A growing body of evidence suggests and supports the biophilia hypothesis, and demonstrates both the restorative and additive capacity of our biophilic responses. In addition, research suggests that cultivating our innate biophilic tendencies through experiences with natural environments plays a fundamentally important role in addressing the four existential anxieties - meaning in life, isolation, freedom, and death - in addition to addressing two positive existential anxieties - identity and happiness. Existential Positive Psychology (EPP) is concerned with the study of ultimate concerns through integrating both positive and negative aspects of the human condition to create a better future for self and others. EPP stresses the importance of an authentic self-identity. Three types of mature happiness are supported:
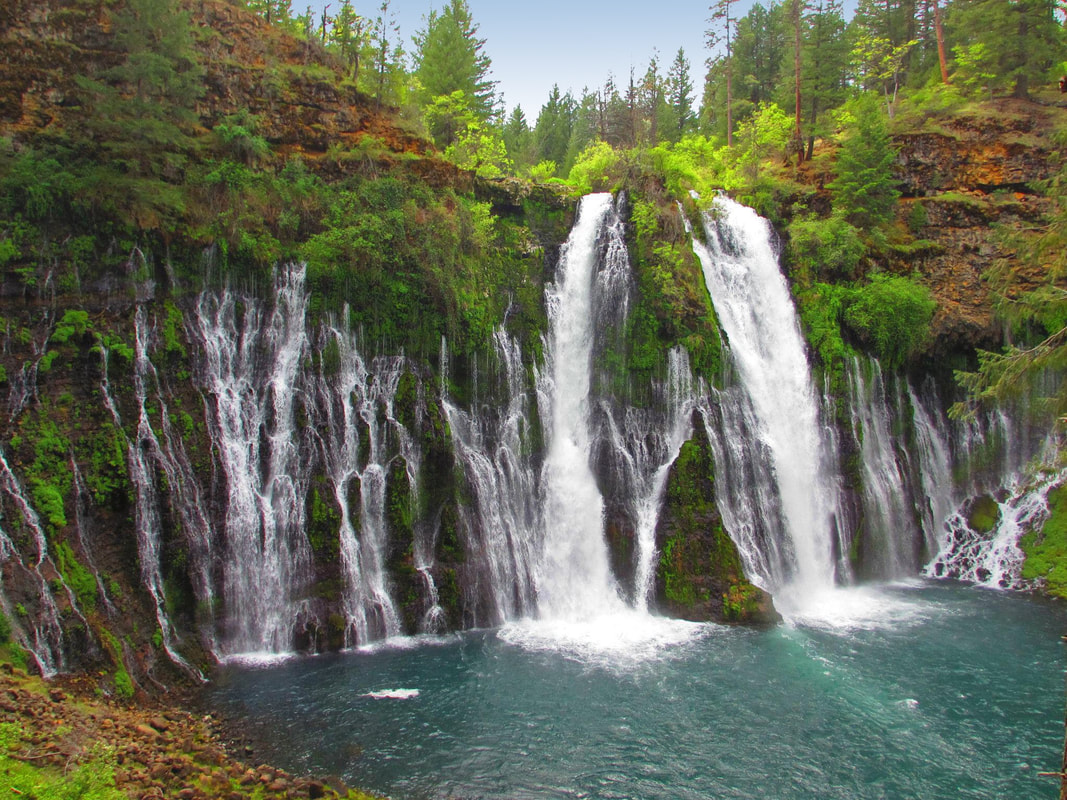
Eco-Existential Positive Psychology Nature provides benefits to individual well-being and it is important to recognize the symbiotic, bi-directional relationship between human well-being and the well-being of the larger natural world. Our actions have a profound effect on the ecological system of the Earth. Thus, it is vital (for our own well-being and that of the Earth) that we move away from an anthropocentric, ego-centric view wherein nature provides for our health and well-being "free of charge". We must move toward a eco-centered view, wherein our relationship to the rest of the natural world is seen as a mutually beneficial, cyclical relationship of flourishing. Indeed, empirical evidence supports the existence of such a mutually enhancing relationship between individual human well-being and the larger natural world’s well-being. Exposure to nature and an increased sense of nature connectedness increases human well-being in a variety of ways (Hartig, Kaiser, & Bowler, 2001; Hartig, Kaiser, & Strumse, 2007; Hine, Peacock, & Pretty, 2007; Hoot & Friedman, 2011; Schultz &. Zelezny, 1998). Increased time spent indoors using technology means that we are also losing our connection with the natural world. If this disturbing trend of humankind’s increased distancing from direct experiences in nature continues, the well-being of the planet’s ecosystem will continue to degrade. Experiences in nature play a fundamental role in addressing the six existential anxieties.
Affiliating with nature affords us the opportunity to be fully flourishing human beings — which in turn will allow the larger-than-human natural world an opportunity to fully flourish, as individuals shift from an ego-centered view and lifestyle, to an eco-centered view and lifestyle. It is only through embracing life in its totality that we can uplift humanity and improve the human condition. It is hoped that the perspective of Eco-Existential Positive Psychology will contribute to an expanded awareness of the potential role of nature connectedness and nature involvement in a life well lived. References Hartig, T., Kaiser, F. G., & Bowler, P. A. (2001). Psychological restoration in nature as a positive motivation for ecological behavior. Environment and Behavior, 33, 590–607.
Hartig, T., Kaiser, F. G., & Strumse, E. (2007). Psychological restoration in nature as a source of motivation for ecological behaviour. Environmental Conservation, 34, 291–299. Hine, R., Peacock, J., & Pretty, J. (2007). Evaluating the impact of environmental volunteering on behaviours and attitudes to the environment. Colchester, UK: University of Essex. Hoot, R. E., & Friedman, H. (2011). Connectedness and environmental behavior: Sense of interconnectedness and pro-environmental behavior. International Journal of Transpersonal Studies, 30, 89–100. Passmore, H. & Howell, A. (2014). Eco-Existential Positive Psychology: Experiences in Nature, Existential Anxieties, and Well-Being. The Humanistic Psychologist, 42, pp.370-388. https://doi.org/10.1080/08873267.2014.920335 Schultz, P. W., & Zelezny, L. C. (1998). Values and proenvironmental behavior: A five-country survey (Mexico,Nicaragua, Peru, Spain, and United States). Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 29, 540–558.
0 Comments
|
The Awareness domain contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of self in an effort to intellectualize health concepts.
The Lifestyle domain builds off intellectual concepts and offers practical applications.
Taking care of yourself is at the core of the other domains because the others depend on your health and wellness.
Archives
May 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

