|
U.S. President Donald Trump on Friday, January 19, 2018 said he signed into law a bill renewing the National Security Agency’s warrantless internet surveillance program. “Just signed 702 Bill to reauthorize foreign intelligence collection,” Trump wrote on Twitter, referring to legislation passed by the U.S. Congress that extends Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA). The law is renewed for six years and with minimal changes the National Security Agency (NSA) program, which gathers information from foreigners overseas and also collects an unknown amount of communications belonging to Americans. Without Trump’s signature, Section 702 had been set to expire on Friday, though intelligence officials had said the surveillance program could continue to operate until April. Under the law, the NSA is allowed to eavesdrop on vast amounts of digital communications from foreigners living outside the United States via U.S. companies like Facebook, Verizon, and Google. But the program also incidentally scoops up Americans’ communications, including when they communicate with a foreign target living overseas, and can search those messages without a warrant. The White House, U.S. intelligence agencies and congressional Republican leaders have said the program is indispensable to national security, vital to protecting U.S. allies and needs little or no revision. Privacy advocates say it allows the NSA and other intelligence agencies to grab data belonging to Americans in a way that represents an affront to the U.S. Constitution. ReferencesVolz, D. (2018). Trump signs bill renewing NSA's internet surveillance program. [online] Reuters. Available at: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-trump-cyber-surveillance/trump-signs-bill-renewing-nsas-internet-surveillance-program-idUSKBN1F82MK?feedType=RSS&feedName=domesticNews [Accessed 23, Jan. 2018].
0 Comments
From Corbettreport.com: When WWII ended and the American deep state welded the national security establishment into place with the National Security Act, the world entered into a new era: the era of the military-industrial complex. But when the Cold War ended and the “Clash of Civilizations” became the new existential threat, the deep state found an opening for another paradigm shift. As the all-pervasive threat of terrorism became the carte blanche for total surveillance, the powers-that-shouldn’t-be found the organizing principal of our age would not be military hardware, but data itself. Welcome to the age of the information-industrial complex. This is The Corbett Report. Of all the things that President Dwight D. Eisenhower did during his years in office, it is for a single phrase from his farewell address that he is best remembered today: “the military-industrial complex.” “In the councils of government, we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military-industrial complex. The potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist.” It is not difficult to see why these words passed so quickly into the political lexicon. Think of their explanatory power. Why did the US use inflated estimates of Russian missile capabilities to justify stockpiling a nuclear arsenal that was more than sufficient to destroy the planet several times over? The military-industrial complex. Why did America send 50,000 of its own to fight and die in the jungles of Vietnam, killing untold millions of Vietnamese (not to mention Cambodians)? The military-industrial complex. Why did the US use the public’s fear and anger over 9/11 and a phony panic over non-existent weapons of mass destruction to justify the illegal invasion and trillion dollar occupation of Iraq? The military-industrial complex. Why did Nobel Peace Prize laureate Obama expand the fictitious “war on terror” into Pakistan and Yemen and Somalia, refuse to close Guantanamo despite his earlier promises to the contrary, commit US forces to “kinetic military action” in Libya without so much as seeking Congressional approval, and launch a new era of covert drone warfare? The military-industrial complex. Why has Trump not only continued but further expanded the US military presence in Africa, increased US aid to Israel and Saudi Arabia, actively enabled the war crimes in Yemen that have led to the largest cholera outbreak in human history, and killed more civilians in his first 9 months in office than former drone-king Obama killed in his entire 8 year presidency? The military-industrial complex. When you think about it, it’s rather remarkable that such a phrase was ever uttered by a President of the United States, much less a former five-star general. Could you imagine any modern-day President talking about something like the “military-industrial complex” and its attempted “acquisition of unwarranted influence” without immediately dismissing the idea as a conspiracy theory? Over the decades there has been much speculation about Eisenhower’s use of the phrase, and what precisely he was warning against. Some have argued that the phrase was prompted by Eisenhower’s discovery that the Rand Corporation was grossly misrepresenting the Soviet’s military capabilities to John F. Kennedy, who ended up using the Rand invented (and completely fictitious) “missile gap” threat as a cornerstone of his 1960 presidential election campaign. Whatever the case, it is perhaps time to revisit Eisenhower’s most famous speech. What Eisenhower is ultimately describing is the rise of American fascism; the merger of government and corporate power. What term can better capture the nature of early 21st century American political life? Is there any longer any doubt that the military-industrial complex has reached its ultimate expression in firms like Blackwater (aka “Xe” aka “Academi”) and its military contractor brethren? Is there any other word but ‘fascism’ to describe a state of affairs when a Secretary of Defense can commission a study from a private contractor to examine whether the US military should be using more private contractors, only for that same Secretary of Defense to leave office and become president of the company that conducted the study, only to leave that company to become Vice President of the US and begin waging a war that relies heavily on no-bid contracts awarded to that same company based on the recommendation that it made in its original study? Yet this is precisely the case of Dick Cheney and Halliburton. It would be difficult to think of a more blatant example of the military-industrial complex fascism that Eisenhower was warning of. But as it turns out, there was another warning about fascism embedded in that farewell address that has received far less attention than the ‘military-industrial complex’ formulation, perhaps because there is no catchphrase hook to describe it: “Today, the solitary inventor, tinkering in his shop, has been overshadowed by task forces of scientists in laboratories and testing fields. In the same fashion, the free university, historically the fountainhead of free ideas and scientific discovery, has experienced a revolution in the conduct of research. Partly because of the huge costs involved, a government contract becomes virtually a substitute for intellectual curiosity. For every old blackboard there are now hundreds of new electronic computers.” Given that this warning came in 1961, before the age of communications satellites or personal computers or the internet, it was a remarkably prescient observation. If scientific research half a century ago was dominated by federal grants and expensive computer equipment, how much more true is that for us today, half a century later? So what is the problem with this? As Ike explained: “Yet, in holding scientific research and discovery in respect, as we should, we must also be alert to the equal and opposite danger that public policy could itself become the captive of a scientific-technological elite.” Here again the warning is of fascism. But instead of the military-industrial fascism that dominated so much of the 20th century, he was describing here a new fascistic paradigm that was but barely visible at the time that he gave his address: a scientific-technological one. Once again, the threat is that the industry that grows up around this government-sponsored activity will, just like the military-industrial complex, begin to take over and shape the actions of that same government. In this case, the warning is not one of bombs and bullets but bits and bytes, not tanks and fighter jets but hard drives and routers. Today we know this new fascism by its innocuous sounding title “Big Data,” but in keeping with the spirit of Eisenhower’s remarks, perhaps it would be more fitting to call it the “information-industrial complex.” The concept of an information-industrial complex holds equally explanatory power for our current day and age as the military-industrial complex hypothesis held in Eisenhower’s time. Why is a company like Google going to such lengths to capture, track and database all information on the planet? The information-industrial complex. Why were all major telecom providers and internet service providers mandated by federal law to hardwire in back door access to American intelligence agencies for the purpose of spying on all electronic communications? The information-industrial complex. Why would government after government around the world target encryption as a key threat to their national security, and why would banker after banker call for bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to be banned even as they plan to set up their own, central bank-administered digital currencies? The information-industrial complex. The effects of this synthesis are more and more felt in our everyday lives. Every single day hundreds of millions of people around the world are interfacing with Microsoft software or Apple hardware or Amazon cloud services running on chips and processors supplied by Intel or other Silicon Valley stalwarts. Google has become so ubiquitous that its very name has become a verb meaning “to search for something on the internet.” The 21st century version of the American dream is encapsulated in the story of Mark Zuckerberg, a typical Harvard whizkid whose atypical rise to the status of multi-billionaire was enabled by a social networking tool by the name of “Facebook” that he developed. But how many people know the flip side of this coin, the one that demonstrates the pervasive government influence in shaping and directing these companies’ rise to success, and the companies’ efforts to aid the government in collecting data on its own citizens? How many know, for instance, that Google has a publicly acknowledged relationship with the NSA? Or that a federal judge has ruled that the public does not have the right to know the details of that relationship? Or that Google Earth was originally the brainchild of Keyhole Inc., a company that was set up by the CIA’s own venture capital firm, In-Q-Tel, using satellite data harvested from government “Keyhole” class reconnaissance satellites? Or that the former CEO of In-Q-Tel, Gilman Louie, sat on the board of the National Venture Capital Association with Jim Breyer, head of Accel Partners, who provided 12 million dollars of seed money for Facebook? Or that in 1999, a back door for NSA access was discovered in Microsoft’s Windows operating system source code? Or that Apple founder Steve Jobs was granted security clearance by the Department of Defense for still-undisclosed reasons while heading Pixar in 1988, as was the former head of AT&T and numerous others in the tech industry? The connections between the IT world and the government’s military and intelligence apparatus run deep. In fact, the development of the IT industry is intimately intertwined with the US Air Force, the Department of Defense and its various branches (including, famously, DARPA), and, of course, the CIA. A cursory glance at the history of the rise of companies like Mitre Corporation, Oracle, and other household electronics and software firms should suffice to expose the extent of these relations, and the existence of what we might dub an “information-industrial complex.” But what does this mean? What are the ramifications of such a relationship? Although the signs have been there for decades, perhaps the most startling example of what lies at the heart of this relationship has been revealed by the whistleblowers at the heart of the National Security Agency, one of the most secretive arms of the American intelligence apparatus. While Edward Snowden has received the most attention with his “revelation” of the PRISM program, much of the information about the NSA’s ability to surveil all electronic communications has been revealed over the past decade by NSA whistleblowers like Russ Tice, William Binney, Thomas Drake and J. Kirk Wiebe, third-party contractors like Snowden and AT&T whistleblower Mark Klein, and independent journalists like James Bamford. Together, the story they tell is of a truly Orwellian society in which all communications are being captured and analyzed by the NSA, and, with the advent of facilities like the new data center in Utah, presumably stored indefinitely for use at any future time in any future investigation for any pretense by anyone with authorization to access that data. According to Snowden, this includes lowly third-party contractors like himself operating at NSA subcontractors like Booz Allen Hamilton in the vast (and expanding) private intelligence industry that has grown up around the information-industrial complex in the exact same way as private military contractors like Blackwater formed around the military-industrial complex. In some ways, this information-industrial complex is even more insidious than its military-industrial counterpart. For all of the ills caused by the military-industrial complex (and there are many), at the very least it required some sort of excuse to drain the American people’s resources, and its failures (like the Vietnam quagmire or the debacle in Iraq) happened in the clear light of day. In the information-industrial complex, where vast spying programs happen in the shadows and under the cover of “national security” it takes whistleblowers and insiders willing to risk it all even to find out what is being done by these shadowy agencies and their private sector contractors. Even worse, the entire Orwellian spy grid is being run on the flimsiest of pretenses (the “war on terror”) that has no defined end point, and “justifies” turning that spy grid inward, on the American people themselves. Surely Eisenhower never envisaged the monstrosity that this information-industrial complex has become, but the foresight he saw in identifying its early stages over half a century ago is remarkable. The problem is that we are even further away from heeding the warning that he delivered in that 1961 address than we were at that time: “It is the task of statesmanship to mold, to balance, and to integrate these and other forces, new and old, within the principles of our democratic system – ever aiming toward the supreme goals of our free society.” If only this was the rhetoric that was shaping today’s debate on the issue, instead of the well-worn canard that we must “strike a balance” between freedom and security. Sadly, until such time that the National Security Act of 1947 is repealed and the cover of national security is lifted from the dark actors that populate this sector, the information-industrial complex is unlikely to be quashed-or even hampered-anytime soon. ReferencesCorbett, J. (2017). Episode 325 – The Information-Industrial Complex : The Corbett Report. [online] Corbettreport.com. Available at: https://www.corbettreport.com/episode-325-the-information-industrial-complex/ [Accessed 18 Dec. 2017].
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) plans to move forward with progressively implementing facial recognition and other biometric data into screenings at various airports across the United States. The agency began testing out the methods, which also include iris scans and fingerprints, on volunteers in their PreCheck program at airports over the summer. On November 1, the TSA announced plans to expand the program. The TSA Pre-Application program claims to enhance “aviation security by permitting TSA to better focus its limited security resources on passengers who are more likely to pose a threat to civil aviation, while also facilitating and improving the commercial aviation travel experience for the public.” Under the program, individuals are to submit biographic information (including, but not limited to, name, date of birth, gender, prior and current addresses, contact information, country of birth, images of identity documents, proof of citizenship/immigration status) and biometric data (such as fingerprints, iris scans, or facial images) to a TSA contractor, which forwards the information to the agency. From Pilot Program to National Policy In June and July of 2017, the TSA “launched a proof of concept initiative at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport and Denver International Airport to determine whether fingerprints from TSA Pre✓® Application Program applicants,” who volunteered to participate, could be used for identity verification. The TSA is currently “seeking a revision to the currently approved request to allow for the collection of additional biometrics, particularly facial images but may include other biometrics such as iris, from TSA Pre✓® Application Program applicants.” The TSA claims that "the regular collection of biometrics, such as facial images, will provide TSA with the ability to use those biometrics for identity verification at TSA checkpoints, potentially eliminating the need to show identity documents and improving both security and the customer experience.” Some privacy advocates disagree with the attempted expansion. According to the Electronic Frontier Foundation, the TSA’s push to expand its use of biometrics is part of a broader push by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to nationalize the collection and use of biometric data. According to an assessment by the DHS, in 2016 the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) will operate a test at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport, in Atlanta, Georgia in order to identify reliable and cost-effective border management capabilities (such as verifying biometrics of departing travelers) that can be deployed nationwide and across multiple modes of travel. Photos of travelers taken during boarding will be compared against photos taken previously (U.S. passport, U.S. visa, and other DHS encounters) and stored in existing CBP systems. Prior to the departure of each flight, CBP will collect facial images and boarding pass information of all travelers, including U.S. citizens, as they pass through the passenger loading bridge to board their flight. CBP will use this data to test the ability of CBP data systems to confirm a traveler’s identity using a facial biometric comparison as the traveler departs from the United States. Initially, the DHS states that the data will be stored for no longer than one year after the test. Since then the DHS updated it's stance, stating "CBP retains biographic exit records for 15 years for U.S. citizens and lawful permanent residents and 75 years for non-immigrant aliens." These actions would be carried out without congressional authorization. Initially these practices were to be limited to international flights. However, according to John Wagner, deputy assistant commissioner at CBP, the TSA is now seeking to expand the collection of biometric data to domestic flights, as well. DHS Data in the Hands of Third Parties Concerns should also be raised regarding the storage of biometric data in the hands of third parties, including but not limited to airlines. DHS sub-agencies are sharing data with the FBI, and the TSA Pre-check program shares it with private companies it uses as contractors. Americans should be concerned about these proposals because the data collected—your fingerprint, the image of your face, and the scan of your iris—will be stored in the databases of the FBI, DHS, and other non-government third parties (such as commerical airlines and air authorities), which will be searched for immigration, law enforcement, and intelligence checks, including checks against latent prints associated with unsolved crimes. This vast data collection will create a huge security risk. As seen with the 2017 Equifax breach, no government agency or private company is capable of fully protecting your private and sensitive information. While losing your social security or credit card information may result in fraud, those numbers can easily be changed. On the other hand, if your biometrics get into the wrong hands, you can’t change your face. ReferencesDhs.gov. (2016). Departure Information Systems Test. [online] Available at: https://www.dhs.gov/sites/default/files/publications/privacy-pia-cbp-dis%20test-june2016.pdf [Accessed 15 Dec. 2017].
Dhs.gov. (2017). Traveler Verification Service (TVS). [online] Available at: https://www.dhs.gov/sites/default/files/publications/privacy-pia-cbp030-tvs-september2017.pdf [Accessed 15 Dec. 2017]. Lynch, J. (2017). TSA Plans to Use Face Recognition to Track Americans Through Airports. [online] Electronic Frontier Foundation. Available at: https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2017/11/tsa-plans-use-face-recognition-track-americans-through-airports [Accessed 15 Dec. 2017]. Regulations.gov. (2017). Agency Information Collection Activities; Proposals, Submissions, and Approvals: TSA Pre-Check Application Program. [online] Available at: https://www.regulations.gov/document?D=TSA-2014-0001-0021 [Accessed 15 Dec. 2017]. Wedler, C. (2017). TSA Plans to Use Facial Recognition to Track Americans in US Airports. [online] The Anti-Media. Available at: http://theantimedia.org/tsa-facial-recognition-biometrics/ [Accessed 15 Dec. 2017]. The launch of the so-called AWS Secret Region comes six years after AWS introduced GovCloud, its first data-center region for public-sector customers. AWS has since announced plans to expand GovCloud. The new Secret Region signals interest in using AWS from specific parts of the U.S. government. In 2013, AWS and the CIA signed a $600 million contract to keep up with big data analytics. That event singlehandedly helped Amazon in its effort to sign up large companies to use its cloud, whose core services have been available since 2006. Today AWS counts companies such as Comcast, Hess, Intuit and Lionsgate as customers. AWS' competitors include Microsoft, Google, IBM and Oracle. "With the launch of this new Secret Region, AWS becomes the first and only commercial cloud provider to offer regions to serve government workloads across the full range of data classifications, including Unclassified, Sensitive, Secret, and Top Secret," Amazon said in a blog post. The new region is available to customers as a result of AWS' contract with the intelligence community's Commercial Cloud Services, or C2S, group, and it will meet certain government standards, Amazon said. But the region will also be accessible for U.S. government organizations that aren't part of the intelligence community so long as they have their own "contract vehicles" and sufficient secret-level network access, Amazon said. ReferencesAmazon Web Services. (2017). Announcing the New AWS Secret Region | Amazon Web Services. [online] Available at: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/publicsector/announcing-the-new-aws-secret-region/ [Accessed 22 Nov. 2017].
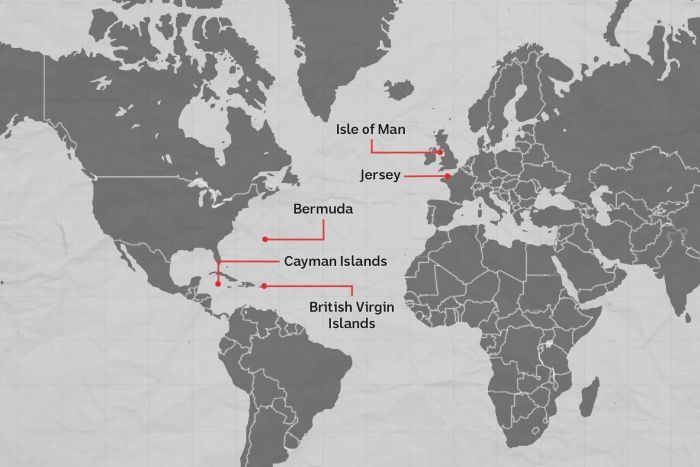
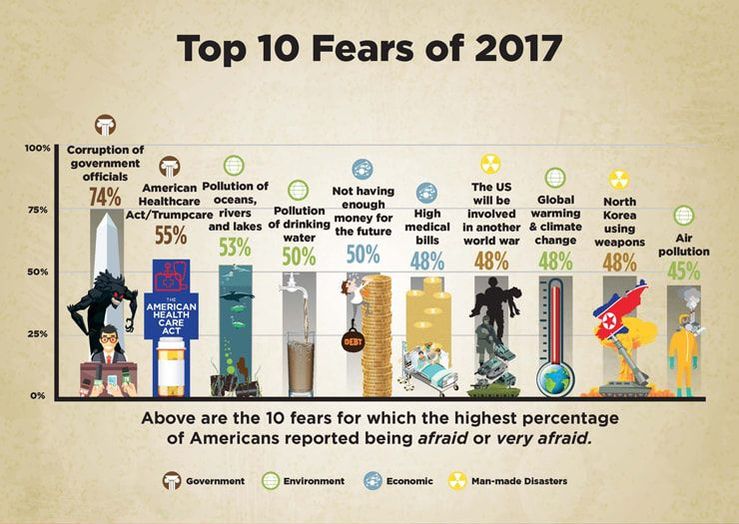
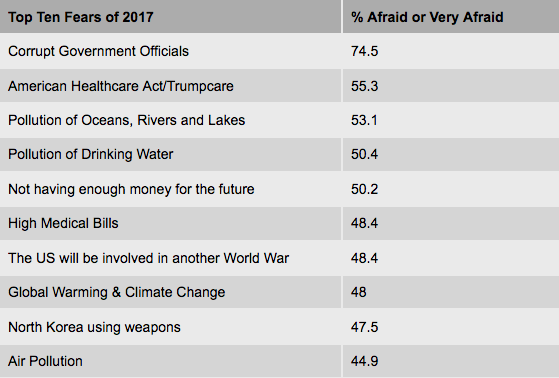
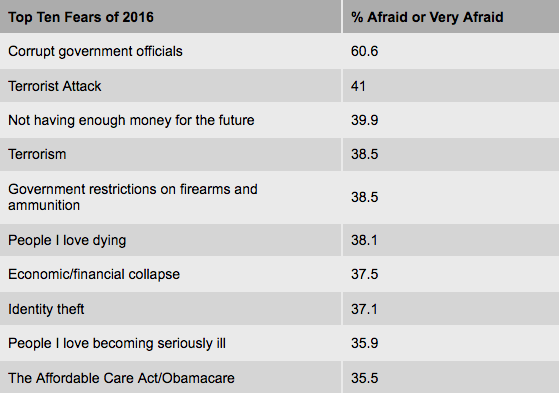
Konkel, F. (2017). Sources: Amazon and CIA ink cloud deal -- FCW. [online] FCW. Available at: https://fcw.com/articles/2013/03/18/amazon-cia-cloud.aspx [Accessed 22 Nov. 2017]. Novet, J. (2017). Amazon launches a cloud service for US intelligence agencies. [online] CNBC. Available at: https://www.cnbc.com/2017/11/20/amazon-launches-aws-secret-region.html?__source=twitter%7Cmain [Accessed 22 Nov. 2017]. The Paradise Papers is a global investigation into the offshore activities of some of the world’s most powerful people and companies. The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists and 95 media partners explored 13.4 million leaked files from a combination of offshore service providers and the company registries of some of the world’s most secretive countries. The files were obtained by the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung. The Paradise Papers documents include nearly 7 million loan agreements, financial statements, emails, trust deeds and other paperwork from nearly 50 years at Appleby, a leading offshore law firm with offices in Bermuda and beyond. The documents also include files from a smaller, family-owned trust company, Asiaciti, and from company registries in 19 secrecy jurisdictions. The records range from complex, 100-page corporate transaction sheets and dollar-by-dollar payment ledgers to simple corporate registries of countries, such as Antigua & Barbuda, that do not publicly list names of company shareholders or directors. As a whole, the 1.4 terabyte data leak exposes offshore holdings of political leaders and their financiers as well as household-name companies that slash taxes through transactions conducted in secret. Financial deals of billionaires and celebrities are also revealed in the documents. The Paradise Papers files include far more information about U.S. citizens, residents and companies than previous ICIJ investigations – at least 31,000 of them. ICIJ collaborated with more than 380 journalists working on six continents in 30 languages. Many team members spent a year using online platforms to communicate and to share documents. Journalists tracked down court records, obtained financial disclosures of politicians in Africa, Europe, and Latin and North America, filed freedom of information requests and conducted hundreds of interviews with tax experts, policymakers and industry insiders. Corrupt governments & corporations can't hide in the information age; transparency & accountability is the only solution. ReferencesICIJ. (2017). Paradise Papers Exposes Donald Trump Russia Links and Piggy Banks of the Wealthiest 1 percent. [online] International Consortium of Investigative Journalists. Available at: https://www.icij.org/investigations/paradise-papers/paradise-papers-exposes-donald-trump-russia-links-and-piggy-banks-of-the-wealthiest-1-percent/ [Accessed 6 Nov. 2017]. Main, L., Wilkinson, M. & Koloff. S. (2017). Paradise Papers: What is the leak and who is behind the firm Appleby?. [online] Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Available at: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2017-11-06/what-are-the-paradise-papers-and-what-is-the-firm-appleby/9075640 [Accessed 6 Nov. 2017]. Chapman University completed its fourth annual Chapman University Survey of American Fears (CSAF). In May of 2017, a random sample of 1,207 adults from across the United States were asked their level of fear about eighty different fears across a huge variety of topics ranging from crime, the government, the environment, disasters, personal anxieties, technology and many others. The goal of the CSAF is to collect annual data on the fears, worries and concerns of Americans, the personal, behavioral and attitudinal characteristics related to those fears, and how those fears are associated with other attitudes and behaviors. The results, perhaps, are not very surprising. Below is a list of the 10 fears for which the highest percentage of Americans reported being “Afraid,” or “Very Afraid.” Americans are more afraid than they use to be. In every wave of the survey before 2017, there was only one item where a majority of Americans said they were "afraid" or "very afraid", and that was corruption of government officials. In this years survey, there were five items where a majority of Americans said they were afraid. Corruption of government officials still topped the list and it increased nearly 14%. ReferencesChapman University. 2017. The Chapman University Survey of American Fears, Wave 4. Orange, CA: Earl Babbie Research Center [producer]. https://blogs.chapman.edu/wilkinson/2017/10/11/americas-top-fears-2017/
Although Congress designed this authority to target non-U.S. persons located outside of the United States, it is clear that Section 702 surveillance programs can and do incidentally collect information about U.S. persons when U.S. persons communicate with the foreign targets of Section 702 surveillance. The USA Liberty Act claims that it will “better protect Americans’ privacy” by requiring the government (e.g., NSA, FBI, etc.) to have “a legitimate national security purpose” before searching an individual’s database. Then when they do have that purpose established, they will be required to “obtain a court order based on probable cause to look at the content of communications, except when lives or safety are threatened, or a previous probable cause-based court order or warrant has been granted.” However, as long as it is relevant to an authorized investigation, the query may be done and an agent can immediately access metadata, such as phone numbers and time stamp information. FISA and Section 702 Section 702 authorizes intelligence agencies to collect the content, or substance of communications, and non-content, or metadata, for broad purposes of defense and foreign affairs both directly through their own technology and also by compelling U.S. companies to produce data. One form of collection, known as “upstream,” involves capturing packets of information directly as they cross the internet backbone through service providers like AT&T and Verizon when there is a belief such packets will include communications “to” and “from”—and under old rules “about”—an intended target. “Downstream” collection is commonly referred to as “PRISM” and involves the government requesting data from retail providers like Yahoo or Gmail. The program’s procedural protections include certification (court-approved justifications for surveillance), targeting (methods to ensure surveillance is individual-specific based on selectors), and minimization guidelines (ex ante requirements to withhold, mask, or purge information). The Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court (FISC) must grant annual approval of the proposed procedures. The U.S. government has repeatedly stressed the importance of the program. Though the majority of information related to 702 is classified, Office of the Director of National Intellience (ODNI) has declassified some examples of 702 successes (Sharma, 2017). Privacy Concerns More than 50 organizations, including the American Civil Liberties Union and the Freedom of the Press Foundation, have joined together to condemn the USA Liberty Act, a bill that reauthorizes and creates additional loopholes for Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA). In a letter to the House Judiciary Committee, the coalition noted that one of the most obvious problems with the USA Liberty Act is that it fails to address concerns with the “backdoor search loophole,” which allows the government to “conduct warrantless searches for the information of individuals who are not targets of Section 702, including U.S. citizens and residents.” The problem is that warrantless surveillance is — regardless of the reasons given — a violation of the Fourth Amendment guarantee against unreasonable searches. As Dr. Ron Paul explained, “There is no ‘terrorist’ exception in the Fourth Amendment. Saying a good end (capturing terrorists) justifies a bad means (mass surveillance) gives the government a blank check to violate our liberties.” Snowden Revelations
In accordance with the Privacy Act of 1974, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) proposes to modify a current DHS system of records titled, “Department of Homeland Security/U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services, U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement, U.S. Customs and Border Protection—001 Alien File, Index, and National File Tracking System of Records.” This system of records contains information regarding transactions involving an individual as he or she passes through the U.S. immigration process. DHS is updating the DHS/USCIS/ICE/CBP-001 Alien File, Index, and National File Tracking System of Records to include the following substantive changes, related to social media:
References Federal Register. (2017). Privacy Act of 1974; System of Records. [online] Available at: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2017/09/18/2017-19365/privacy-act-of-1974-system-of-records [Accessed 19 Oct. 2017].
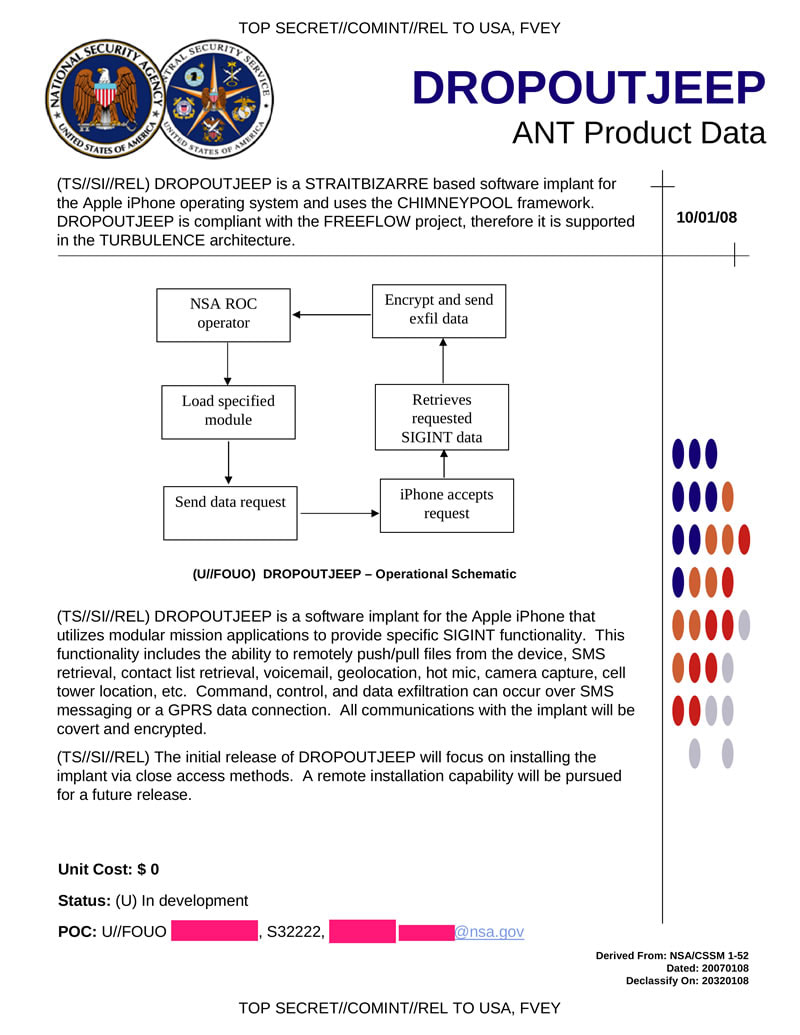
If you haven't already been informed, the new iPhone X was announced September 12, 2017. While the $1,000 device represents a whole new era of technological achievement, many of the new capabilities should raise some concern. Most notable is Face ID; the ability to unlock the device with the user's face and eyes. This feat is accomplished by a number of new sensors built into the front-facing screen, including a dot projector, infrared camera, flood illuminator and proximity sensor. By projecting a field of over 30,000 invisible dots out into the environment, together these sensors are able to constantly scan for and map the geometry of the user's face to unlock the device from multiple angles, even in the dark. In other words, your face is your password. The technology is able model faces and adapt to the changing landscape and aspects of a person’s face as they grow and change. Apple states that the biometric data is stored locally on the device and claims that Face ID cannot be fooled by photographs of faces. Beyond the obvious question, "why is this necessary?", delving deeper into the device and it's data ties with the intelligence agencies, should raise skepticism regarding the true intentions behind the technology. Privacy Violation: Governments Spying Via iPhones According to hundreds of leaked documents via Wikileaks, as many as 160 intelligence contractors in the mass surveillance industry may have access to the data on a single cellular device. Intelligence agencies, military forces and police authorities are able to silently, and on mass, and secretly intercept calls and take over computers without the help or knowledge of the telecommunication providers - no matter the country. Users’ physical location can be tracked if they are carrying a mobile phone, even if it is only on stand by. In addition, systems to infect every Facebook user, or smart-phone owner of an entire population group are and have been on the intelligence market since the rise of the patriot act, due to events that took place on September 11, 2001. Companies like Phoenexia in the Czech Republic collaborate with the military to create speech analysis tools. These speech analysis tools are able to identify individuals by gender, age and stress levels and track them based on ‘voiceprints’. DROPOUTJEEP, a spyware said to be one of the tools employed by the NSA's ANT (Advanced or Access Network Technology) division, is able to gain backdoor access to various electronic devices. DROPOUTJEEP can infiltrate virtually all areas of the iPhone (not only the iPhone X), including voice mail, contact lists, instant messages, and cell tower location. The general response among people who have justified and have been normalized to privacy violation after reading this is, "I have nothing to hide." Why is it that one closes the door when they use the restroom? Or why does one have a password on their phone is the first place? Akin to freedom of speech, privacy is, or should be, a basic human right. But the reality is that the right to privacy no longer exists. By waiving your freedom of privacy and saying, "I have nothing to hide", is equivalent to waiving your freedom of speech and saying, "I have nothing to say." Normalizing Facial Scanning Have you had your fingerprints taken for government ID? Your irises scanned? Your earlobes measured? A microchip implanted? Are you prepared to? Where will you draw the line? Acknowledged or not, this technology is normalizing facial scanning. Let us not be naive, this is a coordinated plan to institute a worldwide biometric id system to track every human on the planet. Faces Contain a Significant Amount of Data The science of judging one’s character from their facial characteristics, or physiognomy, dates back to ancient China and Greece. Aristotle and Pythagoras were among its disciples, and the latter used to select his students based on their facial features. Cesare Lombroso, the founder of criminal anthropology, believed that criminals could be identified by their facial features. There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that character can influence one’s facial appearance, and vice versa. The appearance of an individual's face drives first impressions of others, influencing our expectations and behavior toward them, which, in turn, shapes their character. The existence of such links between facial appearance and character is supported by the fact that people can accurately judge others’ character, psychological states, and demographic traits from their faces. Some people can easily and accurately identify others’ gender, age, race, or emotional state — even from a glimpse of their faces. However others may lack the ability to detect or interpret them. Case in point, a patent filed in 2014 by Facebook described plans to detect users emotions and deliver specific content, based on those emotions, through computing devices such as laptops, mobile phones and tablets that have a digital camera. Recent progress in AI and computer vision has been largely driven by the widespread adoption of deep neural networks (DNN), or neural networks composed of a large number of hidden layers. DNNs mimic the neocortex by simulating large, multi-level networks of interconnected neurons. DNNs excel at recognizing patterns in large, unstructured data such as digital images, sound, or text, and analyzing such patterns to make predictions. DNNs are increasingly outperforming humans in visual tasks such as image classification, facial recognition, or diagnosing skin cancer. The superior performance of DNNs offers an opportunity to identify links between characteristics and facial features that might be missed or misinterpreted by the human brain. Michal Kosinski, a Stanford University professor, conducted research suggesting that artificial intelligence (AI) can detect the sexual orientation of people based on photos. He mentions that sexual orientation was just one of many characteristics that algorithms would be able to predict through facial recognition. Using photos, AI will be able to identify people’s political views, whether they have high IQs, whether they are predisposed to criminal behavior, whether they have specific personality traits and many other private, personal details that could carry huge social consequences, he said. Faces contain a significant amount of information, and using large datasets of photos, sophisticated computer programs can uncover trends and learn how to distinguish key traits with a high rate of accuracy. With Kosinski’s AI, an algorithm used online dating photos to create a program that could correctly identify sexual orientation 91% of the time with men and 83% with women, just by reviewing a handful of photos. A Feature Able to be Used Against One's Will The iPhone X’s facial recognition capabilities could spell disaster for those wanting to keep their private data from the prying eyes of law enforcement. While the convenience of not having to lift a finger to unlock a phone is being touted as a selling point by Apple, the potential for privacy invasion at the hands of police has people worried. Police require a warrant to unlock and check your phone, but they don’t need one to compel you to use your fingerprint to unlock it. Run through the following scenario: Police demand access to your iPhone X. Cannot compel you without warrant? No problem, they turn phone to face you, unlocks with FaceID. In 2014, a Virginia judge ruled police could force users to unlock their phones using their fingerprints. In February 2016, a judge in Los Angeles signed a search warrant to make a woman unlock her iPhone with her fingerprint. Due to Fifth Amendment protections around self-incrimination in the US, police can’t force a person to give over their passcode, as it’s considered “knowledge.” Albeit, a fingerprint or a face, however, is a different scenario. This is worrying for the vast amount of people who are unlawfully detained and illegally searched. Data Being Used Against the User Beyond the violation of privacy, there are larger implications by which the intelligence agencies are able to hijack individual computers and phones (including iPhones, Blackberries and Androids), take over the device, record its every use, movement, and even the sights and sounds of the room it is in. With the help of this facility, and many others like it, each day the NSA is able to intercept and store 1.7 billion electronic communications. Since it's inception, this secret industry has boomed and is worth billions of dollars per year. There are commercial firms that now sell special software that analyze this data and turn it into powerful tools that can be used by military and intelligence agencies. Around the world, mass surveillance contractors are helping intelligence agencies spy on individuals and ‘communities of interest’ on an industrial scale. The Wikileaks Spy Files reveal the details of which companies are making billions selling sophisticated tracking tools to government buyers, flouting export rules, and turning a blind eye to dictatorial regimes that abuse human rights. Sentient World Simulation
Remarkably, this is precisely what is happening. It is called the “Sentient World Simulation.” The program’s aim, according to its creator, is to be a “continuously running, continually updated mirror model of the real world that can be used to predict and evaluate future events and courses of action.” In practical terms that equates to a computer simulation of the planet complete with billions of “nodes” representing every person on the earth. The project is based out of Purdue University in Indiana at the Synthetic Environment for Analysis and Simulations Laboaratory. It is led by Alok Chaturvedi, who in addition to heading up the Purdue lab also makes the project commercially available via his private company, Simulex, Inc. which boasts an array of government clients, including the Department of Defense and the Department of Justice, as well as private sector clients like Eli Lilly and Lockheed Martin. The program can be used to predict what would happen in the event of a large scale tsunami, for example, or how people would react during a bioterror attack. Businesses can use the models to predict how a new product would fare in the market, what kind of marketing plans would be most effective, or how best to streamline a company’s organization. The original concept paper for the project was published in 2006 and in 2007 it was reported that both Homeland Security and the Defense Department were already using the system to simulate the American public’s reaction to various crises. In the intervening five years, however, there has been almost no coverage at all of the Sentient World Simulation or its progress in achieving a model of the earth. The Sentient World Simulation is one example of one program run by one company for various governmental and Fortune 500 clients. But it is a significant peek behind the curtain at what those who are really running our society want: complete control over every facet of our lives achieved through a complete invasion of everything that was once referred to as “privacy.” Ultimately, it should be noted that all technology can be used as either a tool or as a weapon. But when the technology is in the hands of multinational, monopoly corporations with government influences and coercion, it may be best to side with skepticism and not with open arms. ReferencesCorbett, J. (2012). Sentient World Simulation: Meet Your DoD Clone : The Corbett Report. [online] Corbettreport.com. Available at: https://www.corbettreport.com/sentient-world-simulation-meet-your-dod-clone/ [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. Krannert.purdue.edu. (2017). Seas Labs. [online] Available at: http://www.krannert.purdue.edu/centers/perc/html/aboutperc/seaslabs/seaslabs.htm [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. Priest, D. and Arkin, W. (2010). A hidden world, growing beyond control (Printer friendly version)| washingtonpost.com. [online] Projects.washingtonpost.com. Available at: http://projects.washingtonpost.com/top-secret-america/articles/a-hidden-world-growing-beyond-control/print/ [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. RT International. (2017). iPhone X facial recognition could give cops easy access to your cell. [online] Available at: https://www.rt.com/news/403229-iphone-face-id-police/ [Accessed 24 Sep. 2017]. Wang, Y., & Kosinski, M. (2017). Deep neural networks are more accurate than humans at detecting sexual orientation from facial images. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology Wikileaks.org. (2014). WikiLeaks - The Spy Files. [online] Available at: https://wikileaks.org/the-spyfiles.html [Accessed 15 Sep. 2017].
Project Popeye - Cloud Seeding During Vietnam War
Project Popeye was a highly classified weather modification program in Southeast Asia during 1967–1972. The objective of the program was to produce sufficient rainfall along these lines of communication to interdict or at least interfere with truck traffic between North and South Vietnam.
A test phase of Project Popeye was approved by State and Defense and conducted during October 1966 in a strip of the Lao Panhandle generally east of the Bolovens Plateau in the valley of the Se Kong River. The test was conducted without consultation with Lao authorities (but with Ambassador Sullivan’s knowledge and concurrence). During the test phase, more than 50 cloud seeding experiments were conducted. The results are viewed by DOD as outstandingly successful.
The experiments were deemed undeniably successful, indicating that, at least under weather and terrain conditions such as those involved, the U.S. Government has realized a capability of significant weather modification. If anything, the tests were “too successful”—neither the volume of induced rainfall nor the extent of area affected can be precisely predicted (Department of State - Office of the Historian, 1967). Project Stormfury - An Attempt to Modify Hurricanes
Project Stormfury was an attempt to weaken tropical cyclones by flying aircraft into them and seeding with silver iodide.
The project was run by the United States Government from 1962 to 1983.The hypothesis was that the silver iodide would cause supercooled water in the storm to freeze, disrupting the inner structure of the hurricane. This led to the seeding of several Atlantic hurricanes. However, it was later shown that this hypothesis was incorrect. In reality, it was determined most hurricanes do not contain enough supercooled water for cloud seeding to be effective. Additionally, researchers found that unseeded hurricanes often undergo the same structural changes that were expected from seeded hurricanes. This finding called Stormfury’s successes into question, as the changes reported now had a natural explanation. The last experimental flight was flown in 1971, due to a lack of candidate storms and a changeover in NOAA’s fleet. More than a decade after the last modification experiment, Project Stormfury was officially canceled. Although a failure in its goal of reducing the destructiveness of hurricanes, Project Stormfury was not without merit. The observational data and storm lifecycle research generated by Stormfury helped improve meteorologists’ ability to forecast the movement and intensity of future hurricanes. Former CIA Director, John Brennan, Discusses SAI or "Chemtrails"
A number of government agencies have developed plans for research and operational programs in weather and climate modification. Here is a report from 1966, in which various agencies expressed interest in the ability to modify the weather. In 2015, the National Academy of Sciences conducted a 21-month geoengineering study, which happened be funded by the "U.S Intelligence community", also known as the Central Intelligence Agency (National Academy of Sciences, 2015). Below is a video of John Brennan, former CIA director from March 2013 to January 2017, speaking about stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI), commonly referred to as "chemtrails", at the Council on Foreign Relations.
Research Suggests Climate Engineering is Ineffective
Scientists at Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research (Kiel, Germany) conducted a study where they evaluated effectiveness and risks of different geoengineering techniques, such as SRM (solar radiation management), afforestation, artificial ocean upwelling, ocean iron fertilization and ocean alkalinization.
The researchers discovered that even when applied continuously and at scales as large as currently deemed possible, all methods are, individually, either relatively ineffective with limited (o8%) warming reductions, or they have potentially severe side effects and cannot be stopped without causing rapid climate change (Keller, Feng and Oschlies, 2014). To assess their true potential and verify their side effects, such interventions require full-scale experiments that may have long-term and possibly compromise the very planetary mechanisms and ecosystems we’re trying to save. Potential Proof of Weather Manipulation
In the photos below, several abnormal cloud formations with a seemingly unnatural origin, containing straight lines and 90° angles, can be observed.
Based on the information aforementioned, toxic materials, heavy metals, and harmful chemicals are able to be positioned in the atmosphere of the planet. Many speculate that these particles may be manipulated by powerful radio frequency signals, in which a strange impact on clouds can be observed. In addition, it is claimed that these square clouds are created via electrically conductive heavy metal nanoparticles (that are constantly being sprayed into our atmosphere by the the geoengineers) which are able to be manipulated with the global grid of radio frequency transmitters. Some suggest that these radio frequencies have originated from ionospheric heaters like HAARP (High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program) in Gakona, Alaska, the most notable U.S. geoengineering facility. HAARP wasscheduled for shut down by the U.S. Air Force in May, 2014. There are many other transmission installations around the world, some officially known and others completely secret. U.S. Senate Document Reveals Weather Modification
The United States Federal government has been involved for over 60 years in a number of aspects of weather modification, through activities of both the Congress and executive branch. Since 1947, weather modification bills pertained to research support, operations, policy studies, regulations, liabilities, activity reporting, establishment of panels and committees, and international concerns have been introduced in the Congress. There have been hearings on many of these proposed measures, and oversight hearings have also been conducted on pertinent ongoing programs. In the 750-page document below, various topics regarding weather modification are discussed, including but not limited to:
Weather Warfare Explained Further
References
Department of State - Office of the Historian. (1967). Foreign Relations of the United States, 1964–1968, Volume XXVIII, Laos - Office of the Historian. [online] Available at: https://history.state.gov/historicaldocuments/frus1964-68v28/d274#fnref:1.5.4.4.14.336.7.6 [Accessed 12 Sep. 2017].
Keller, D., Feng, E. and Oschlies, A. (2014). Potential climate engineering effectiveness and side effects during a high carbon dioxide-emission scenario. Nature Communications, 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4304 Wigington, D. (2016). Is Climate Engineering Real? Square Cloud Formations Are Undeniable Proof. [online] Geoengineering Watch. Available at: http://www.geoengineeringwatch.org/is-climate-engineering-real-square-cloud-formations-are-undeniable-proof/ [Accessed 12 Sep. 2017].
The global war on terror has entered the digital age and it’s no longer a question of if there will be an attack on the world wide web but when! In this video Dan Dicks of Press For Truth speaks with James Corbett of The Corbett Report about what a possible cyber attack scenario might look like, who the perpetrators are likely to be, who the scapegoat will be to take the fall and most importantly what we all can do about it BEFORE it happens.
transcript from The International Forecaster: 5. The "Visual Microphone" As we all know, what we call "sound" is essentially a wave propagating through a medium like air, displacing particles and causing oscillations in the pressure and velocity of those particles. These oscillations are detected by our ears and converted into nerve impulses that our brain interprets as sound. So what if you can't directly perceive that wave itself, but the effect of that wave on another subject? Could you reconstruct that sound just from seeing the effect of the sound wave? Well, let's not keep anybody in suspense here. The answer is yes. Yes, you can. As a team of researchers from Microsoft, Adobe and MIT demonstrated in 2014, it is possible to examine video of everyday objects in environments where a sound is playing for the minute, almost imperceptible vibrations that the sound causes on the object's surface. These vibrations can then be "reconstructed" and a recognizable version of that sound can be reproduced from the video alone...without any audio being recorded. The technology itself is truly incredible. Check out the video if you haven't yet done so to see what these researchers were able to accomplish. They reconstruct "Mary Had A Little Lamb" from the vibrations on the leafs of a house plant in the room where the song was being played using nothing other than a high speed camera. They reconstruct a voice recording of a man reciting "Mary Had A Little Lamb" from the vibrations on a bag of chips using a high speed camera filming the chips through a soundproof window. Most impressive of all, they even reconstruct a recognizable version of the song from a ketchup packet taken with nothing but an ordinary, consumer version 60 fps DSLR camera. This is a truly remarkable technology and goes to show just how incredible the products of human ingenuity really are...and just how advanced the spying capabilities of the intelligence agencies already are. If you think MIT researchers are working on technology like this without the full knowledge of the alphabet soupers, you're not living in the real world. Even Cracked.com, a humor website that derides "conspiracy theories" every chance it gets, knows precisely what this tech will be (is already being?) used for: "The researchers say they can do the same thing with a piece of foil or even a potted plant, which has far-reaching implications in the field of, well, spying on people. And probably other things." But mostly spying. 4. X-ray Backscatter Vans Remember those ridiculous "X-ray specs" they used to sell in the back of comic books? The ones that were guaranteed to help you see through solid objects? Somehow even at the age of 8 you knew they were a bunch of baloney (even if you still joked with your friends about how you would use them). Well you can stop worrying about it: they were baloney and you were right not to buy them. But you might be happy to hear that the technology to actually see through objects does exist now...until you hear it was developed for the Department of Homeland Security. It's been almost a decade since the DHS revealed the prototype of the LEXID, a handheld x-ray imaging device that allows agents to see through walls. (Surely you remember me covering that in Episode 025 of my podcast, right?) At the time the full working devices were slated to be a year away from being ready to deploy on the street into the hot little hands of the upstanding men and women of the Department of Fatherland Security. But four years later we instead got roving backscatter x-ray scanner vans. That was when American Science & Engineering (the company in Massachusetts, not the concept) announced they had already sold 500 of their Z Backscatter Vans (or "ZBVs") to "U.S. and foreign government agencies." The vans are designed to rove around the streets blasting everything in sight with X-rays in order to (we are told) discover contraband and dangerous cargo in vehicles and other hiding places. Sound dangerous? It sure is. But are we really expecting the DHS to care whether or not they're sending random innocent people to an early grave when there's billions in federal funding for such technologies to burn through and cool spying tech like this to play with? Of course not. 3. Stingrays Back in November 2014 the story broke that the increasingly inaccurately named Department of "Justice" was sending up a fleet of Cessnas with devices that could mimic cellphone towers in order to collect communication data on criminal suspects. The devices (dubbed "Stingrays" by people who apparently think the scheme isn't already Bond villain cartoonish enough) spoof cellphones into giving up their identity and location data, and allowed the DOJ to scoop up the cell phone conversations and text messages of thousands of people per flight, all supposedly justified because they were looking for a handful of bad guys' data. Sound like a clear violation of Fourth Amendment rights? It certainly is, but that didn't even cause the FBI to blink. Once the program was exposed they simply declared: "Warrants? We don't need no stinking warrants!" (or the legalese equivalent thereof) and continued on their merry cellphone spoofing way. To the surprise of absolutely no one, it came out a couple of months later that the Stingrays were not merely being deployed by the top elite law enforcement professionals of the FBI but local law enforcement, too, and that the Bureau had tried with all its might to keep that knowledge from ever seeing the light of day. So yes, it is quite possible that your cellphone call is being scooped up by a fake cellphone tower and stored in the vaults of some bureau or agency, somewhere or other. And if all of that doesn't sound quite Orwellian enough...don't worry! The latest revelations from a leak last December show that the Stingray is just one of a catalogue of items that the police state can (and does) use to spy on your cell phone. Perhaps unsurprisingly, it seems that local law enforcement have been increasingly dipping into the military-industrial tech treasure chest for their spying needs, a phenomenon prompted by the problem-reaction-solution set up of events like the San Bernardino shooting. These technologies allow for precise tracking and geolocation of a targeted cellphone in more ways than can even be elaborated here. 2. TEMPEST But don't let all this fool you into thinking that the spymasters need physical access to you or your location at all in order to see/hear what you're doing. We're sadly well past that point, as described by Jacob Applebaum in a speech at the annual Chaos Communication Congress in 2013. Now Applebaum himself is a character who probably deserves his own investigation but the bag of NSA goodies that he revealed at 30c3 is nonetheless informative. His presentation, entitled "To Protect and Infect," broke down a series of exploits, backdoors, and good old-fashioned skullduggery that the NSA uses to scoop information out of computers and devices around the world, from secret hardware implants in USB connections to provide wireless backdoors into target networks (dubbed "COTTONMOUTH") to the no-less-imaginatively entitled HOWLERMONKEY. That's a radiofrequency transmitter that the NSA can surreptitiously implant directly into your computer when it is in transit through the mail. But by far the most intriguing part of the presentation came near the end when he revealed this nugget: "Well, what if I told you that the NSA had a specialized technology for beaming energy into you and to the computer systems around you, would you believe that that was real or would that be paranoid speculation of a crazy person?... That exists, by the way." The idea here, apparently, is that by using a continuous wave radar unit, the agents of evil can beam up to 1 kilowatt energy directly into you, effectively lighting up you (and any electronic equipment you're in contact with) like a Christmas tree so that active radar can exfiltrate your data. According to Der Spiegel, “Most of this equipment involves a combination of hardware implants which emit a very inconspicuous signal, and a radio unit aimed, from outside, at the space being monitored. Reflected radar waves are changed by the signal emitted by the implant hidden in the targeted space.” According to the documents published by Der Spiegel, the technology can capture the location of a specific object in the room, words spoken in the room, and even what is displayed on a monitor in the room, all without the need of any active listening device in the room. Even disregarding how utterly insane that sounds, is it safe? Won't that kind of RF energy being beamed directly into people cause cancer? Who knows? Who cares! The eyes in the sky could care less as long as they get their target data. OK, this is all incredibly creepy. But what if you've already typed out your super secret love letter and the NSA wasn't able to intercept it in real time? What if they weren't able to spoof it out of your phone or irradiate you so you glowed like a candle for their radars to scoop up every word? What if it's already a done deal? A fait accomplis? Surely they can't get the info, then, right? What are they going to do, scoop it right out of your brain? 1. Brain Scanners Essentially, yes. They are going to scoop the info out of your brain. As the International Business Times puts it: "Scientists have created a mind-reading machine that allows them to reconstruct images in a person's mind using brain scans." Sound sensational? Well it's not as far off the mark as such hyperbole might sound at first glance. In 2014 researchers at New York University and the University of California showed 300 pictures of faces to six test subjects who were undergoing fMRI scans in order to build up a database of how their brains reacted to facial data. They then showed them pictures of new faces and used the resulting fMRI data to reconstruct crude (but recognizable) versions of those faces. In other words, they "read their mind" and were able to pictorially represent what the subjects were looking at. The technology is still a long way off from being "mind reading devices" in the Buck Rogers sense, but it's a significant step on the way. And this is only the technology that is publicly known about. Are we really to believe that this is truly the cutting edge of such technology and that they don't have something more cutting edge in the skunkworks of DARPA? Scared yet? Well don't be. That's just what they want. Nothing to fear but fear itself "OK, OK, we get it, James!" you're saying right now. "They can see everything, read everything, hear everything. There's no escape. We might as well just give up." Absolutely not. It is important to understand and be knowledgeable about the types of technology that the police state has at its disposal. But let's keep in mind that the only perfect prison is the one that we create in our own minds. The one that stops us from acting out of fear that the jailers will see us. We should always keep in mind that stories about what the intelligence agencies have up their sleeve is always exaggerated and over-played. Their most effective tool is to merely convince you that they see and hear everything. But more often than not, they're flat out lying... ReferencesDavis, A., Rubinstein, M., Wadhwa, N., Mysore, G., Durand, F., & Freeman, W. (2014). The Visual Microphone: Passive Recovery of Sound from Video. Retrieved from https://people.csail.mit.edu/mrub/papers/VisualMic_SIGGRAPH2014.pdf
Kravets, D. (2017). FBI says search warrants not needed to use “stingrays” in public places. Ars Technica. Retrieved 9 July 2017, from https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2015/01/fbi-says-search-warrants-not-needed-to-use-stringrays-in-public-places/ Lee, H., & Kuhl, B. (2016). Reconstructing Perceived and Retrieved Faces from Activity Patterns in Lateral Parietal Cortex. Journal Of Neuroscience, 36(22), 6069-6082. http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4286-15.2016 Stingray Tracking Devices: Who's Got Them?. (2017). American Civil Liberties Union. Retrieved 9 July 2017, from https://www.aclu.org/map/stingray-tracking-devices-whos-got-them ZBV® - American Science & Engineering. (2017). As-e.com. Retrieved 9 July 2017, from http://as-e.com/products-solutions/cargo-vehicle-inspection/mobile/product/zbv/ Did you ever wonder how we keep people fighting with each other? Or obeying our silly rules? Or actually loving their captors and slavemasters? This morning we're going to brief you on just that. Are you ready to begin?
SpaceX, also known as Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, is a private aerospace manufacturer and space transport services company - founded by Elon Musk in May of 2002. The first operation performed by SpaceX for the military began in May of 2017. SpaceX launched a satellite for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), an agency that is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and the United States Department of Defense. The Intelligence Community is composed of the NRO, along with the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), National Security Agency (NSA), Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA), and National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), among other U.S. intelligence agencies. In August of 2017, SpaceX will transport the X-37B into orbit, one of the Pentagon's classified spy crafts. SpaceX has been offered to launch the craft largely due to the it's ability to cut costs. Launches starting at roughly $61 million, SpaceX has been able to undercut United Launch Alliance, a joint venture of Lockheed Martin Space Systems and Boeing Defense, Space & Security. In addition to becoming a new military contractor, SpaceX also aids NASA in resupply missions to the International Space Station. SpaceX plans to fly astronauts to the ISS next year. Furthermore, SpaceX said it would also fly two private space tourists around the moon in 2018, although their identities or trip payments have not been disclosed. ReferencesBachman, Justin. (2017). Musk’s SpaceX Joins the Military. Bloomberg.com. Retrieved 14 June 2017, from https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2017-06-12/musk-s-spacex-joins-the-military In the wake of London and Manchester, politicians around the world are trying to convince the public that the free flow of information on the internet is a terror threat. In reality, independent online media are exposing the real terrorists: the politicians and their deep state handlers who are funding, arming, aiding and enabling false flag terror.
Real-time cameras connected to facial recognition software will monitor the masses in and around the city center. The cameras will be used identify people who exist on pre-determined watch lists, which usually includes "terrorists" and other criminals, such as ticket touts. The police force has also been provided funding for a separate trial of software that enables them to cross reference CCTV (Closed-circuit television) images and other pictures with their database that is composed of roughly 500,000 custody images. Police vehicles have been spotted around the city being labelled as using the facial recognition software. A spokeswoman from the Police Department stated that, "the facial recognition technology is currently being tested as proof of concept, in order to determine its potential and feasibility within a challenging, real-world policing environment. While early indications are proving positive, we will continue to develop our understanding of its capabilities and its limitations. South Wales Police has made significant progress in the development of its technology in the past 18 months, and that work is only set to continue as we strive to ensure we arm our officers with the very best technology commercially available – providing the public benefit is both proven and justifiable. The technology will be tested in a variety of circumstances and location in the months to come, assisting in our assessment of the viability of the project moving forward". Chief Superintendent Jon Edwards previously stated, “South Wales Police has secured funding from the Home Office to develop automated facial recognition technology for policing. The UEFA Champions League finals in Cardiff give us a unique opportunity to test and prove the concept of this technology in a live operational environment, which will hopefully prove the benefits and the application of such technology across policing. This will be one of the largest security operations ever undertaken in the Welsh capital and the use of technology will support the policing operation which aims to keep people safe during what will be a very busy time in Cardiff.” This facial recognition software is just one of the tools adopted from the military that is being used by the police. As the police becomes more militarized, this concept will spread around the world as being normal. References Mosalski, R. (2017). The first arrest using new facial recognition software has been made. walesonline. Retrieved 11 June 2017, from http://www.walesonline.co.uk/news/local-news/first-arrest-using-facial-recognition-13126934
|
This feed contains research, news, information, observations, and ideas at the level of the world.
Archives
April 2024
Categories
All
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

