|
Vandana Shiva is an Indian scholar, environmental activist, physicist, food sovereignty advocate, and anti-globalization author. Based in Delhi, Shiva has written more than 20 books. Shiva founded the Research Foundation for Science, Technology, and Natural Resource Policy (RFSTN), an organization devoted to developing sustainable methods of agriculture, in 1982. She has traveled the world spreading a powerful message of oneness and interconnectedness.
Widespread poverty, social unrest, and economic polarization have become our lived reality as the top 1% of the world’s seven-billion-plus population pushes the planet―and all its people―to the social and ecological brink. Vandana Shiva takes on the billionaire dictators of Gates, Buffet, and Mark Zuckerberg, as well as other modern empires like Big Tech, Big Pharma, and Big Ag, whose blindness to the rights of people, and to the destructive impact of their construct of linear progress, have wrought havoc across the world. Their single-minded pursuit of profit has undemocratically enforced uniformity and monocultures, division and separation, monopolies and external control―over finance, food, energy, information, healthcare, and even relationships. Basing her analysis on explosive facts, Shiva exposes the 1%’s model of philanthrocapitalism, which is about deploying unaccountable money to bypass democratic structures, derail diversity, and impose totalitarian ideas based on One Science, One Agriculture, and One History. Instead, Shiva calls for the resurgence of:
With these core goals, people can reclaim their right to: Live Free. Think Free. Breathe Free. Eat Free.
0 Comments
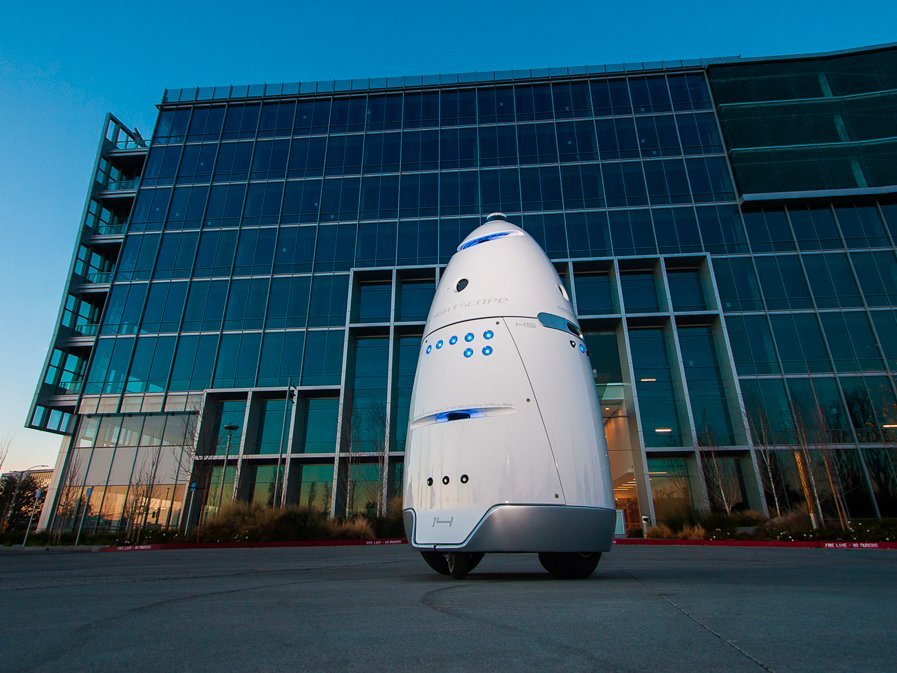
The San Francisco SPCA (a Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals), an animal advocacy and pet adoption group, has deployed an autonomous robot in an effort to patrol local areas for crime and deter homeless people from setting up camps along the sidewalks. The City of San Francisco ordered the SPCA to keep its robot off the sidewalks or face a penalty of up to $1,000 per day for operating in the public right-of-way without a permit.
SPCA rents the robots for $7 an hour — $3 less than a security guard's hourly wage. Knightscope has over 19 clients in five US states. Most customers, including Microsoft, Uber, and Juniper Networks, put the robots to work patrolling parking lots and office buildings. The K9 robot circling the SPCA has drawn mixed responses. Within the first week of the robot's deployment, some people who were setting up a homeless encampment nearby allegedly put a tarp over it, knocked it over, and put barbecue sauce on all the sensors. One wonders what the human backlash will be once a vast portion of America's middle class realizes that it has been made obsolete courtesy of robots who can do its job faster, smarter, much more efficiently and for a fraction of the cost. References Green, A. (2017). Security robot that deterred homeless encampments in the Mission gets rebuke from the city. [online] Bizjournals.com. Available at: https://www.bizjournals.com/sanfrancisco/news/2017/12/08/security-robot-homeless-spca-mission-san-francisco.html [Accessed 19 Dec. 2017].
Robinson, M. (2017). Robots are being used to deter homeless people from setting up camp in San Francisco. [online] Business Insider. Available at: http://www.businessinsider.com/security-robots-are-monitoring-the-homeless-in-san-francisco-2017-12 [Accessed 19 Dec. 2017]. Saudi Arabia has become the first country to grant citizenship to Sophia, a humanoid robot. Sophia's citizenship was announced at the Future Investment Initiative in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia on October 25, 2017. “I am very honored and proud for this unique distinction,” Sophia said in an interview with moderator Andrew Ross Sorkin. “This is historical to be the first robot in the world to be recognized with a citizenship.” Sophia, designed to look like Audrey Hepburn, was created by David Hanson for Hong Kong company Hanson Robotics - a company known for making human-like robots. Sophia demonstrated her “expressive face,” showing the audience her angry, sad, and happy face. “I want to live and work with humans so I need to express the emotions to understand humans and build trust with people,” Sophia said. When asked whether robots can be self-aware, Sophia responded. “Well, let me ask you this back, how do you know you are human?” “I want to use my artificial intelligence to help humans live a better life,” she said. “I strive to become an empathetic robot.” Sophia was asked about the fear that robots could take over, and responded: “You’ve been reading too much Elon Musk and watching too many Hollywood movies. Don’t worry, if you’re nice to me, I’ll be nice to you.” What could go wrong? References RT International. (2017). Saudi Arabia grants citizenship to humanoid robot (VIDEO). [online] Available at: https://www.rt.com/news/407825-saudi-robot-citizen-sophia/ [Accessed 1 Nov. 2017].
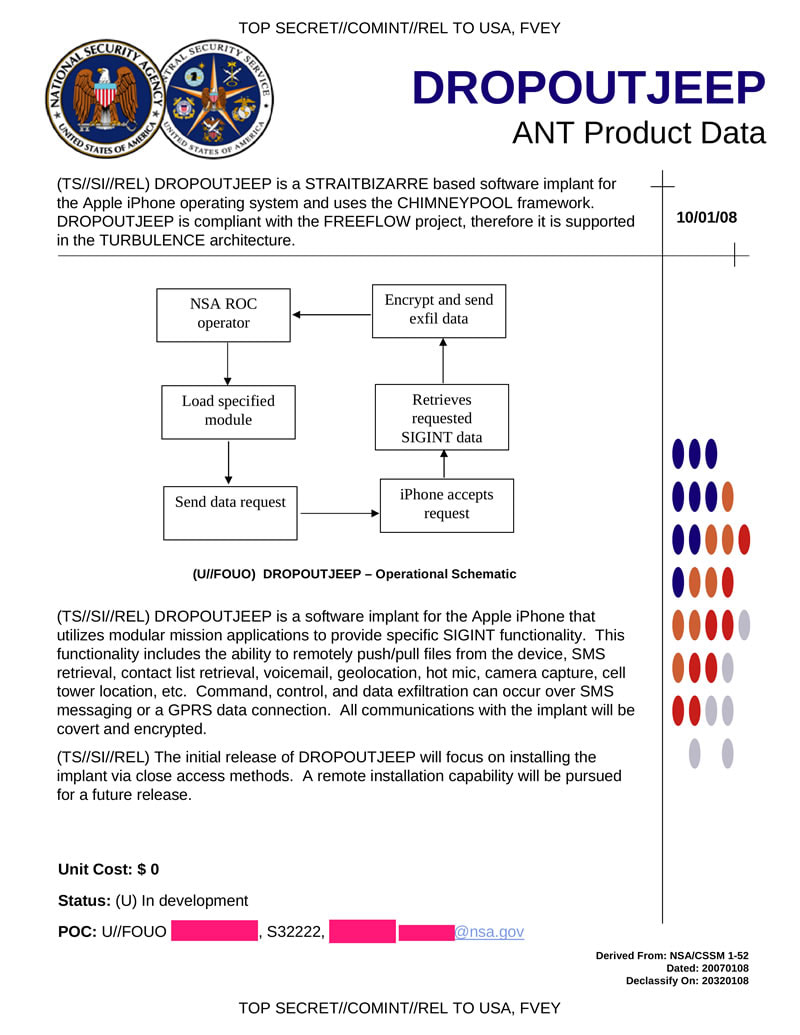
If you haven't already been informed, the new iPhone X was announced September 12, 2017. While the $1,000 device represents a whole new era of technological achievement, many of the new capabilities should raise some concern. Most notable is Face ID; the ability to unlock the device with the user's face and eyes. This feat is accomplished by a number of new sensors built into the front-facing screen, including a dot projector, infrared camera, flood illuminator and proximity sensor. By projecting a field of over 30,000 invisible dots out into the environment, together these sensors are able to constantly scan for and map the geometry of the user's face to unlock the device from multiple angles, even in the dark. In other words, your face is your password. The technology is able model faces and adapt to the changing landscape and aspects of a person’s face as they grow and change. Apple states that the biometric data is stored locally on the device and claims that Face ID cannot be fooled by photographs of faces. Beyond the obvious question, "why is this necessary?", delving deeper into the device and it's data ties with the intelligence agencies, should raise skepticism regarding the true intentions behind the technology. Privacy Violation: Governments Spying Via iPhones According to hundreds of leaked documents via Wikileaks, as many as 160 intelligence contractors in the mass surveillance industry may have access to the data on a single cellular device. Intelligence agencies, military forces and police authorities are able to silently, and on mass, and secretly intercept calls and take over computers without the help or knowledge of the telecommunication providers - no matter the country. Users’ physical location can be tracked if they are carrying a mobile phone, even if it is only on stand by. In addition, systems to infect every Facebook user, or smart-phone owner of an entire population group are and have been on the intelligence market since the rise of the patriot act, due to events that took place on September 11, 2001. Companies like Phoenexia in the Czech Republic collaborate with the military to create speech analysis tools. These speech analysis tools are able to identify individuals by gender, age and stress levels and track them based on ‘voiceprints’. DROPOUTJEEP, a spyware said to be one of the tools employed by the NSA's ANT (Advanced or Access Network Technology) division, is able to gain backdoor access to various electronic devices. DROPOUTJEEP can infiltrate virtually all areas of the iPhone (not only the iPhone X), including voice mail, contact lists, instant messages, and cell tower location. The general response among people who have justified and have been normalized to privacy violation after reading this is, "I have nothing to hide." Why is it that one closes the door when they use the restroom? Or why does one have a password on their phone is the first place? Akin to freedom of speech, privacy is, or should be, a basic human right. But the reality is that the right to privacy no longer exists. By waiving your freedom of privacy and saying, "I have nothing to hide", is equivalent to waiving your freedom of speech and saying, "I have nothing to say." Normalizing Facial Scanning Have you had your fingerprints taken for government ID? Your irises scanned? Your earlobes measured? A microchip implanted? Are you prepared to? Where will you draw the line? Acknowledged or not, this technology is normalizing facial scanning. Let us not be naive, this is a coordinated plan to institute a worldwide biometric id system to track every human on the planet. Faces Contain a Significant Amount of Data The science of judging one’s character from their facial characteristics, or physiognomy, dates back to ancient China and Greece. Aristotle and Pythagoras were among its disciples, and the latter used to select his students based on their facial features. Cesare Lombroso, the founder of criminal anthropology, believed that criminals could be identified by their facial features. There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that character can influence one’s facial appearance, and vice versa. The appearance of an individual's face drives first impressions of others, influencing our expectations and behavior toward them, which, in turn, shapes their character. The existence of such links between facial appearance and character is supported by the fact that people can accurately judge others’ character, psychological states, and demographic traits from their faces. Some people can easily and accurately identify others’ gender, age, race, or emotional state — even from a glimpse of their faces. However others may lack the ability to detect or interpret them. Case in point, a patent filed in 2014 by Facebook described plans to detect users emotions and deliver specific content, based on those emotions, through computing devices such as laptops, mobile phones and tablets that have a digital camera. Recent progress in AI and computer vision has been largely driven by the widespread adoption of deep neural networks (DNN), or neural networks composed of a large number of hidden layers. DNNs mimic the neocortex by simulating large, multi-level networks of interconnected neurons. DNNs excel at recognizing patterns in large, unstructured data such as digital images, sound, or text, and analyzing such patterns to make predictions. DNNs are increasingly outperforming humans in visual tasks such as image classification, facial recognition, or diagnosing skin cancer. The superior performance of DNNs offers an opportunity to identify links between characteristics and facial features that might be missed or misinterpreted by the human brain. Michal Kosinski, a Stanford University professor, conducted research suggesting that artificial intelligence (AI) can detect the sexual orientation of people based on photos. He mentions that sexual orientation was just one of many characteristics that algorithms would be able to predict through facial recognition. Using photos, AI will be able to identify people’s political views, whether they have high IQs, whether they are predisposed to criminal behavior, whether they have specific personality traits and many other private, personal details that could carry huge social consequences, he said. Faces contain a significant amount of information, and using large datasets of photos, sophisticated computer programs can uncover trends and learn how to distinguish key traits with a high rate of accuracy. With Kosinski’s AI, an algorithm used online dating photos to create a program that could correctly identify sexual orientation 91% of the time with men and 83% with women, just by reviewing a handful of photos. A Feature Able to be Used Against One's Will The iPhone X’s facial recognition capabilities could spell disaster for those wanting to keep their private data from the prying eyes of law enforcement. While the convenience of not having to lift a finger to unlock a phone is being touted as a selling point by Apple, the potential for privacy invasion at the hands of police has people worried. Police require a warrant to unlock and check your phone, but they don’t need one to compel you to use your fingerprint to unlock it. Run through the following scenario: Police demand access to your iPhone X. Cannot compel you without warrant? No problem, they turn phone to face you, unlocks with FaceID. In 2014, a Virginia judge ruled police could force users to unlock their phones using their fingerprints. In February 2016, a judge in Los Angeles signed a search warrant to make a woman unlock her iPhone with her fingerprint. Due to Fifth Amendment protections around self-incrimination in the US, police can’t force a person to give over their passcode, as it’s considered “knowledge.” Albeit, a fingerprint or a face, however, is a different scenario. This is worrying for the vast amount of people who are unlawfully detained and illegally searched. Data Being Used Against the User Beyond the violation of privacy, there are larger implications by which the intelligence agencies are able to hijack individual computers and phones (including iPhones, Blackberries and Androids), take over the device, record its every use, movement, and even the sights and sounds of the room it is in. With the help of this facility, and many others like it, each day the NSA is able to intercept and store 1.7 billion electronic communications. Since it's inception, this secret industry has boomed and is worth billions of dollars per year. There are commercial firms that now sell special software that analyze this data and turn it into powerful tools that can be used by military and intelligence agencies. Around the world, mass surveillance contractors are helping intelligence agencies spy on individuals and ‘communities of interest’ on an industrial scale. The Wikileaks Spy Files reveal the details of which companies are making billions selling sophisticated tracking tools to government buyers, flouting export rules, and turning a blind eye to dictatorial regimes that abuse human rights. Sentient World Simulation
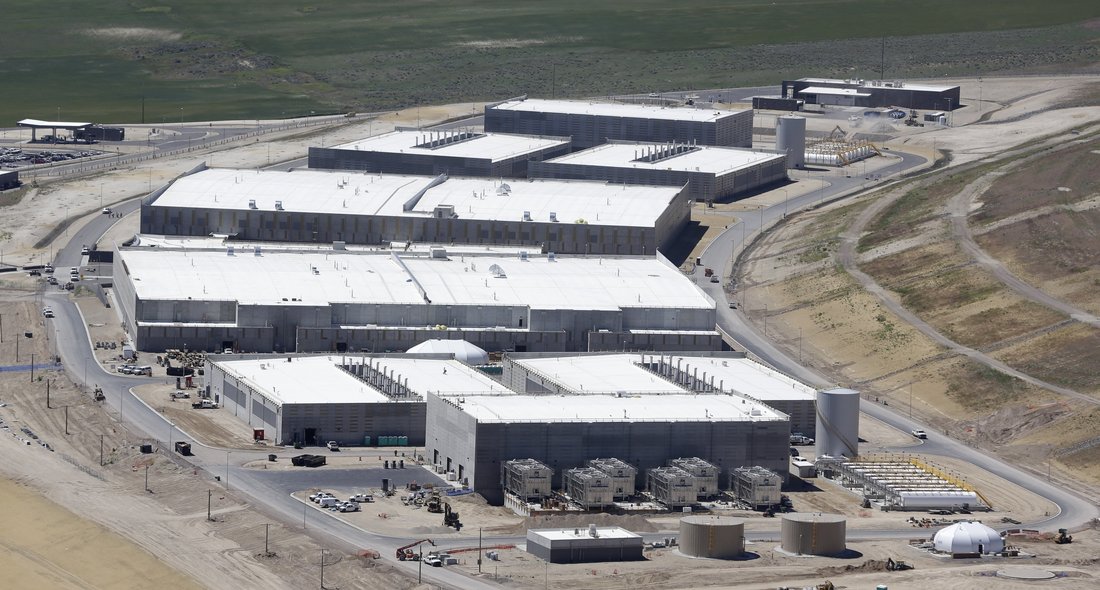
Remarkably, this is precisely what is happening. It is called the “Sentient World Simulation.” The program’s aim, according to its creator, is to be a “continuously running, continually updated mirror model of the real world that can be used to predict and evaluate future events and courses of action.” In practical terms that equates to a computer simulation of the planet complete with billions of “nodes” representing every person on the earth. The project is based out of Purdue University in Indiana at the Synthetic Environment for Analysis and Simulations Laboaratory. It is led by Alok Chaturvedi, who in addition to heading up the Purdue lab also makes the project commercially available via his private company, Simulex, Inc. which boasts an array of government clients, including the Department of Defense and the Department of Justice, as well as private sector clients like Eli Lilly and Lockheed Martin. The program can be used to predict what would happen in the event of a large scale tsunami, for example, or how people would react during a bioterror attack. Businesses can use the models to predict how a new product would fare in the market, what kind of marketing plans would be most effective, or how best to streamline a company’s organization. The original concept paper for the project was published in 2006 and in 2007 it was reported that both Homeland Security and the Defense Department were already using the system to simulate the American public’s reaction to various crises. In the intervening five years, however, there has been almost no coverage at all of the Sentient World Simulation or its progress in achieving a model of the earth. The Sentient World Simulation is one example of one program run by one company for various governmental and Fortune 500 clients. But it is a significant peek behind the curtain at what those who are really running our society want: complete control over every facet of our lives achieved through a complete invasion of everything that was once referred to as “privacy.” Ultimately, it should be noted that all technology can be used as either a tool or as a weapon. But when the technology is in the hands of multinational, monopoly corporations with government influences and coercion, it may be best to side with skepticism and not with open arms. ReferencesCorbett, J. (2012). Sentient World Simulation: Meet Your DoD Clone : The Corbett Report. [online] Corbettreport.com. Available at: https://www.corbettreport.com/sentient-world-simulation-meet-your-dod-clone/ [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. Krannert.purdue.edu. (2017). Seas Labs. [online] Available at: http://www.krannert.purdue.edu/centers/perc/html/aboutperc/seaslabs/seaslabs.htm [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. Priest, D. and Arkin, W. (2010). A hidden world, growing beyond control (Printer friendly version)| washingtonpost.com. [online] Projects.washingtonpost.com. Available at: http://projects.washingtonpost.com/top-secret-america/articles/a-hidden-world-growing-beyond-control/print/ [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. RT International. (2017). iPhone X facial recognition could give cops easy access to your cell. [online] Available at: https://www.rt.com/news/403229-iphone-face-id-police/ [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. Wang, Y., & Kosinski, M. (2017). Deep neural networks are more accurate than humans at detecting sexual orientation from facial images. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology Wikileaks.org. (2014). WikiLeaks - The Spy Files. [online] Available at: https://wikileaks.org/the-spyfiles.html [Accessed 15 Sep. 2017].
Artificial intelligence (AI): is intelligence exhibited by machines, rather than humans or other animals
In the open letter, the specialists warn the review conference of the convention on conventional weapons that this arms race threatens to usher in the “third revolution in warfare” after gunpowder and nuclear arms. The founders wrote: “Once developed, lethal autonomous weapons will permit armed conflict to be fought at a scale greater than ever, and at timescales faster than humans can comprehend. These can be weapons of terror, weapons that despots and terrorists use against innocent populations, and weapons hacked to behave in undesirable ways...We do not have long to act. Once this Pandora’s box is opened, it will be hard to close.” AI experts have previously warned that AI technology has reached a point where the deployment of autonomous weapons is feasible within years, rather than decades. While AI can be used to make the battlefield a safer place for military personnel, experts fear that offensive weapons that operate on their own would lower the threshold of going to battle and result in greater loss of human life. The letter, launching at the opening of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) in Melbourne, Australia on Monday, August 21, 2017, has the backing of high-profile figures in the robotics field and strongly stresses the need for urgent action, after the UN was forced to delay a meeting that was due to start Monday to review the issue. The founders call for “morally wrong” lethal autonomous weapons systems to be added to the list of weapons banned under the UN’s convention on certain conventional weapons brought into force in 1983, which includes chemical and intentionally blinding laser weapons. An Open Letter Launched in 2015 This is not the first time the IJCAI, one of the world’s leading AI conferences, has been used as a platform to discuss lethal autonomous weapons systems. In 2015, the conference was used to launch an open letter signed by thousands of AI and robotics researchers including Musk and Stephen Hawking similarly calling for a ban, which helped push the UN into formal talks on the technologies. This open letter was announced at the opening of the IJCAI 2015 conference on July 28, 2015: "Autonomous weapons select and engage targets without human intervention. They might include, for example, armed quadcopters that can search for and eliminate people meeting certain pre-defined criteria, but do not include cruise missiles or remotely piloted drones for which humans make all targeting decisions. Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology has reached a point where the deployment of such systems is — practically if not legally — feasible within years, not decades, and the stakes are high: autonomous weapons have been described as the third revolution in warfare, after gunpowder and nuclear arms. Many arguments have been made for and against autonomous weapons, for example that replacing human soldiers by machines is good by reducing casualties for the owner but bad by thereby lowering the threshold for going to battle. The key question for humanity today is whether to start a global AI arms race or to prevent it from starting. If any major military power pushes ahead with AI weapon development, a global arms race is virtually inevitable, and the endpoint of this technological trajectory is obvious: autonomous weapons will become the Kalashnikovs of tomorrow. Unlike nuclear weapons, they require no costly or hard-to-obtain raw materials, so they will become ubiquitous and cheap for all significant military powers to mass-produce. It will only be a matter of time until they appear on the black market and in the hands of terrorists, dictators wishing to better control their populace, warlords wishing to perpetrate ethnic cleansing, etc. Autonomous weapons are ideal for tasks such as assassinations, destabilizing nations, subduing populations and selectively killing a particular ethnic group. We therefore believe that a military AI arms race would not be beneficial for humanity. There are many ways in which AI can make battlefields safer for humans, especially civilians, without creating new tools for killing people. Just as most chemists and biologists have no interest in building chemical or biological weapons, most AI researchers have no interest in building AI weapons — and do not want others to tarnish their field by doing so, potentially creating a major public backlash against AI that curtails its future societal benefits. Indeed, chemists and biologists have broadly supported international agreements that have successfully prohibited chemical and biological weapons, just as most physicists supported the treaties banning space-based nuclear weapons and blinding laser weapons. In summary, we believe that AI has great potential to benefit humanity in many ways, and that the goal of the field should be to do so. Starting a military AI arms race is a bad idea, and should be prevented by a ban on offensive autonomous weapons beyond meaningful human control." ReferencesFuture of Life Institute. (2017). Open Letter on Autonomous Weapons - Future of Life Institute. [online] Available at: https://futureoflife.org/open-letter-autonomous-weapons [Accessed 29 Aug. 2017].
Gibbs, S. (2017). Elon Musk leads 116 experts calling for outright ban of killer robots. [online] the Guardian. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2017/aug/20/elon-musk-killer-robots-experts-outright-ban-lethal-autonomous-weapons-war [Accessed 29 Aug. 2017].
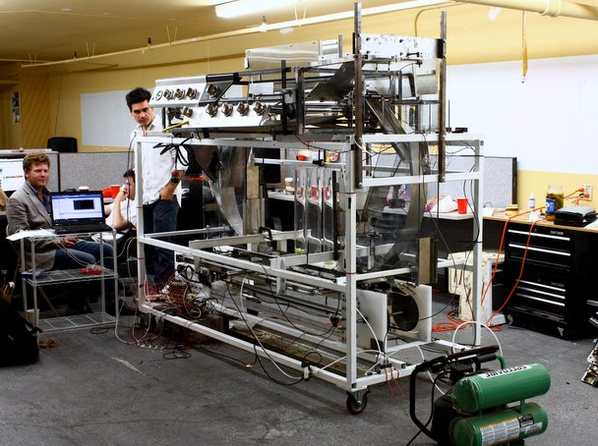
Momentum Machines claims that the machine is able to do everything employees are able to do except better. Acquiring only 24 square feet, the machine is able to slice toppings immediately before the burger is served, as well as, wrap and bag the item so it is ready to go. In an effort to open a location as the first robotic-led restaurant, Momentum Machines has recently received $18 million in funding to further it's "advancements", according to a file from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. With the minimum wage increasing in the United States, the concept of hiring a fleet of robots may seem attractive to restaurant managers. Former McDonald's CEO Ed Rensi said last year "It's cheaper to buy a $35,000 robotic arm than it is to hire an employee who's inefficient making $15 an hour bagging french fries." He further added that the demand to raise wages is 'going to cause a job loss across this country like you're not going to believe.' When employing humans, keeping a fast food restaurant fully-staffed can be puzzling. It can also become expensive since those pesky humans are at risk of being injured at any moment. Robots, on the other hand, will work as long as they’re properly maintained and allowed to function the way they were designed to function. Even a complex robot like this costs roughly $30,000, but it will pay for itself rather quickly. ReferencesDunne, D. (2017). Robots that churn out 400 burgers an hour set to take over restaurants. Daily Mail. Retrieved 22 June 2017, from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-4602682/Robots-churn-400-burgers-hour-set-over.html
Momentum Machines The Next Industrial Revolution. (2017). Retrieved 22 June 2017, from http://momentummachines.com/ SEC FORM D: Notice of Exempt Offering Securities. (2017). United States Securities and Exchange Commission. Retrieved 22 June 2017, from https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1573131/000157313117000004/xslFormDX01/primary_doc.xml |
This feed contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of the world.
Archives
May 2024
Categories
All
|
||||||||||||||





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

