|
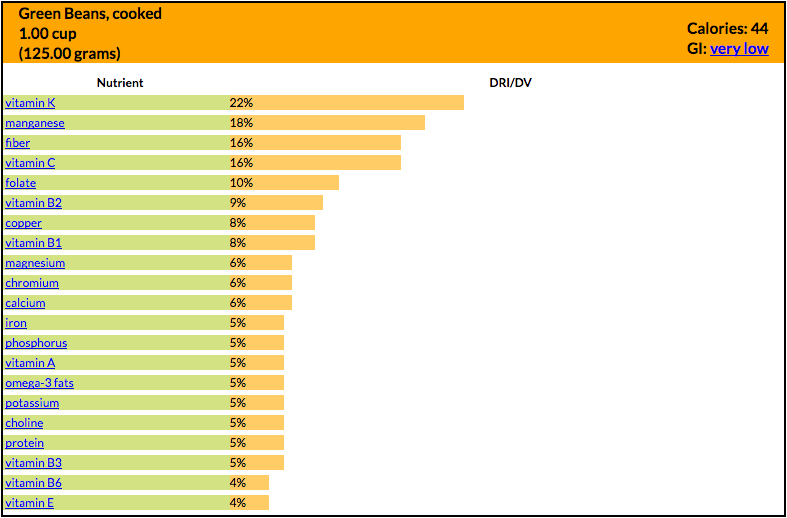
The nutrient richness of green beans is partially a reflection of the wealth of antioxidant carotenoid phytonutrients - including lutein, beta-carotene, violaxanthin, and neoxanthin - that they contain. They are also a concentrated source of vitamin K, which is essential for bone mineralization. They are also a particularly helpful food for providing us with the mineral silicon, important for bone health and healthy formation of connective tissue. Green beans are one of only a few varieties of beans that are typically eaten fresh. Commonly referred to as string beans, green beans are delicious are versatile - great as a side dish or incorporated into a salad. One concern of green beans is that they are a concentrated source of oxalates, which when accumulated may place the kidneys, of certain individuals, at risk of calcium oxalate kidney stone formation due to supersaturation of urine with calcium oxalate salts. Nutrients and Health Benefits Health-Promoting Benefits
Researchers have discovered that flavonoids to play an important role in the prevention of diseases like cancer and heart disease, while offering a wide range of pharmacological benefits, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, neuroprotective, and antidiabetic effects, to name a few (M. Calderon-Montano et al., 2011). Emphasizing the "green" in green beans, another study shows that green and yellow vegetables may lower the risk of heart disease and atherosclerosis (Adams et al., 2006). Selecting Green Beans In order to select the most flavorful green beans, look for the ones that are sold loose so you can sort through them and select the best quality beans. The freshest beans feel smooth, have a vibrant green color, are firm, and "snap" when bent. To ensure uniform cooking, aim to select green beans of similar size. Seeking the freshest green beans will increase the likelihood of higher nutritional content. As with all vegetables, it is recommended to select organically grown green beans when possible. Avoid green beans that have brown spots or areas that are soft, bruised, wrinkled, or have tough skin. Beans that are beginning to turn yellow are no longer fresh. If you are unable to obtain fresh green beans, many valuable nutrients can still be obtained from green beans that have been frozen or canned. Fresh green beans are ideal. Storing Green Beans For the best flavor and nutrition, green beans should be enjoyed soon after they are purchased. Prevent them from becoming limp and yellow. The longer you keep them the more nutrients and flavor you are likely to lose. It is not recommended to store green beans for longer than 7 days. Many factors affect the shelf life of green beans. A colder temperature will help minimize the rate of respiration and thereby help keep green beans fresh for a longer period of time. Place green beans in an airtight storage bag and wrap the bag tightly, squeezing out as much of the air as possible. Do not wash green beans before refrigeration. If you do not have access to fresh green beans on a year-round basis, and you desire to freeze green beans, it is recommended to first steam them for 2-3 minutes. Remove them from heat and let them cool thoroughly before placing them in freezer bags and storing them in your freezer. Green beans are able to retain many of the valuable nutrients for 3-6 months after freezing. Preparing Green Beans Green beans should be properly cleaned and cut to help ensure they will have the best flavor. Rinse well in a colander under running water after cutting off the end that was attached to stem. It is preferred to cut of the end that is attached to the stem. Take a handful of beans and align the ends that were attached by to the stems by tapping them into alignment with the knife and removing them with one cut. Cooking Green Beans To maximize the nutritional benefits, green beans should be cooked just long enough to soften its fibers for better digestion and overall greater enjoyment. Researchers have well established that improper cooking, too much heat and long cooking times, can easily damage many nutrients present in green beans. The most nutritious way to cook green beans is a quick-steam at roughly 212 F for only 7 minutes. Use exact cooking times, and avoid using high heat to get water to a rapid boil and full steam. Vegetables, such as green beans, can continue to cook if they are left in the pot after the heat is turned off. Therefore it is suggested to immediately remove green beans from the pot to prevent overcooking. References Adams, M., Golden, D., Chen, H., Register, T. and Gugger, E. (2006). A Diet Rich in Green and Yellow Vegetables Inhibits Atherosclerosis in Mice. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(7), pp.1886-1889. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.7.1886
M. Calderon-Montano, J., Burgos-Moron, E., Perez-Guerrero, C. and Lopez-Lazaro, M. (2011). A Review on the Dietary Flavonoid Kaempferol. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 11(4), pp.298-344. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955711795305335 Mateljan, G. (2017). Green Beans [online] Whfoods.com. Available at: http://www.whfoods.com/genpage.php?tname=foodspice&dbid=134 [Accessed 29 Jan. 2018]. Mercola.com. (2017). What Are Green Beans Good For? - Mercola.com. [online] Available at: http://foodfacts.mercola.com/green-beans.html [Accessed 29 Jan. 2018].
0 Comments
|
This portal contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of self in an effort to address lifestyle applications.
Archives
June 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

