|
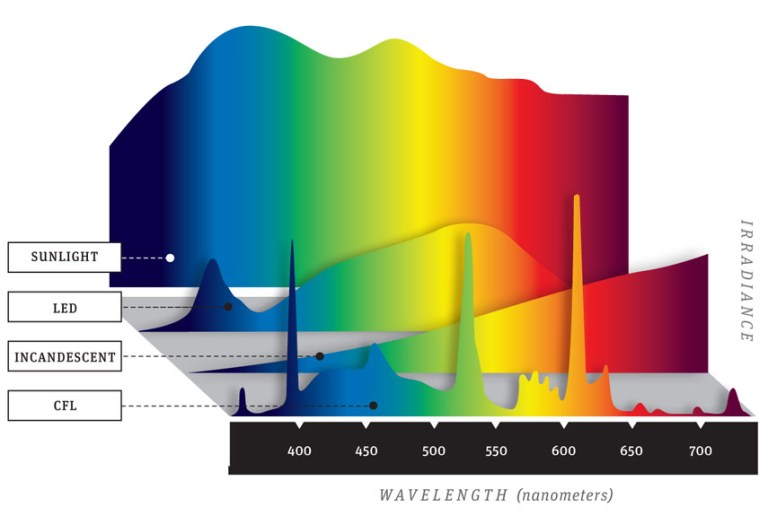
Transcript: "You hear all this talk about blue light being harmful, but do you know what blue light actually is? Blue light is one of the types of light that form the white light we get from the Sun. Together with red, orange, yellow, green, violet, and indigo. This is called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum of visible light. At the end we have the UV light, which can't actually be seen by the human eye. The energy of these waves increases as we go towards the end, which makes blue lights one of the highest intensity types of visible light. Light is made of EM waves that emit energy and it's this energy that we perceive as light. These waves come in different wavelengths, which means we get different colors of light. These are the different colors of light that we can perceive from the EM spectrum. So blue light is actually everywhere; it's in the light that travels from the Sun all the way to the Earth. Because the wavelength of blue light is so small they collide with air molecules a lot more than any other color and they get scattered everywhere - that's actually what makes the sky blue. That's why your body uses this blue light from the Sun to make the difference between day and night and regulate your sleep cycle. But our eyes natural filters barely provide us with enough protection from blue light on a particularly sunny day. The blue light from your devices is even worse. LED devices emit much stronger blue light than we get from the Sun. Spending hours staring at a screen can cause eye damage and fatigue. This is due to most lower energy waves being absorbed by the cornea, the eyes outer membrane. Blue light goes straight through due to its high energy and slowly deteriorates the retina. And because our brains use blue light to differentiate between day and night and boost alertness, spending time on your phone tablet or laptop late at night fools your body into thinking it should keep you awake. It's all of them - phones, tablets, any gadget with an illuminated display. They all use blue LEDs because they are energy efficient and cheaper to produce, but your body disagrees. Basically, what keeps you awake and alert during the day can severely affect the quality of your sleep at night. Blue light has also been shown to suppress secretion of melatonin, a hormone that is produced at night and helps your body prepare for sleep. Melatonin isn't just linked to poor
sleep, scientists have also managed to find a correlation between melatonin deprivation and conditions like cancer, diabetes and clinical depression. Do you still think your tablet is that harmless? Well there is a way you can prevent it. Scientists have now designed special screen protectors that stop the blue light from reaching your eyes and causing damage to your retina at a microscopic level. This glass has tiny ridges that block blue waves and let the other less harmful light go through. These glasses can block up to 60% of blue light and 99% of UV rays. People have reported that their sleeping patterns were significantly improved after only a few days. There was also significant reduction in eye strain and headaches. Or you can go for full protection and buy eyewear that you can use for all blue light-emitting devices: computers, TV laptops, or your phone. These work in a slightly different way - the protectors as the yellow, absorbs rather than blocks blue and UV light, and lets other types of light go through. No matter what you do, whether its buying a protective glass or reducing the time you spend on your device make sure you stay on the lookout for the unseen damage that your day-to-day gadgets can do to your health."
1 Comment
|
The Awareness domain contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of self in an effort to intellectualize health concepts.
The Lifestyle domain builds off intellectual concepts and offers practical applications.
Taking care of yourself is at the core of the other domains because the others depend on your health and wellness.
Archives
May 2024
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

