticals shouldn’t have a place in modern medicine or that every disease can be cured simply by positive thinking. But it is important to recognize that we have powerful internal resources to call upon and integrate into our overall health. Humans have an innate desire to believe in magic. That’s why it’s so tempting to turn to magical pills and potions when something in our life isn’t going the way we want it to. But just like we saw before, magic doesn’t necessarily require wands and spells. We’re the drivers of our biology, and we have the ability to rewrite our data. The magic is already within us. Rapé is a legal sacred shamanic medicine that has been used by healers of the Amazon basin for thousands of years. It is pronounced ‘ha-peh’ in English, but is also referred to as ‘hape’, ‘hapi’, or ‘rapay’ by Westerners. These medicines are very rare, sacred, powerful, and profoundly healing and cleansing, and are made in a very sacred and labor intensive process. Rapé is a complex herbal snuff composed of a blend of pulverized Amazonian medicinal plants, trees, leaves, seeds, and other sacred ingredients, often with a tabacco base. Traditionally, Rapé is applied by using a pipe made from bamboo, which is blow through each nostril on both sides. It can be self-administered using a "kuripe", a V-shaped self-applicator pipe which connects the mouth to the nostrils. It can also be administered by another person using a "tepi", a blow pipe which connects the blower’s mouth to the other person’s nostrils. As the blend is blown high up into the nostrils, it immediately focuses the mind, stops the chattering, and opens the entire freed mindspace for your intentions. Furthermore, rapé helps releasing emotional, physical, and spiritual illnesses and eases negativity and confusion, enabling a thorough grounding of your mind. Likewise, rapé is used to re-align the user with their energy channels and with their higher self, and to intensify their connection with the world and the universe. In addition, rapé paves the way for detoxifying the body and cleans out all excess mucus, toxins, and bacteria, thereby, assisting in fighting colds, sniffles and certain kinds can even help with the flu. Blowing the Tepi involves an intimate connection between the rapé giver and receiver. Both are closely connected by mouth, nose and by breath, and both need to open and allow the other spirit and intention to enter, permitting the healing to take place. After blowing, it is recommended to sit with the medicine and meditate for about a half hour or so. It is best to remain with the eyes closed, while inhaling and exhaling slowly (more effective through the nose), enabling a thorough grounding and maintenance of focus. Today, indigenous tribes in the Amazon basin continue to use rapé in all aspects of life, from formal ritual use in rites of puberty, initiation, cashiri drinkings festivals, social gatherings and healing ceremonies, to simply tuning into Nature and the healing power of sacred plant medicines alone or with friends. Traditionally, rapé is applied by using a pipe made from bamboo or bone, which is blown through each nostril on both sides. You always blow into the left nostril first to represent a metaphorical death, and then into the right nostril to represent rebirth. You always put the shorter end of either pipe in your mouth to blow, and the longer end goes inside the nostril. According to the Brazilian Yawanawa Tribe, there are three different ways to blow rapé:
Some recommend working with rapé twice per day to begin with – once in the morning and once in the evening. However, this depends on each person’s tolerance levels and also their personal situation. If you are going through a particularly stressful and sick period, you may decide to use it more regularly. For some people several times a week is fine, or only during Ayahuasca or other medicine ceremonies. For others, they may need to work intensively with these medicines to do some very deep work, purging, and intensive healing. Please listen to your body, intuition, and the spirit of these sacred medicines – they will guide you, as to what’s best for you personally. A half a pea-sized amount of rapé for each nostril for beginners, and then increasing the dosage after prolonged use of one type of rapé. However, everyone has naturally difference tolerance levels, so some people may require larger doses, and others smaller doses. Please experiment to see what works for you personally. If you have a lot of phlegm or mucous in the back of your throat, dripping down your throat, or in your mouth, then spit it out immediately, as it’s toxic or negative energy that is being released and expelled. You do not want to swallow it back inside. In order to prevent the rapé from dripping into your throat, you will want to keep your head down so it will drip down through your nose and not in your throat. You should try to keep the rapé in your nostrils for as long as comfortably possible so the medicine can be absorbed through the bloodstream. It is best to breathe in through the nose if possible for this. Then, you can blow your nose with tissue as many times as it’s necessary for you. References Chakra Openings. (2019). How to use Rapé. [online] Available at: https://chakraopenings.com/pages/what-is-rape [Accessed 4 May 2019].
Liana, L. (2017). Rapé - the Sacred Amazonian Snuff You Blow Up Your Nose. [online] EntheoNation. Available at: https://entheonation.com/blog/rape-amazonian-snuff/ [Accessed 4 May 2019]. How many hugs have you had today? Neuroeconomist Paul Zak, also known as "Dr. Love," recommends at least eight hugs a day to feel happier and more connected, as well as nurture relationships. As psychotherapist Virginia Satir said: "We need 4 hugs a day for survival. We need 8 hugs a day for maintenance. We need 12 hugs a day for growth." There may very well be a "hug threshold" that allows your body to produce ample amounts of oxytocin, which is released in response to physical touch such as breast-feeding, orgasm, hugs, snuggling, holding hands, partner dance, massage, bodywork, and prayer. The neuropeptide oxytocin, released by your pituitary gland, is a naturally occurring hormone in the body with incredibly powerful, health-giving properties. This "love hormone" is also a key reason why the simple act of hugging is such an incredible way to enhance bonding with others but also boost your physical, and emotional, health. How Hugging Makes You Healthier Hugging increases levels of oxytocin, a neurotransmitter that acts as a hormone. This, in turn, has been observed to have beneficial physiological effects on your cardiovascular health and emotional happiness. One group of researchers observed, for example, a reduction in blood pressure among adults following a brief episode of warm contact with their partner. A 20-second hug, along with 10 minutes of hand-holding, reduces the harmful physical effects of stress, including its impact on your blood pressure and heart rate (Grewen, Anderson, Girdler & Light, 2003). This makes sense, since positive physical contact as hugging and reduces cortisol, increases oxytocin, and lowers systolic blood pressure in stressful situations (Holt-Lunstad, Birmingham & Light, 2008). But researchers suggest there is even more to it than that. The skin contains a network of tiny, egg-shaped rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors called Pacinian corpuscles with a large receptive field that can sense pressure and vibration and which are in contact with the brain through the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve winds its way through the body and provides input and receives sensation from the heart, liver, and digestive tract. (Freberg, 2006). The vagus nerve is also connected to oxytocin receptors. One theory is that stimulation of the vagus triggers an increase in oxytocin, which in turn leads to the cascade of health benefits. A 10-second hug a day can lead to biochemical and physiological reactions in your body that can significantly improve your health. Hugging has been observed to stimulates your nervous system while decreasing feelings of loneliness, combating fear, increasing self-esteem, defusing tension, and showing appreciation. According to researchers, hugging has been observed to (Forsell & Åström, 2012):
The effects of connection There's no doubt that physical touch of all kinds feels good. Whether it is a hug or a handshake, physical touch has a powerful effect on the human psyche resulting in us feeling happy, regardless if you are the toucher or touchee; connection, big or small, results in happiness. Yet, many people are touch-deprived. One poll found that one-third of people receive no hugs on a daily basis while 75 percent said they wanted more hugs. Findings such as these, coupled with the emotional and health benefits of human touch, have led to the emergence of cuddle therapy centers, where people can pay for a lunchtime cuddle. However, some have questioned whether or not physical contact from strangers has the same impact as those from someone you know and trust. While cuddling with a spouse or partner has been shown to boost satisfaction in relationships, some researchers have observed that hugs are only beneficial if trust is involved. Neurophysiologist Jürgen Sandkühler, Head of the Centre for Brain Research at the Medical University of Vienna actually cautioned against worldwide "free hugs" campaigns (where strangers offer hugs to others), saying that this may be perceived as threatening and actually increase emotional burden and stress. However, significant benefits have been found from cuddling with a pet, which shows hugs don't have to only be between humans to be beneficial to your heart and overall health. The Importance of Hugging On average, people spend on hour a month hugging. That doesn't seem like much, but when you consider that the average hug is 3 seconds long, that adds up to be a lot of hugs. And if you had any doubt about the importance of touch, consider that children who lack physical connection have delays in walking, talking, and reading. The act of hugging has a near-immediate impact on health, lowering your heart rate and inducing a calming effect while also leading to a more upbeat mood. Touch is described as a universal language that can communicate distinct emotions with startling accuracy. Researchers observed that touch alone can reveal emotions including anger, fear, disgust, love, gratitude, and sympathy, with accuracy rates of up to 83 percent (Hertenstein, Holmes, McCullough & Keltner, 2009). Hugging is a way to encourage your body to release oxytocin, and the more oxytocin your pituitary gland releases, the better able you are to handle life's stressors. Moreover, oxytocin quite likely plays a role in why pet owners heal more quickly from illness, why couples live longer than singles, and why support groups work for people with addictions and chronic diseases. Oxytocin has also been found to reduce the cravings of drug and alcohol addiction, as well as for sweets. It even has a positive influence on inflammation and wound healing. Even beyond this, regular hugs have the added benefit of:
Do You Need a Hug? Often making a concerted effort to hug the people close to you is one of the best ways to get more hugs in return. This can include your spouse, children, and other family members along with close friends. But even if you're not currently in a life situation conducive to getting daily hugs and producing enough of your own oxytocin on a regular basis, the good news is there are some alternatives you can use to help you deal in a healthy way with your emotional response to stress and anxiety. With the already known and still-to-emerge health and quality of life benefits to be derived from the natural release of oxytocin in your body, your best course of action is to make sure you're cultivating warm, loving, intimate relationships, no matter what stage of life you're in. Additionally, if you have a pet, just a few minutes petting your dog or cat can promote the release of your body's "happiness" hormones, including oxytocin. Since touch anywhere on your body, as well as positive interactions and psychological support, are known to increase oxytocin levels, you might also consider:
References Chillot, R. (2013). The Power of Touch. Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/articles/201303/the-power-touch
Forsell, L., & Åström, J. (2012). Meanings of Hugging: From Greeting Behavior to Touching Implications. Comprehensive Psychology, 1, 02.17.21.CP.1.13. https://doi.org/10.2466/02.17.21.CP.1.13 Freberg, L. (2006). Discovering biological psychology (2nd ed.). Wadsworth: Cengage Learning. Grewen, K., Anderson, B., Girdler, S., & Light, K. (2003). Warm Partner Contact Is Related to Lower Cardiovascular Reactivity. Behavioral Medicine, 29(3), 123-130. https://doi.org/10.1080/08964280309596065 Hertenstein, M., Holmes, R., McCullough, M., & Keltner, D. (2009). The communication of emotion via touch. Emotion, 9(4), 566-573. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016108 Holt-Lunstad, J., Birmingham, W., & Light, K. (2008). Influence of a “Warm Touch” Support Enhancement Intervention Among Married Couples on Ambulatory Blood Pressure, Oxytocin, Alpha Amylase, and Cortisol. Psychosomatic Medicine, 70(9), 976-985. https://doi.org/10.1097/psy.0b013e318187aef Mercola, J. (2014). How Hugging Makes You Healthier and Happier. Retrieved from https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2014/02/06/hugging.aspx Richardson, J. (2014). 9 Reasons You Need To Be Giving and Receiving Hugs Everyday. Retrieved from http://preventdisease.com/news/14/012314_9-Reasons-Need-Giving-Receiving-Hugs-Everyday.shtml Zhivotovskaya, E. (2012). Oxytocin: Go Out and Touch Someone. Retrieved from https://positivepsychologynews.com/news/emiliya-zhivotovskaya/2012032321636
Ayurveda offers insight into the earlier stages and enables those monitoring their health to take care of any small imbalances well before developing any serious illness. The length of the each stage may vary from weeks, to months, even years, depending on the person and the degree of aggravation. The six stages of disease development are:
1. Accumulation The first stage, accumulation, represents imbalance, a build up or collection of something in the body. Being exposed to and acquiring a pathogen via the external environment is an example of accumulation. This stage can also be caused by the internal environment, such as from eating an imbalanced diet leading to excess inflammation or mucous. Accumulation in the body leads to the the next stage, aggravation. 2. Aggravation As the imbalanced elements continue to increase, the symptoms become more aggravated and will begin to be noticed throughout the body. This stage is a sign of continued accumulation. This stage can manifest, as seen in the Kapha state, as loss of appetite, indigestion, nausea, excess saliva, oversleeping, sluggishness; or as seen in the Pitta state, as increased acidity, burning sensations in the abdomen, lowered vitality, or insomnia; or as seen in the Vata state, as pain in the lower abdomen, excess flatulence, and light-headedness. 3. dissemination Once the site of origin is full with excess accumulation and is aggravated, it will begin to overflow into or disseminate throughout the rest of the body using different channels of transportation. Overflow typically begins in the GI tract, then spilling into the circulating plasma and blood, allowing the accumulation to spread systemically, and eventually seeping into the organs and tissues (dhātus). Simultaneously, the symptoms at the site of origin will grow worse. 4. Localization The excess accumulation will then move to wherever a weak site exists in the body. This is where and when diseases begin to develop. This stage is also where genetics matter; the weak spots are determined by genetics - as the saying goes, genetics loads the gun, environment pulls the trigger. This stage can manifest, as seen in the Vata state, as arthritis. In a Pitta state, this can be seen as an ulcer, and in the Kapha state, manifestation may begin in the lungs. At this stage, healing is still regarded as simple. 5. Manifestation This is the first state of the development of illness for which modern Western medicine can detect signs of disease. It is at this stage where diseases progress and become fully developed, showing signs of clinical features. Manifested imbalances are given names at this stage, such as arthrosclerosis, cancer, colitis, etc. It is at this stage where conventional medicine attempts to mask the symptoms by offering pharmaceutical drugs. 6. Complication Complications of the dis-ease begin at this final stage. Often times, conventional medicine attempts to solve the problem by simply removing the affected tissue (e.g., small intenstine, colon, thyroid, etc.) from the body. The symptoms become clear enough so that the elemental cause (i.e., dosha constitution such as Vata, Kapha, Pitta) may be determined. Some medical professionals describe this stage as the chronic phase of development. For example, if one develops inflammation in the manifestation stage, in this stage, complications set in, and the inflammation may grow worse into a chronic problem. Being aware of the stages of the dis-ease process is helpful because one can gain a better understanding in how prevent, and perhaps even reverse, it. To be clear, the information provided here is not claiming to treat, cure or diagnose disease. ReferencesCabral, S. (2018). The 6 Stages of the Disease Process (Ayurvedic Principle). [podcast] The Cabral Concept. Available at: https://itunes.apple.com/us/podcast/cabral-concept-by-stephen/id1071469441?mt=2
Tirtha, S. (2007). The Āyuveda encyclopedia. Bayville, NY. Ayurveda Holistic Center Press. What causes addiction? Easy, right? Drugs cause addiction. But maybe it is not that simple.
Research from Bruce K. Alexander indicates that addiction is not caused by the chemical, it is caused by the environment. The answer to addiction is not sobriety, it is connection. What is the fastest way to health? It's simply honesty being honest with yourself. We each have four doctors within ourselves: Dr. Happiness, which is what is our concept of what makes us happy (what am you living for?); Dr. Quiet which is how do you create adequate rest to regenerate yourself to have a clear mind and to let my body recover from any stress; Dr. Diet (how do you tune into your body's particular nutritional needs?); and Dr. Movement, which is the difference between Working Out and Working In and putting those movement types to use in your life.
Wim Hof is an autodidact and taught himself how to control his heart rate, breathing and blood circulation. All this is regulated by the autonomic nervous system. Conventional science says that the autonomic nervous system is a part of the body you just can´t control, yet Wim can, by steering his hypothalamus (an area in the brain which regulates the body temperature). Where the body temperature of an untrained person drops dangerously after exposing it to extreme cold, Wim is able to retain his core temperature around 37 degrees Celsius, constantly. Even after 1 hour and 52 minutes sitting in ice, Wim’s core temperature stays the same. Scientists around the world baffled by this exceptional performance. In the Netherlands, Prof. Maria Hopman of the UMC St Radboud Nijmegen examined Wim’s physiology as he was affected by the cold, while he was up to his neck in a cylinder filled with ice cubes.
Wim Hof, aka "The Iceman" holds the world record for the longest ice bath lasting over one hour and 52 minutes and 20 other world records for feats performed while withstanding the cold. He has climbed Mount Everest and Mount Kilimanjaro in just shorts and shoes. His method enables him to control his core body temperature and immune system, which can be learned by anyone including. Wim's ultimate goals are to end all disease to facilitate a paradigm shift towards health to promote care for our planet and to bring back love and happiness for all people by encouraging them to get in touch with the cold, and he plans to do all this under the scrutiny of science. The anti-cancer assertions made by medical cannabis advocates are no longer just based on anecdotal success stories. In the following video, Dr. Christina Sanchez, a molecular biologist at the Complutense University of Madrid, explains how her research supports the claim that cannabis kills cancer. Through several human and animal experimental observations, researchers, such as Dr. Sanchez, have discovered that the application of the popular psychoactive compound found in cannabis, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), has the potential to induce apoptosis in carcinogenic cells; in other words, THC kills cancer cells. This treatment significantly differs from other cancer treatments, such as chemotheraphy, because THC is able to distinguish between healthy and unhealthy cells, whereas chemotherapeutic agents cannot, resulting in a myriad of undesirable and deleterious side effects. According to Dr. Sanchez, "One of the advantages of cannabinoids, or cannabinoid based medicines, would be that they target a specifically, tumor cells. They don’t have any toxic effect on normal, non-tumoral cells. This is an advantage with respect to standard chemotherapy that target basically everything." Sanchez has further revealed that the cancer-killing effect of THC is potentiated by the presence of cannabidiol (CBD), a very potent antioxidant that protects the brain from stress and oxidative damage. These synergistic effects of both THC and CBD could make for a very safe and effective cancer concoction. Sanchez states, "I cannot understand why in the states cannabis is under schedule I, because it is pretty obvious not only from our work but from work from many other researchers that the plant has very wide therapeutic potential." Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System The human body responds to the cannabinoids found in cannabis because it also makes its own endogenous cannabinoids. These endocannabinoids, which are lipid-based retrograde neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors and proteins that are expressed throughout the mammalian central and peripheral nervous system, have been observed to mediate homeostasis via a variety of physiological and cognitive processes. This endocannabinoid system, named after the plant that led to its discovery, is a biological system of the body has many important regulatory functions affecting fertility, pregnancy, reproduction, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, locomotor behavior, exercise-induced euphoria, and memory. The endogenous cannabinoid system is perhaps the most important physiologic system involved in establishing and maintaining human health. Endocannabinoids and their receptors are found throughout the body: in the brain, organs, connective tissues, glands, and immune cells. In each tissue, the cannabinoid system performs different tasks, but the goal is always the same: homeostasis, the maintenance of a stable internal environment despite fluctuations in the external environment. A growing body of evidence continues to validate the miraculous healing capabilities of cannabinoids. Supporting the cultivation of cannabis and continued scientific research will lead to more availability of various cannabis strains specifically designed to have high doses and specific ratios of certain cannabinoids to serve as a safe and effective therapeutic treatment for a variety of disorders and diseases. The use of medical marijuana and cannabis-derived medicines in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, epilepsy, chronic pain, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, insomnia, depression, etc., will continue to grow. Cannabis may yet become one of the most useful natural remedies to some of the most crippling diseases of mankind. ReferencesHunt, Anna. (2018). Molecular Biologist Explains How Cannabis Kills Cancer Cells. [online] Waking Times. Available at: http://www.wakingtimes.com/2017/12/21/molecular-biologist-explains-cannabis-kills-cancer-cells/ [Accessed 6 Jul. 2018].
Ideally, you want your plate to look like a mosaic, painted with various colors from different foods. Create a rainbow of colors on your plate, with fruits and vegetables. Eating a variety of different foods offer more nutrients.
In this powerful TED talk, Dr. William Li discusses the powerful synergistic effects of combining food. |
The Awareness domain contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of self in an effort to intellectualize health concepts.
The Lifestyle domain builds off intellectual concepts and offers practical applications.
Taking care of yourself is at the core of the other domains because the others depend on your health and wellness.
Archives
May 2024
Categories
All
|




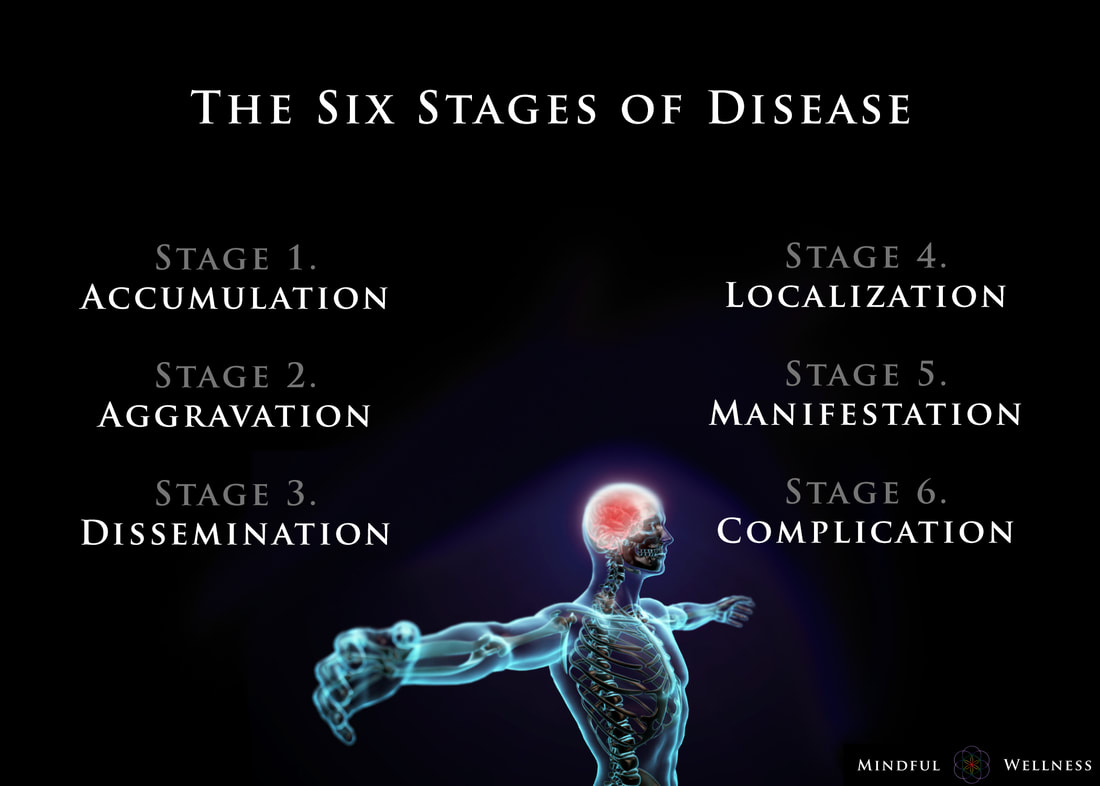
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

